
In a right-angled isosceles triangle the ratio of the circumradius and inradius is?
A). $2\left( \sqrt{2+1} \right):1$
B). $\left( \left( \sqrt{2+1} \right):1 \right)$
C). $2:1$
D). $\sqrt{2}:1$
Answer
597k+ views
Hint: Apply the formula of inradius in the coordinate geometry. Use properties of triangles to solve them. Use the given conditions to find the angles to the triangles. Now, Find relation between inradius and angles. Then take the ration from that relation.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given the condition on the triangle in the question is written as: The triangle is a right angle isosceles. So, one angle is ${{90}^{\circ }}$ and other angles are equal.
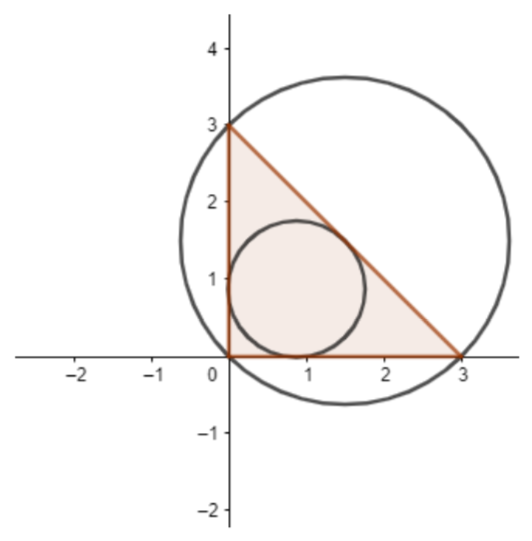
Let us assume equal angles to be x.
Now the sum of all angles is ${{180}^{\circ }}$ . So, we get –
$90+2x=180{}^\circ $ .
From this equation, we get $x=45{}^\circ $ .
Let us assume $A=45$ , $B=90$ , $C=45$ .
By properties of triangle we have the formula of ‘r’ as:
$r=\dfrac{\left( abc \right)}{4SR}$
We know the formula given by (in triangles):
$\begin{align}
& a=2R\sin A,b=2R\sin B,c=2R\sin C \\
& S=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2} \\
\end{align}$
By substituting these into our equation, we get the ‘r’ as:
$r=\dfrac{\left( 2R\sin A \right)\left( 2R\sin B \right)\left( 2R\sin C \right)}{4\left( \dfrac{\sin A+\sin B+\sin C}{2} \right)\left( 2R \right)\left( R \right)}$
By cancelling R terms in the above equation, we get it as:
$r=\dfrac{2R\left( \sin A \right)\left( \sin B \right)\left( \sin C \right)}{\left( \sin A+\sin B+\sin C \right)}$
By substituting $\sin x=2\sin \dfrac{x}{2}\cos \dfrac{x}{2}$ , we get it as:
$r=2R\text{ }2.2.2\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}.\dfrac{\cos \dfrac{A}{2}\cos \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2}}{2\left( \sin \dfrac{A}{2}\cos \dfrac{A}{2}+\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{B}{2}+\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2} \right)}$
By cancelling 2 in the above equation and write 8 as (4).(2), we get it as :
\[r=\left( 4R\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2} \right).\dfrac{2\cos \dfrac{A}{2}\cos \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2}}{\left( \sin \dfrac{A}{2}\cos \dfrac{A}{2}+\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{B}{2}+\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2} \right)}\]
By simplifying we can write it as follows:
\[r=\dfrac{4R\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\times 2}{\dfrac{\sin \dfrac{A}{2}}{\cos \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2}}+\dfrac{\sin \dfrac{B}{2}}{\cos \dfrac{A}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2}}+\dfrac{\sin \dfrac{C}{2}}{\cos \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{A}{2}}}\]
We know that $\sin \dfrac{A}{2}=\cos \left( \dfrac{B+C}{2} \right)$
By applying formula $\cos \left( A+B \right)=\cos A\cos B+\sin A\sin B$ , we get –
$\sin \dfrac{A}{2}=\cos \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2}-\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}$
