
Illustrate only a plant cell seen under an electron microscope. How is it different from animal cells?
Answer
508.5k+ views
Hint: Plant cells are eukaryotic cells found in green plants, which are photosynthetic eukaryotes belonging to the Plantae kingdom. Primary cell walls containing cellulose, hemicelluloses, and pectin, the existence of plastids capable of photosynthesis and starch storage, a large vacuole that regulates turgor pressure, and the absence of flagella or centrioles are all distinguishing characteristics.
Animal cells are eukaryotic cells with a plasma membrane surrounding them and a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. Animal cells, unlike the eukaryotic cells of plants and fungus, lack a cell wall.
Complete explanation:
Part A: Plant cells appear as huge rectangular interlocking bricks under the microscope. Each cell's cell wall is clearly visible around it. When dyed, the cell wall is rather thick and visible. The cytoplasm is mildly coloured, with a darkly pigmented nucleus towards the cell's perimeter.
This transmission electron micrograph clearly shows the cell wall, nucleus, vacuoles, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and ribosomes.
Plant cells require a cell wall, but animal cells do not, since plants require a stiff framework in order to grow up and out. Plant cells only have the shapes of their cell walls, but animal cells can have a variety of shapes.
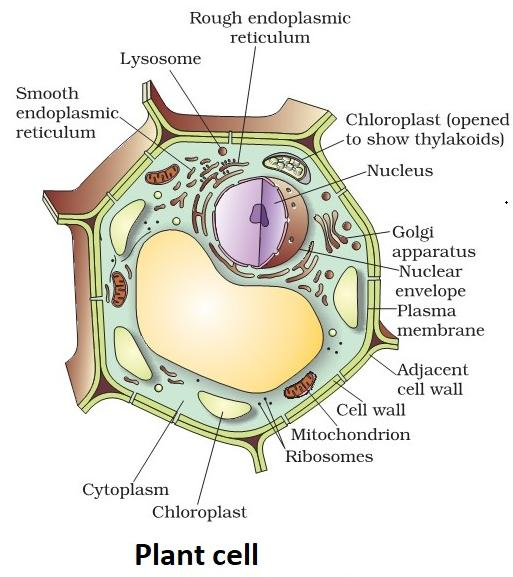
Part B: An electron microscope image of a plant cell.
The presence of chloroplast in plant cells is one of the most significant differences between them and animal cells.
In plant cells, the presence of a big central vacuole.
The presence of a cell wall.
Note:
All living things are made up of cells, which are the structural, functional, and biological components. A cell has the capability of self-replication. As a result, they've earned the moniker "life's building blocks".
Proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids are among the biomolecules found in the cytoplasm.
Cell organelles, which are suspended in the cytoplasm, are also present.
In the same way as factories have multiple personnel and departments working toward a common objective, cells do as well. Distinct types of cells provide different functions. Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes are the two types of cells based on their cellular structure.
Animal cells are eukaryotic cells with a plasma membrane surrounding them and a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. Animal cells, unlike the eukaryotic cells of plants and fungus, lack a cell wall.
Complete explanation:
Part A: Plant cells appear as huge rectangular interlocking bricks under the microscope. Each cell's cell wall is clearly visible around it. When dyed, the cell wall is rather thick and visible. The cytoplasm is mildly coloured, with a darkly pigmented nucleus towards the cell's perimeter.
This transmission electron micrograph clearly shows the cell wall, nucleus, vacuoles, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and ribosomes.
Plant cells require a cell wall, but animal cells do not, since plants require a stiff framework in order to grow up and out. Plant cells only have the shapes of their cell walls, but animal cells can have a variety of shapes.

Part B: An electron microscope image of a plant cell.
The presence of chloroplast in plant cells is one of the most significant differences between them and animal cells.
In plant cells, the presence of a big central vacuole.
The presence of a cell wall.
Note:
All living things are made up of cells, which are the structural, functional, and biological components. A cell has the capability of self-replication. As a result, they've earned the moniker "life's building blocks".
Proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids are among the biomolecules found in the cytoplasm.
Cell organelles, which are suspended in the cytoplasm, are also present.
In the same way as factories have multiple personnel and departments working toward a common objective, cells do as well. Distinct types of cells provide different functions. Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes are the two types of cells based on their cellular structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




