
In a dithecous anther, each pollen sac contains 1000 MMC. What is the total number of pollen grain produced by the anther?
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: A dithecous anther contains two theca or two lobes and each theca contains a pollen sac. So, it is also called tetrasporangiate. Microspore mother cells are diploid and each microspore mother cell divides to form four microspores. Out of four microspores, three of them degenerate and one forms pollen grain.
Complete answer:
The total number of pollen grains produced by an anther is 4000 as each pollen sac in a dithecous anther contains 1000 MMC. A dithecous or tetrasporangiate anther has four chambers or pollen sac. These pollen sacs contain microspore mother cells which give rise to four microspores. Out of these four haploid microspores, three degenerate and one becomes the pollen grain. So, as each pollen sac contains 1000 MMC, the total number of pollen grains produced by the anther would be 4000.
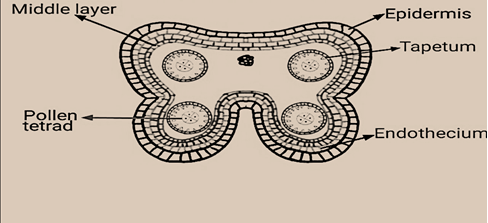
- An anther consists of four layers- outer epidermis, endothecium, middle layers, and tapetum. Tapetum is responsible for the nourishment of pollen grains.
- Epidermis is the protective layer. Endothecium consists of an outer thin layer and an inner layer of alpha cellulosic fibers which is hygroscopic in nature. The middle layer is ephemeral and helps in the dehiscence of the anther.
- Tapetum contains enzymes and hormones. It is of two types- glandular and invasive. Glandular tapetum secretes pro ubisch bodies which in turn produces ubisch which produces sporopollenin.
Note: An anther gives rise to pollen grain which contains the male gamete. The pollen grain is covered by an outer layer of exine and an inner layer of intine. The exine is made up of sporopollenin which is resistant to every microbial action and remains as such in solid or sediments. Sporopollenin keeps the pollen non degraded for a long time. Pollen grain has germ pores where sporopollenin is not present.
Complete answer:
The total number of pollen grains produced by an anther is 4000 as each pollen sac in a dithecous anther contains 1000 MMC. A dithecous or tetrasporangiate anther has four chambers or pollen sac. These pollen sacs contain microspore mother cells which give rise to four microspores. Out of these four haploid microspores, three degenerate and one becomes the pollen grain. So, as each pollen sac contains 1000 MMC, the total number of pollen grains produced by the anther would be 4000.

- An anther consists of four layers- outer epidermis, endothecium, middle layers, and tapetum. Tapetum is responsible for the nourishment of pollen grains.
- Epidermis is the protective layer. Endothecium consists of an outer thin layer and an inner layer of alpha cellulosic fibers which is hygroscopic in nature. The middle layer is ephemeral and helps in the dehiscence of the anther.
- Tapetum contains enzymes and hormones. It is of two types- glandular and invasive. Glandular tapetum secretes pro ubisch bodies which in turn produces ubisch which produces sporopollenin.
Note: An anther gives rise to pollen grain which contains the male gamete. The pollen grain is covered by an outer layer of exine and an inner layer of intine. The exine is made up of sporopollenin which is resistant to every microbial action and remains as such in solid or sediments. Sporopollenin keeps the pollen non degraded for a long time. Pollen grain has germ pores where sporopollenin is not present.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




