
In an inflorescence where flowers are grown laterally in acropetal succession, the position of the youngest floral bud shall be
(a)Proximal
(b)Distal
(c)Intercalary
(d)Anywhere
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: In acropetal succession, the stem keeps growing and does not terminate. This type of inflorescence is also known as ‘Racemose inflorescence'.
Complete answer:
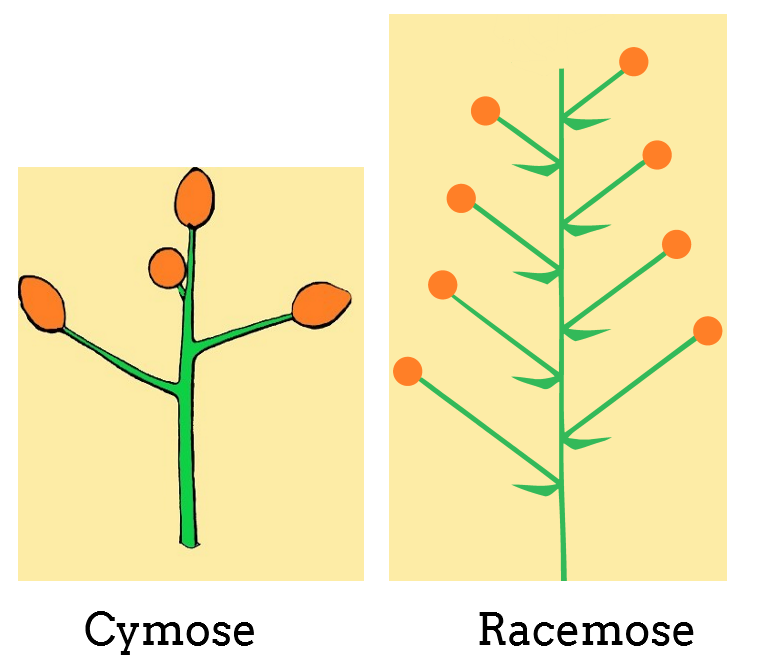
Acropetal succession in a plant is defined as the growth of the floral component from base to the apex. This means that in an inflorescence acquiring acropetal succession, the youngest floral bud shall occupy the distal position or the apex while the older flowers will lie proximal to the stem i.e. towards the base.
Consequently, the newly formed fruit remains uncovered. Example- mustard, radish, snapdragon, wheat, barley, etc. Types of racemose inflorescence include Raceme, Spike, Spikelet, Panicle, Catkin, Spadix, Corymb, and Umbel.
Basipetal succession- The growth of the inflorescence where the stem terminates into an apical flower is known as basipetal succession. It is also known as Cymose inflorescence. Hence, the newer flowers lie proximal or close to the stem base while the older flowers lie distally. It is seen in drosera, dianthus, calotropis, hibiscus, etc.
So, the correct answer is ‘Distal’.
Note: -Spikelet type of inflorescence is the characteristic feature of the Poaceae or the Gramineae family that consists of grasses.
-The central longitudinal axis of the inflorescence is known as Rachis and the stem holding all the branches is known as Peduncle.
-The racemose and cymose inflorescence is known as the open and closed type of inflorescence respectively.
Complete answer:
Acropetal succession in a plant is defined as the growth of the floral component from base to the apex. This means that in an inflorescence acquiring acropetal succession, the youngest floral bud shall occupy the distal position or the apex while the older flowers will lie proximal to the stem i.e. towards the base.
Consequently, the newly formed fruit remains uncovered. Example- mustard, radish, snapdragon, wheat, barley, etc. Types of racemose inflorescence include Raceme, Spike, Spikelet, Panicle, Catkin, Spadix, Corymb, and Umbel.
Basipetal succession- The growth of the inflorescence where the stem terminates into an apical flower is known as basipetal succession. It is also known as Cymose inflorescence. Hence, the newer flowers lie proximal or close to the stem base while the older flowers lie distally. It is seen in drosera, dianthus, calotropis, hibiscus, etc.
So, the correct answer is ‘Distal’.
Note: -Spikelet type of inflorescence is the characteristic feature of the Poaceae or the Gramineae family that consists of grasses.
-The central longitudinal axis of the inflorescence is known as Rachis and the stem holding all the branches is known as Peduncle.
-The racemose and cymose inflorescence is known as the open and closed type of inflorescence respectively.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