\[r=\dfrac{4R\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}.2}{\dfrac{\cos \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2}-\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}}{\cos \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2}}+\dfrac{\cos \dfrac{A}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2}-\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}}{\cos \dfrac{A}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2}}+\dfrac{\cos \dfrac{A}{2}\cos \dfrac{B}{2}-\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}}{\cos \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{A}{2}}}\]
By simplifying the above equation, we get it as:
\[r=\dfrac{4R\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}.2}{3-\tan \dfrac{A}{2}.\tan \dfrac{B}{2}-\tan \dfrac{B}{2}.\tan \dfrac{C}{2}-\tan \dfrac{A}{2}.\tan \dfrac{C}{2}}\]
By trigonometric knowledge, we know the equation given by:
\[\tan \dfrac{A}{2}\tan \dfrac{B}{2}+\tan \dfrac{C}{2}\tan \dfrac{B}{2}+\tan \dfrac{A}{2}\tan \dfrac{C}{2}=1\]
By substituting this equation of tangent in denominator we can cancel 2, we get the relation as:
$r=4R\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}$
Now writing the term required ratio of R and r, we get it as:
$\dfrac{R}{r}=\dfrac{1}{4\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}}$
By substituting the values of A,B,C we get it as:
$\dfrac{R}{r}=\dfrac{1}{4\sin 45\sin 22\dfrac{1}{2}\sin 22\dfrac{1}{2}}$
We know $\sin 45=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}; $ $\sin 22\dfrac{1}{2}=\sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2\sqrt{2}}}$
By substituting the values we get the final answer as:
$\dfrac{R}{r}=\dfrac{1}{4\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right){{\left( \sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2\sqrt{2}}} \right)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{4.\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}.\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2\sqrt{2}}}$
By simplifying the value of ratio above we get it as:
$\dfrac{R}{r}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}-1}$
By rationalizing we get the value of $\dfrac{R}{r}$ as –
$\dfrac{R}{r}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}-1}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{2}+1}{\sqrt{2}+1}=\sqrt{2}+1$ .
So, the ratio R:r is given by $\sqrt{2}+1$.
So, option (b) is correct.
Note: Be careful while finding the angles, As the whole answer depends on them. While calculating the formula of r keep the R like that only because we need the ratio of R:r. Alternately you can keep $22\dfrac{1}{2}$ like that itself and apply ${{\sin }^{2}}\dfrac{A}{2}=\sqrt{\dfrac{1-\cos }{2}}$ because you know the value of cos 45 anyways you set some result.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given the condition on the triangle in the question is written as: The triangle is a right angle isosceles. So, one angle is ${{90}^{\circ }}$ and other angles are equal.

Let us assume equal angles to be x.
Now the sum of all angles is ${{180}^{\circ }}$ . So, we get –
$90+2x=180{}^\circ $ .
From this equation, we get $x=45{}^\circ $ .
Let us assume $A=45$ , $B=90$ , $C=45$ .
