
In a mature dicot stem which has undergone secondary growth, the youngest layer of secondary xylem is situated
A. In between the pith and primary xylem
B. Just outside the vascular cambium
C. Just inner to the vascular cambium
D. Just inner to the phellogen
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: The vascular bundles in dicot stem are arranged in ring shape. Dicot stems are so-called because of the presence of two cotyledon or embryonic leaves called a dicotyledonous stem or dicot stems. Secondary growth refers to the presence of vascular bundles.
Complete answer:
Dicots are the flowering plants that consist of two cotyledons and the presence of cambium is seen in them as secondary growth of tissue takes place. Secondary growth is a result of the division of cambium. The parallel arrangement of meristematic cells between the vascular bundle xylem and phloem is called cambium. They do not regulate the function of transportation of water, food, or minerals like xylem and phloem. Cambium is nothing but the meristematic cells found between the xylem and phloem of vascular bundles. Cambium is responsible for the production of vascular tissues in plants and hence named vascular cambium. Depending upon the location cambium is further categorized as fascicular cambium and interfascicular cambium. The cambium present between the conducting tissue xylem and phloem is called a fascicular cambium. Interfascicular cambium is the cambium present between the two vascular bundles. It is referred to as a secondary meristem. During the secondary growth of plants, vascular cambium is formed by the fusion of fascicular cambium and interfascicular cambium. Cambium regulates the function of the production of secondary xylem towards the pith and the growth of secondary phloem towards the bark. Secondary xylem is present just inner of the vascular cambium and grows towards the pith.
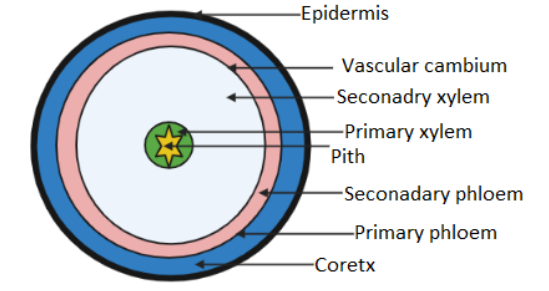
So, option C is the correct option.
Note: Vascular cambium is considered as the main growth tissue in the roots and stems of many plants mainly in dicots and gymnosperms and also in some vascular plants. Secondary growth is not seen in monocots and they lack the presence of cambium. Vascular cambium is also seen in a few leaf types.
Complete answer:
Dicots are the flowering plants that consist of two cotyledons and the presence of cambium is seen in them as secondary growth of tissue takes place. Secondary growth is a result of the division of cambium. The parallel arrangement of meristematic cells between the vascular bundle xylem and phloem is called cambium. They do not regulate the function of transportation of water, food, or minerals like xylem and phloem. Cambium is nothing but the meristematic cells found between the xylem and phloem of vascular bundles. Cambium is responsible for the production of vascular tissues in plants and hence named vascular cambium. Depending upon the location cambium is further categorized as fascicular cambium and interfascicular cambium. The cambium present between the conducting tissue xylem and phloem is called a fascicular cambium. Interfascicular cambium is the cambium present between the two vascular bundles. It is referred to as a secondary meristem. During the secondary growth of plants, vascular cambium is formed by the fusion of fascicular cambium and interfascicular cambium. Cambium regulates the function of the production of secondary xylem towards the pith and the growth of secondary phloem towards the bark. Secondary xylem is present just inner of the vascular cambium and grows towards the pith.

So, option C is the correct option.
Note: Vascular cambium is considered as the main growth tissue in the roots and stems of many plants mainly in dicots and gymnosperms and also in some vascular plants. Secondary growth is not seen in monocots and they lack the presence of cambium. Vascular cambium is also seen in a few leaf types.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




