
Illustrate the law of conservation of energy by discussing the energy changes which occur when we draw a pendulum bob to one side and allow it to oscillate. Why does the bob eventually come to rest? What happens to its energy eventually? Is it a violation of the law of conservation of energy?
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: The continuous decrease in height is because of the energy loss of the bob from the energy it was first imparted with while lifting it to a certain height. This continuous decrease makes the bob to ultimately come to rest. So, we can see that the loss of energy is taking place during its course of motion.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that, according to the law of conservation of energy, if we consider an isolation system, then its total energy always remains constant and the energy neither gets created nor destroyed.
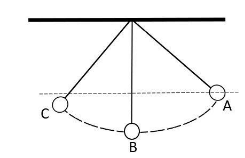
To understand that, let us take a pendulum bob attached to a string and is hanging without oscillation and is at point B initially. Now, if we lift the bob till point A without the string getting loose, the bob will gain potential energy due to increase in its height and when freed will swing till point B, where its potential energy will start to decrease and will gain kinetic energy due to motion. After point C it will again start to rise till point C gaining potential energy and losing kinetic energy. But the interesting thing that we can see here is that the height of point C is less than that of point A and this will continue until the pendulum bob will again come to rest at point B.
The reason behind this is that the bob while swinging is resisted by the air and its collision with air particles make the bob loose some part of its energy continuously and which get transferred to the surroundings. This loss in energy causes the bob to loosen height in every swing and ultimately makes it come to rest.
Thus, we can notice that the law of conservation of energy is not being violated and the energy lost by the bob is getting transferred to its surroundings.
Note:
In the example, we have taken above, the string attached with the pendulum has been considered as non-flexible but in practical situations, the strings are flexible and that also contributes in the loss of energy from the pendulum bob.
We can also describe the given situation by writing the equations for kinetic and potential energy at different points and them comparing them to understand the energy loss in between. The height attained will continuously be changing and also the velocity. The formulas, we can use are,
Kinetic energy, $K_E =\dfrac{1}{2}mv^2$ and
Potential energy, $P_E =mgh$, where m is the mass of bob, v is its velocity at a specific point and h is the height attained by the bob.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that, according to the law of conservation of energy, if we consider an isolation system, then its total energy always remains constant and the energy neither gets created nor destroyed.

To understand that, let us take a pendulum bob attached to a string and is hanging without oscillation and is at point B initially. Now, if we lift the bob till point A without the string getting loose, the bob will gain potential energy due to increase in its height and when freed will swing till point B, where its potential energy will start to decrease and will gain kinetic energy due to motion. After point C it will again start to rise till point C gaining potential energy and losing kinetic energy. But the interesting thing that we can see here is that the height of point C is less than that of point A and this will continue until the pendulum bob will again come to rest at point B.
The reason behind this is that the bob while swinging is resisted by the air and its collision with air particles make the bob loose some part of its energy continuously and which get transferred to the surroundings. This loss in energy causes the bob to loosen height in every swing and ultimately makes it come to rest.
Thus, we can notice that the law of conservation of energy is not being violated and the energy lost by the bob is getting transferred to its surroundings.
Note:
In the example, we have taken above, the string attached with the pendulum has been considered as non-flexible but in practical situations, the strings are flexible and that also contributes in the loss of energy from the pendulum bob.
We can also describe the given situation by writing the equations for kinetic and potential energy at different points and them comparing them to understand the energy loss in between. The height attained will continuously be changing and also the velocity. The formulas, we can use are,
Kinetic energy, $K_E =\dfrac{1}{2}mv^2$ and
Potential energy, $P_E =mgh$, where m is the mass of bob, v is its velocity at a specific point and h is the height attained by the bob.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




