
In an experiment of convection heat transfer, water inside the pipe is heated by which of the following principles,
A. free convection + conduction
B. free convection
C. forced convection
D. mixed convection
Answer
558k+ views
Hint: Conduction, convection and radiation three different methods of heat transfer. The experiment is about convection heat transfer of water in a pipe. When water is passed in a pipe and the pipe is heated, water heats up too.
Complete step-by-step solution:
To understand heat transfer methods better one can imagine a scenario when in a classroom a copy needs to be passed at the last bench starting from the first bench. Now one can throw the copy at the last bench. This is an analogy for the radiation method of heat transfer. Person on the first bench can also get up and go to the last bench and deliver the copy. This is the case about convection heat transfer. Another method is that the person on the first bench passes the copy to the second bench and eventually one by one it reaches the last bench. This is the case for conduction.
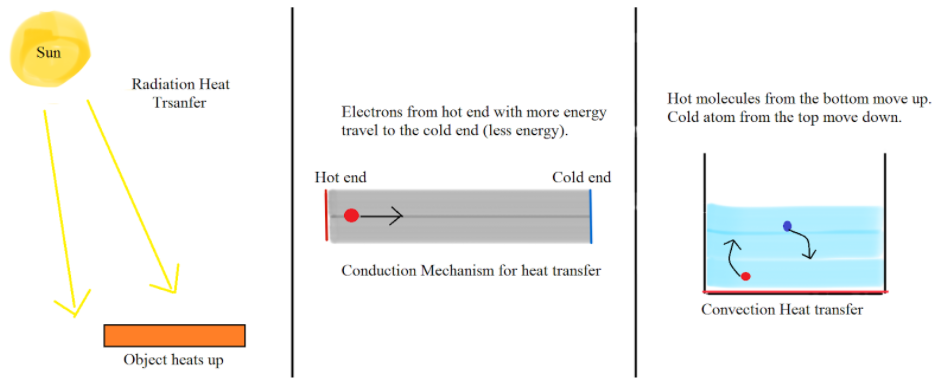
Conduction heat transfer can be observed to take place in a conductor. We commonly observe this when we leave our metal stick in the pot while cooking. After some time, we observe the other end of the stick to be hot as we touch it.
Convective heat transfer mechanism takes place in fluids. When we heat water at the upper, the water at the bottom heats up first as the molecules are in direct contact with the container. After this, the molecules at the bottom due to their high energy move to the top and heat the water uniformly.
As in the question the water in the pipe heats due to you first the heat of the pipe and then due to its internal convection currents. Heat from the pipe gets transferred by conduction to the water molecules which then carry away the heat and distributed equally in the water. Therefore the correct answer is option (A) free convection + conduction heats the water in the pipe.
Note: In forced convection mechanism, the fluid flow is monitored by some external source which helps in heating the fluid evenly. When natural flow due to free convection is present along with forced convection, we get mixed convection. None of these options apply to the question asked if we leave the water completely undisturbed externally.
Complete step-by-step solution:
To understand heat transfer methods better one can imagine a scenario when in a classroom a copy needs to be passed at the last bench starting from the first bench. Now one can throw the copy at the last bench. This is an analogy for the radiation method of heat transfer. Person on the first bench can also get up and go to the last bench and deliver the copy. This is the case about convection heat transfer. Another method is that the person on the first bench passes the copy to the second bench and eventually one by one it reaches the last bench. This is the case for conduction.

Conduction heat transfer can be observed to take place in a conductor. We commonly observe this when we leave our metal stick in the pot while cooking. After some time, we observe the other end of the stick to be hot as we touch it.
Convective heat transfer mechanism takes place in fluids. When we heat water at the upper, the water at the bottom heats up first as the molecules are in direct contact with the container. After this, the molecules at the bottom due to their high energy move to the top and heat the water uniformly.
As in the question the water in the pipe heats due to you first the heat of the pipe and then due to its internal convection currents. Heat from the pipe gets transferred by conduction to the water molecules which then carry away the heat and distributed equally in the water. Therefore the correct answer is option (A) free convection + conduction heats the water in the pipe.
Note: In forced convection mechanism, the fluid flow is monitored by some external source which helps in heating the fluid evenly. When natural flow due to free convection is present along with forced convection, we get mixed convection. None of these options apply to the question asked if we leave the water completely undisturbed externally.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




