
In a given circuit ${{R}_{1}}=15\Omega $, ${{R}_{2}}=45\Omega $, ${{R}_{3}}=60\Omega $ and ${{R}_{4}}=30\Omega $ is connected to a 24V source. Find the total resistance and current in the given circuit and also find current through $30\Omega $ resistor and potential difference through $15\Omega $ resistor.
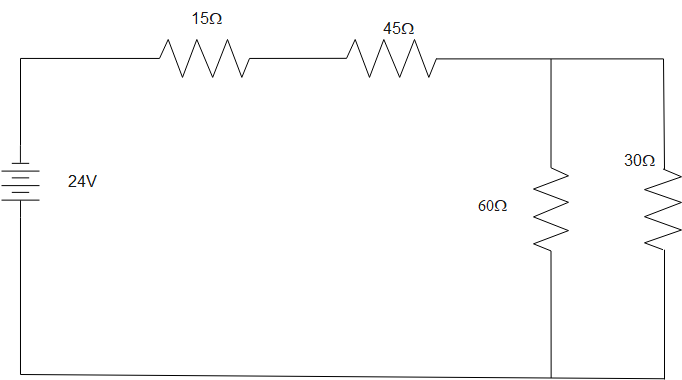

Answer
554.1k+ views
Hint: One can use the ohm’s law (V=IR) and Kirchhoff’s voltage law (KVL) or Kirchhoff’s current law (KCL) to solve the given problem. According to KVL, the algebraic sum of all the voltages within a loop must be zero. And KCL states that algebraic sum of all currents entering and leaving a node must be zero, where negative sign is considered for exiting current and positive for entering currents
Complete answer:
This question consists of four parts:
In the first one we need to evaluate the total resistance within the circuit given. First step would be to evaluate the resultant resistance for the 60 and 30 resistors connected in parallel. The resultant resistance for these two will be:
$\dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}}$
$\dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{1}{30}+\dfrac{1}{60}$
R = 20 $\Omega $
The equivalent circuit diagram after first step is given below:
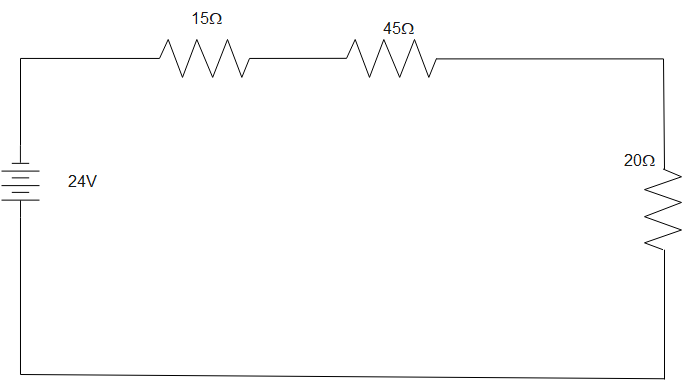
Now, the second step is to evaluate total resistance in the circuit due to 15, 45, and 20 resistors connected in series.
R = R1 + R2 + R3 = 15 + 45 + 20 = 80 $\Omega $
Hence, the total resistance within the circuit is 80
Now, we are asked to evaluate the total current in the circuit. We already know total resistance as calculated in (a) part. Current can be calculated using ohm’s law:
$I=\dfrac{V}{R}=\dfrac{24}{80}=0.3A$
Hence, total current in the circuits is 0.3 A.
To evaluate the current through 30 resistors use KVL. Let current I1 flows through a 30$\Omega $ resistor. Consider two loops, 1 & 2, in the circuit as shown in figure given below:
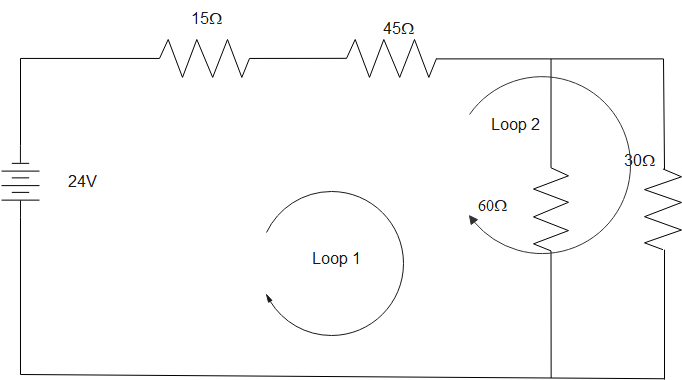
Applying KVL in loop 1:
$-24+0.3\times 15+0.3\times 45+30\times {{I}_{1}}=0$ -- (1)
Applying KVL in loop 1:
$-24+0.3\times 15+0.3\times 45+60\times 0.3-{{I}_{1}}=0$ -- (2)
Now solving equation (1) and (2) will give us I1:
${{I}_{1}}$ = 0.2 A
Therefore, the current flowing through the 30 resistor is 0.2 A.
To evaluate the potential difference across a resistor, we need to know the current flowing through and using ohm’s law, i.e., V = IR. Current following through 15 resistor is 0.3A as depicted in circuit drawn in part (c), Hence potential difference across 15 resistor is:
$V=I\times R=0.3\times 15=4.5V$
Now, the current flowing through 60 resistor is ( 0.3 – 0.2 =) 0.1 A which can be evaluated from part (c). Therefore potential difference across it will be:
$V=I\times R=0.1\times 60=4V$
Note:
To evaluate potential difference across 60 resistors in part (d), one can also simply evaluate voltage across 30 resistors, without evaluating current through it, which is also 6 V as they are connected in parallel and potential difference across resistors connected in parallel is equal. Kirchhoff’s laws are the fundamental base of whole electronics. Using these laws one can fully understand analog electronics and solve any type of problem. While applying KVL, we should always look for the terminal of the battery through which current is entering and put the sign in the equation accordingly, i.e., + for positive terminal and – for negative terminal.
Complete answer:
This question consists of four parts:
In the first one we need to evaluate the total resistance within the circuit given. First step would be to evaluate the resultant resistance for the 60 and 30 resistors connected in parallel. The resultant resistance for these two will be:
$\dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}}$
$\dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{1}{30}+\dfrac{1}{60}$
R = 20 $\Omega $
The equivalent circuit diagram after first step is given below:

