
If you remove the cell wall from a plant cell and place it into a drop of water
(a) the cell would begin to grow
(b) the cell would shrink
(c) the cell would burst
(d) nothing would happen
Answer
570.6k+ views
Hint: Cellulose is only found around plant cells and a few other organisms. If a plant cell is like a water balloon, and it is like a cardboard box that protects the balloon. The balloon is helped from the outside world by a structure that gives protection and support.
Complete answer:
The cell wall provides over-expansions when water enters the cell and hinders the bursting of plant cells by preventing unreasonable endosmosis. When the cell wall is removed, water would enter the cell and the cell would burst subsequently.
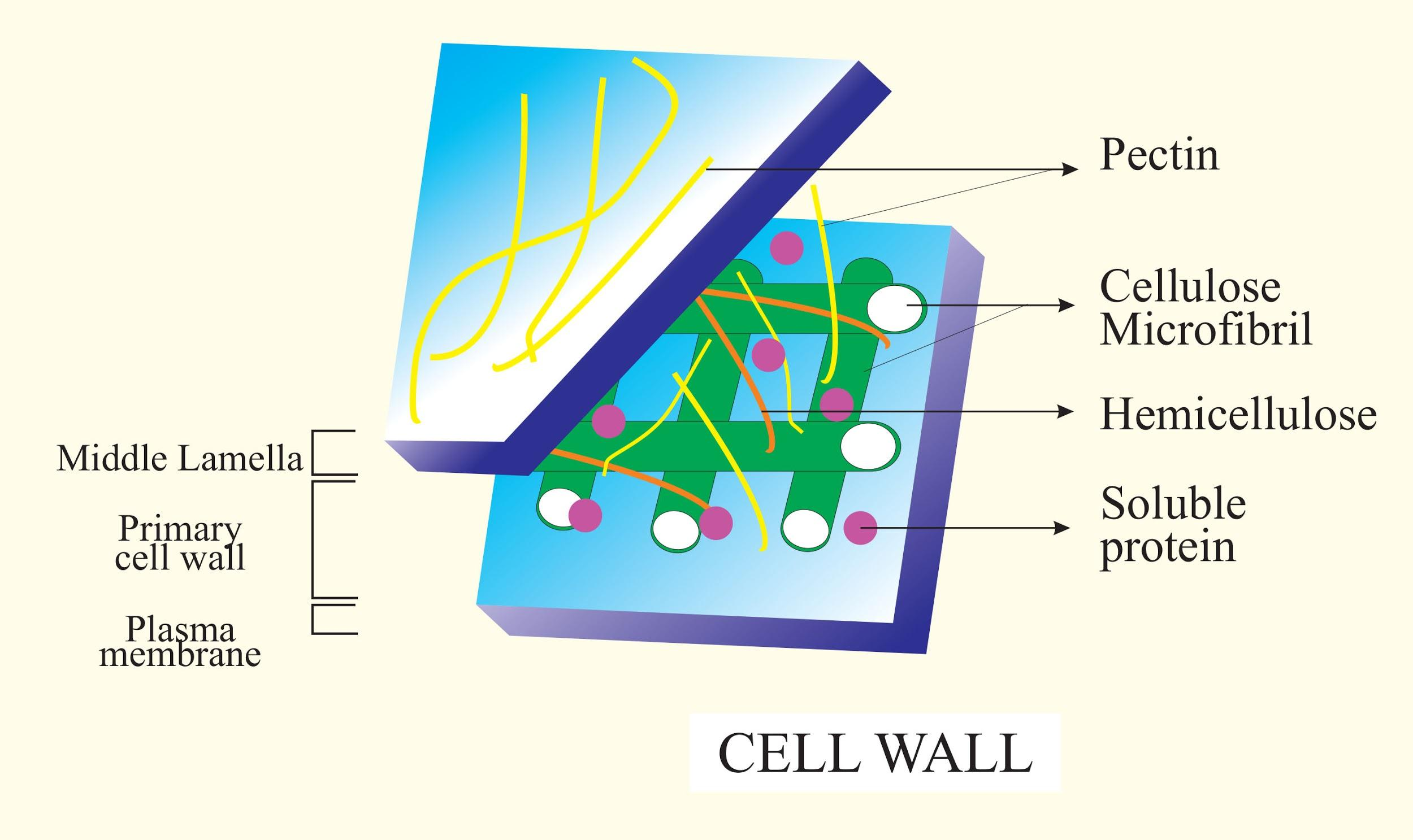
Additional Information: The principal part of the plant cell wall is cellulose, a carbohydrate that forms long fibers and gives the cell wall its rigidity. The cellulose fibers formed together and it forms bundles called microfibrils. And the other important carbohydrates that include hemicellulose, pectin, and lignin. Plant cells that are currently developing have primary cell walls, which are thin. When the cells are completely developed, they create secondary cell walls. The secondary cell wall is a thick layer that is formed within the primary cell wall. This layer is what is generally implied when referring to a plant’s cell wall.
So the correct answer is ‘the cell would burst’.
Note: The cell walls of plant cells assist them with keeping up turgor pressure, which is the pressure of the cell membrane pressing against the cell wall. Ideally, plant cells should have lots of water within them, leading to high turbidity. The Bacteria have a structure that is called a cell wall. Fungi and some protozoa also have cell walls. They are not the same as the plant cell walls and it is made up of cellulose.
Complete answer:
The cell wall provides over-expansions when water enters the cell and hinders the bursting of plant cells by preventing unreasonable endosmosis. When the cell wall is removed, water would enter the cell and the cell would burst subsequently.
Additional Information: The principal part of the plant cell wall is cellulose, a carbohydrate that forms long fibers and gives the cell wall its rigidity. The cellulose fibers formed together and it forms bundles called microfibrils. And the other important carbohydrates that include hemicellulose, pectin, and lignin. Plant cells that are currently developing have primary cell walls, which are thin. When the cells are completely developed, they create secondary cell walls. The secondary cell wall is a thick layer that is formed within the primary cell wall. This layer is what is generally implied when referring to a plant’s cell wall.
So the correct answer is ‘the cell would burst’.
Note: The cell walls of plant cells assist them with keeping up turgor pressure, which is the pressure of the cell membrane pressing against the cell wall. Ideally, plant cells should have lots of water within them, leading to high turbidity. The Bacteria have a structure that is called a cell wall. Fungi and some protozoa also have cell walls. They are not the same as the plant cell walls and it is made up of cellulose.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




