
In a moss, the sporophyte
(a)Manufactures food for itself as well as for the gametophyte.
(b)Arises from a spore produced from the gametophyte.
(c)Produce gametes that give rise to the gametophyte.
(d)None of the above.
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: Gametes develop in the multicellular haploid gametophyte. Fertilization gives rise to a multicellular diploid sporophyte, which produces haploid spores via meiosis. This type of life cycle is called a haplodiplontic life cycle.
Complete answer:
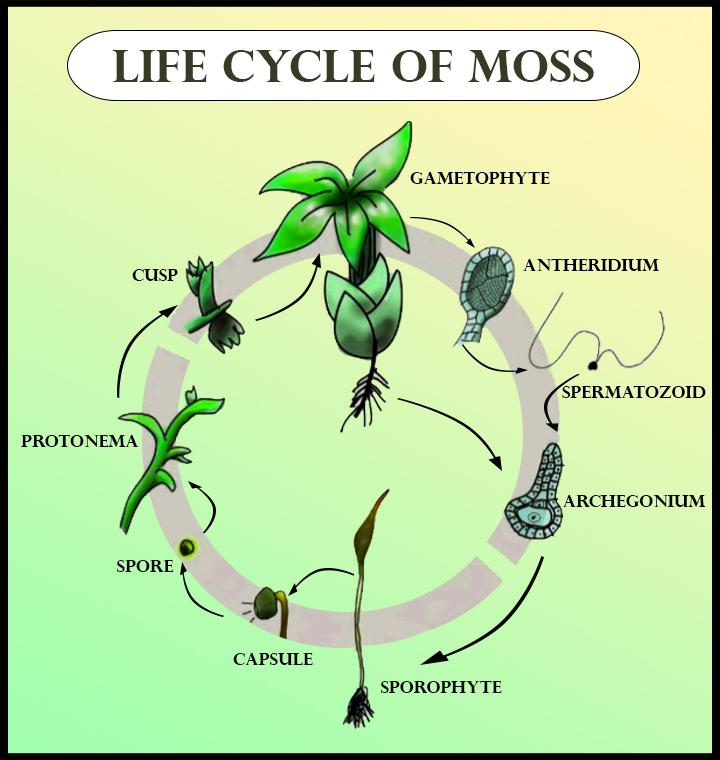
In mosses, the male gamete (sperm released from antheridia) fuses with the female gamete ( egg cells within the archegonium) to result in the immature sporophytes. The sporophyte matures and releases the spores. These spores germinate to form the protonema (an immature transitory stage), that matures into the gametophyte (gamete bearing structure). Its tip branches to bear the male and the female gametophytes i.e antheridia and archegonia. So, in mosses, the gametophyte arises from spores produced from the sporophyte and the sporophyte arises from the fusion of gametes.
Additional Information: -The moss life cycle follows the pattern of alternation of generations. Rhizoids form at the base of the gametophore. Gametangia of both sexes develop on separate gametophores. The male organ (the antheridium) produces much sperm, whereas the archegonium (the female organ) forms a single egg. During fertilization, the sperm swims down the neck to the venter and unites with the egg inside the archegonium to produce a zygote.
The life cycle of mosses: The alternation of generations cycle begins when the gametophyte germinates from a haploid spore and forms a protonema. Apical meristem-like cells divide and lead to gametophores. The archegonium (female organ) and antheridium (male organ) are seen on separate gametophores. After fertilization, the zygote divides and grows into a sporophyte, which stays attached to the gametophyte. Spores released from the sporophyte germinate and produce gametophytes; the process begins again.
So, the correct answer is, “Produce gametes that give rise to the gametophyte.”
Note:
Complete answer:
In mosses, the male gamete (sperm released from antheridia) fuses with the female gamete ( egg cells within the archegonium) to result in the immature sporophytes. The sporophyte matures and releases the spores. These spores germinate to form the protonema (an immature transitory stage), that matures into the gametophyte (gamete bearing structure). Its tip branches to bear the male and the female gametophytes i.e antheridia and archegonia. So, in mosses, the gametophyte arises from spores produced from the sporophyte and the sporophyte arises from the fusion of gametes.
Additional Information: -The moss life cycle follows the pattern of alternation of generations. Rhizoids form at the base of the gametophore. Gametangia of both sexes develop on separate gametophores. The male organ (the antheridium) produces much sperm, whereas the archegonium (the female organ) forms a single egg. During fertilization, the sperm swims down the neck to the venter and unites with the egg inside the archegonium to produce a zygote.
The life cycle of mosses: The alternation of generations cycle begins when the gametophyte germinates from a haploid spore and forms a protonema. Apical meristem-like cells divide and lead to gametophores. The archegonium (female organ) and antheridium (male organ) are seen on separate gametophores. After fertilization, the zygote divides and grows into a sporophyte, which stays attached to the gametophyte. Spores released from the sporophyte germinate and produce gametophytes; the process begins again.

So, the correct answer is, “Produce gametes that give rise to the gametophyte.”
Note:
| Liverworts | Mosses |
| -These are the non-vascular plants consisting of leaves like lobes or stems. | Mosses are the non-vascular plants which have leafy stems. |
| -Belongs to the division Marchantiophyta. | -Belong to the division Bryophyta. |
| -The gametophyte is a thallose or foliose. | -The gametophyte is foliose. |
| -Rhizoids are unicellular. | -Rhizoid is pluricellular. |
| -Protonemata are reduced. | -Produce prominent protonemata. |
| -Leaf-like structures are arranged in two or three rows in a flattened pattern. | -Leaf-like structures are arranged in a spiral or whorl. |
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




