
If the side of a regular hexagon is 6cm, then its area will be
(a)108 sq. cm
(b)\[\dfrac{108}{3}\]sq. cm
(c)\[108\sqrt{3}\]sq. cm
(d)\[54\sqrt{3}\]sq. cm
Answer
600.3k+ views
Hint: Draw a hexagon ABCDEF, the diagonals AD, BE and CF divide the hexagon into 6 equal equilateral triangles. Find the area of the equilateral triangle. Using the formula root \[\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}{{a}^{2}}\], where a is the side of the triangle. Thus the area of the hexagon is equal to six times the area of the equilateral triangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given the side of the regular hexagon as 6cm. Let us consider ABCDEF as a regular hexagon. Let ‘O’ be the center of the regular hexagon.
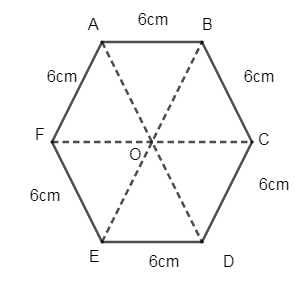
Now let us join the diagonals of the hexagons AD, BE and CF.
By the properties of the regular hexagon, the three diagonals divide the hexagon, into 6 congruent equilateral triangles.
Now their equilateral triangle will have the side as 6cm.
We know that the area of the equilateral triangle is given by the formula,
\[A=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}{{a}^{2}}\]
Here a = side = 6cm
\[\therefore \] Area of one equilateral triangle = \[\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}{{\left( 6 \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}\times 6\times 6=3\times 3\times \sqrt{3}=9\sqrt{3}\]
Thus we got the area of one equilateral triangle = \[9\sqrt{3}\].
\[\therefore \] Area of the regular hexagon = 6 \[\times \] area of one equilateral triangle.
\[\therefore \] Area of the regular hexagon = \[6\times 9\sqrt{3}=54\sqrt{3}c{{m}^{2}}\]
Thus we got the area of the regular hexagon as \[54\sqrt{3}c{{m}^{2}}\].
\[\therefore \] Option (d) is the correct answer.
Note: We can also find the area of the hexagon using the formula, \[\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}{{a}^{2}}\].
\[\therefore \] Area of hexagon = \[\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}\times {{6}^{2}}=\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}\times 6\times 6=3\sqrt{3}\times 3\times 6=54\sqrt{3}c{{m}^{2}}\].
If you can’t remember the formula, you can solve it by splitting it into equilateral triangles.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given the side of the regular hexagon as 6cm. Let us consider ABCDEF as a regular hexagon. Let ‘O’ be the center of the regular hexagon.

Now let us join the diagonals of the hexagons AD, BE and CF.
By the properties of the regular hexagon, the three diagonals divide the hexagon, into 6 congruent equilateral triangles.
Now their equilateral triangle will have the side as 6cm.
We know that the area of the equilateral triangle is given by the formula,
\[A=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}{{a}^{2}}\]
Here a = side = 6cm
\[\therefore \] Area of one equilateral triangle = \[\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}{{\left( 6 \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}\times 6\times 6=3\times 3\times \sqrt{3}=9\sqrt{3}\]
Thus we got the area of one equilateral triangle = \[9\sqrt{3}\].
\[\therefore \] Area of the regular hexagon = 6 \[\times \] area of one equilateral triangle.
\[\therefore \] Area of the regular hexagon = \[6\times 9\sqrt{3}=54\sqrt{3}c{{m}^{2}}\]
Thus we got the area of the regular hexagon as \[54\sqrt{3}c{{m}^{2}}\].
\[\therefore \] Option (d) is the correct answer.
Note: We can also find the area of the hexagon using the formula, \[\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}{{a}^{2}}\].
\[\therefore \] Area of hexagon = \[\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}\times {{6}^{2}}=\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}\times 6\times 6=3\sqrt{3}\times 3\times 6=54\sqrt{3}c{{m}^{2}}\].
If you can’t remember the formula, you can solve it by splitting it into equilateral triangles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