Now, the second step is to evaluate total resistance in the circuit due to 15, 45, and 20 resistors connected in series.
R = R1 + R2 + R3 = 15 + 45 + 20 = 80 $\Omega $
Hence, the total resistance within the circuit is 80
Now, we are asked to evaluate the total current in the circuit. We already know total resistance as calculated in (a) part. Current can be calculated using ohm’s law:
$I=\dfrac{V}{R}=\dfrac{24}{80}=0.3A$
Hence, total current in the circuits is 0.3 A.
To evaluate the current through 30 resistors use KVL. Let current I1 flows through a 30$\Omega $ resistor. Consider two loops, 1 & 2, in the circuit as shown in figure given below:

Applying KVL in loop 1:
$-24+0.3\times 15+0.3\times 45+30\times {{I}_{1}}=0$ -- (1)
Applying KVL in loop 1:
$-24+0.3\times 15+0.3\times 45+60\times 0.3-{{I}_{1}}=0$ -- (2)
Now solving equation (1) and (2) will give us I1:
${{I}_{1}}$ = 0.2 A
Therefore, the current flowing through the 30 resistor is 0.2 A.
To evaluate the potential difference across a resistor, we need to know the current flowing through and using ohm’s law, i.e., V = IR. Current following through 15 resistor is 0.3A as depicted in circuit drawn in part (c), Hence potential difference across 15 resistor is:
$V=I\times R=0.3\times 15=4.5V$
Now, the current flowing through 60 resistor is ( 0.3 – 0.2 =) 0.1 A which can be evaluated from part (c). Therefore potential difference across it will be:
$V=I\times R=0.1\times 60=4V$
Note:
To evaluate potential difference across 60 resistors in part (d), one can also simply evaluate voltage across 30 resistors, without evaluating current through it, which is also 6 V as they are connected in parallel and potential difference across resistors connected in parallel is equal. Kirchhoff’s laws are the fundamental base of whole electronics. Using these laws one can fully understand analog electronics and solve any type of problem. While applying KVL, we should always look for the terminal of the battery through which current is entering and put the sign in the equation accordingly, i.e., + for positive terminal and – for negative terminal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