By properties of triangle we have the formula of ‘r’ as:
$r=\dfrac{\left( abc \right)}{4SR}$
We know the formula given by (in triangles):
$\begin{align}
& a=2R\sin A,b=2R\sin B,c=2R\sin C \\
& S=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2} \\
\end{align}$
By substituting these into our equation, we get the ‘r’ as:
$r=\dfrac{\left( 2R\sin A \right)\left( 2R\sin B \right)\left( 2R\sin C \right)}{4\left( \dfrac{\sin A+\sin B+\sin C}{2} \right)\left( 2R \right)\left( R \right)}$
By cancelling R terms in the above equation, we get it as:
$r=\dfrac{2R\left( \sin A \right)\left( \sin B \right)\left( \sin C \right)}{\left( \sin A+\sin B+\sin C \right)}$
By substituting $\sin x=2\sin \dfrac{x}{2}\cos \dfrac{x}{2}$ , we get it as:
$r=2R\text{ }2.2.2\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}.\dfrac{\cos \dfrac{A}{2}\cos \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2}}{2\left( \sin \dfrac{A}{2}\cos \dfrac{A}{2}+\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{B}{2}+\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2} \right)}$
By cancelling 2 in the above equation and write 8 as (4).(2), we get it as :
\[r=\left( 4R\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2} \right).\dfrac{2\cos \dfrac{A}{2}\cos \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2}}{\left( \sin \dfrac{A}{2}\cos \dfrac{A}{2}+\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{B}{2}+\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2} \right)}\]
By simplifying we can write it as follows:
\[r=\dfrac{4R\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\times 2}{\dfrac{\sin \dfrac{A}{2}}{\cos \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2}}+\dfrac{\sin \dfrac{B}{2}}{\cos \dfrac{A}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2}}+\dfrac{\sin \dfrac{C}{2}}{\cos \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{A}{2}}}\]
We know that $\sin \dfrac{A}{2}=\cos \left( \dfrac{B+C}{2} \right)$
By applying formula $\cos \left( A+B \right)=\cos A\cos B+\sin A\sin B$ , we get –
$\sin \dfrac{A}{2}=\cos \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2}-\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}$
\[r=\dfrac{4R\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}.2}{\dfrac{\cos \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2}-\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}}{\cos \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2}}+\dfrac{\cos \dfrac{A}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2}-\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}}{\cos \dfrac{A}{2}\cos \dfrac{C}{2}}+\dfrac{\cos \dfrac{A}{2}\cos \dfrac{B}{2}-\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}}{\cos \dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{A}{2}}}\]
By simplifying the above equation, we get it as:
\[r=\dfrac{4R\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}.2}{3-\tan \dfrac{A}{2}.\tan \dfrac{B}{2}-\tan \dfrac{B}{2}.\tan \dfrac{C}{2}-\tan \dfrac{A}{2}.\tan \dfrac{C}{2}}\]
By trigonometric knowledge, we know the equation given by:
\[\tan \dfrac{A}{2}\tan \dfrac{B}{2}+\tan \dfrac{C}{2}\tan \dfrac{B}{2}+\tan \dfrac{A}{2}\tan \dfrac{C}{2}=1\]
By substituting this equation of tangent in denominator we can cancel 2, we get the relation as:
$r=4R\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}$
Now writing the term required ratio of R and r, we get it as:
$\dfrac{R}{r}=\dfrac{1}{4\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}}$
By substituting the values of A,B,C we get it as:
$\dfrac{R}{r}=\dfrac{1}{4\sin 45\sin 22\dfrac{1}{2}\sin 22\dfrac{1}{2}}$
We know $\sin 45=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}; $ $\sin 22\dfrac{1}{2}=\sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2\sqrt{2}}}$
By substituting the values we get the final answer as:
$\dfrac{R}{r}=\dfrac{1}{4\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right){{\left( \sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2\sqrt{2}}} \right)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{4.\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}.\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2\sqrt{2}}}$
By simplifying the value of ratio above we get it as:
$\dfrac{R}{r}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}-1}$
By rationalizing we get the value of $\dfrac{R}{r}$ as –
$\dfrac{R}{r}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}-1}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{2}+1}{\sqrt{2}+1}=\sqrt{2}+1$ .
So, the ratio R:r is given by $\sqrt{2}+1$.
So, option (b) is correct.
Note: Be careful while finding the angles, As the whole answer depends on them. While calculating the formula of r keep the R like that only because we need the ratio of R:r. Alternately you can keep $22\dfrac{1}{2}$ like that itself and apply ${{\sin }^{2}}\dfrac{A}{2}=\sqrt{\dfrac{1-\cos }{2}}$ because you know the value of cos 45 anyways you set some result.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




