
In a grassland, the top consumers are
(a) Herbivores
(b) Carnivores
(c) Bacteria
(d) Tall pine tree
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: A grassland ecosystem is a landscape that is dominated by the vegetation of grasses. Such an ecosystem harbors a population of domesticated animals and the set of animals which further depends on other animals for food.
Complete step by step answer:
An ecosystem can be defined as a functional unit of nature, where interaction between living organisms takes place among themselves and also with the surrounding physical environment. In a grassland ecosystem, the vegetation is composed of tall grasses or herbaceous woody plants with few or no trees. The biotic components of a grassland ecosystem are made up of producers which usually include grasses like Setaria, Cynodon, etc.
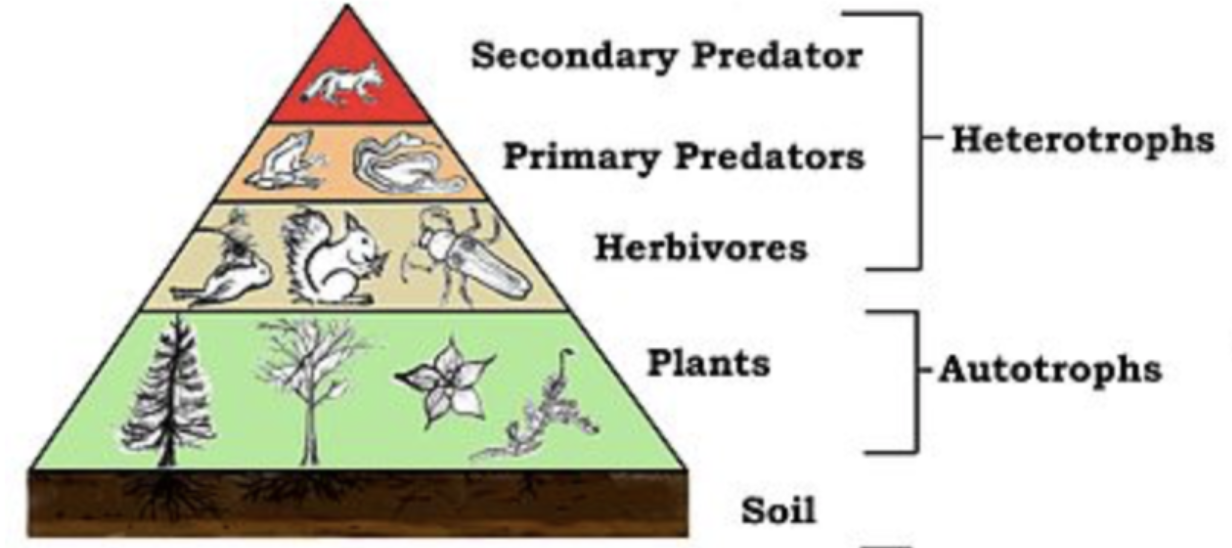
These producers are fed upon by the primary consumers which include the population of herbivores like cows, goats, rabbits, or some small insects like centipedes and millipedes. These are then followed by top consumers which include carnivorous animals like jackals, foxes, etc.
Additional Information:
- Every ecosystem has nonliving or abiotic components and living or biotic components.
- The biotic components include autotrophs, heterotrophs, and decomposers. Autotrophs are the producers who can manufacture their food from simple inorganic substances by fixing energy. E.g. Green plants, algae, chemosynthetic bacteria, etc. Heterotrophs are the organisms that cannot synthesize the organic nutrients for themselves and thus depend on producers or other consumers for their survival.
Decomposers feed on dead organic matter.E.g. Fungi and bacteria.
- The abiotic components include temperature, wind, humidity, solar energy, and precipitation.
So, the correct answer is ‘Carnivores.’
Note:
- In a functional ecosystem, the population of an ecosystem is regulated through their interaction with the external factors or abiotic factors. The biotic components in an area are collectively referred to as a population.
- The activities of a population, in turn, also affect its environment or abiotic components. Thus, a functional ecosystem regulates its environment efficiently.
Complete step by step answer:
An ecosystem can be defined as a functional unit of nature, where interaction between living organisms takes place among themselves and also with the surrounding physical environment. In a grassland ecosystem, the vegetation is composed of tall grasses or herbaceous woody plants with few or no trees. The biotic components of a grassland ecosystem are made up of producers which usually include grasses like Setaria, Cynodon, etc.

These producers are fed upon by the primary consumers which include the population of herbivores like cows, goats, rabbits, or some small insects like centipedes and millipedes. These are then followed by top consumers which include carnivorous animals like jackals, foxes, etc.
Additional Information:
- Every ecosystem has nonliving or abiotic components and living or biotic components.
- The biotic components include autotrophs, heterotrophs, and decomposers. Autotrophs are the producers who can manufacture their food from simple inorganic substances by fixing energy. E.g. Green plants, algae, chemosynthetic bacteria, etc. Heterotrophs are the organisms that cannot synthesize the organic nutrients for themselves and thus depend on producers or other consumers for their survival.
Decomposers feed on dead organic matter.E.g. Fungi and bacteria.
- The abiotic components include temperature, wind, humidity, solar energy, and precipitation.
So, the correct answer is ‘Carnivores.’
Note:
- In a functional ecosystem, the population of an ecosystem is regulated through their interaction with the external factors or abiotic factors. The biotic components in an area are collectively referred to as a population.
- The activities of a population, in turn, also affect its environment or abiotic components. Thus, a functional ecosystem regulates its environment efficiently.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




