
In an orthorhombic crystal, a lattice plane cuts intercepts in the ratio 1:2:3 along a,b and c axes. Find the miller indices of the plane. Sketch the plane and calculate the interplanar spacing, given that a=1A, b=2A and c=3A.
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: We have to calculate Miller indices by taking the reciprocals of intercepts and for calculating the interplanar spacing, we have to use the formula,
$\dfrac{1}{{{d_{hkl}}^2}} = \dfrac{4}{3}\left( {\dfrac{{{h^ + } + hk + {k^2}}}{{{a^2}}}} \right) + \left( {\dfrac{{{l^2}}}{{{c^2}}}} \right)$
Here, h, k, and l are miller indices.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems.
Orthorhombic lattices comes from enlarging a cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two factors, that leads in a rectangular prism with a rectangular base (a by b) and height (c), such that a, b, and c are different.
The intersection of all three bases at 90° angles, so the three lattice vectors remain mutually orthogonal.
We know that Miller indices of a plane are the reciprocals of the intercepts of that corresponding to unit length.
Thus, intercepts are a:b:c=1:2:3.
So let us now take the reciprocals:
$\dfrac{1}{a}:\dfrac{1}{b}:\dfrac{1}{c} = \dfrac{1}{1}:\dfrac{1}{2}:\dfrac{1}{3}$
(or) We can take L.C.M and by taking L.C.M, we get the value of miller indices as 6,3,2.
The value of h is 6.
The value of k is 3.
The value of l is 2.
We can represent the miller indices as $\left( {hkl} \right) = \left( {632} \right)$
Let us now calculate the interplanar spacing for orthorhombic crystals.
$\dfrac{1}{{{d_{hkl}}^2}} = \dfrac{4}{3}\left( {\dfrac{{{h^ + } + hk + {k^2}}}{{{a^2}}}} \right) + \left( {\dfrac{{{l^2}}}{{{c^2}}}} \right)$
Let us now substitute the values of a, c, h, k, and l to calculate the interplanar spacing.
$\dfrac{1}{{{d_{hkl}}^2}} = \dfrac{4}{3}\left( {\dfrac{{{{\left( 6 \right)}^2} + \left( 6 \right)\left( 2 \right) + {{\left( 2 \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( 1 \right)}^2}}}} \right) + \left( {\dfrac{{{{\left( 2 \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( 3 \right)}^2}}}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow $$\dfrac{1}{{{d_{hkl}}^2}} = \dfrac{{760}}{9}$
$ \Rightarrow $${d_{hkl}}^2 = \dfrac{9}{{760}}$
$ \Rightarrow $${d_{hkl}} = \dfrac{3}{{\sqrt {760} }}$
The inter-planar spacing is $\dfrac{3}{{\sqrt {760} }}$.
The plane is sketched as,
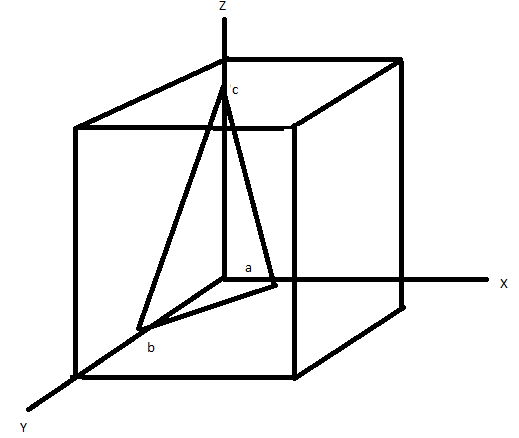
Note:
We have to know that in two dimensions there are two orthorhombic Bravais lattices: primitive rectangular and centered rectangular. In three dimensions, primitive orthorhombic, base-centered orthorhombic, body-centered orthorhombic, and face-centered orthorhombic are the four orthorhombic Bravais lattices.
$\dfrac{1}{{{d_{hkl}}^2}} = \dfrac{4}{3}\left( {\dfrac{{{h^ + } + hk + {k^2}}}{{{a^2}}}} \right) + \left( {\dfrac{{{l^2}}}{{{c^2}}}} \right)$
Here, h, k, and l are miller indices.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems.
Orthorhombic lattices comes from enlarging a cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two factors, that leads in a rectangular prism with a rectangular base (a by b) and height (c), such that a, b, and c are different.
The intersection of all three bases at 90° angles, so the three lattice vectors remain mutually orthogonal.
We know that Miller indices of a plane are the reciprocals of the intercepts of that corresponding to unit length.
Thus, intercepts are a:b:c=1:2:3.
So let us now take the reciprocals:
$\dfrac{1}{a}:\dfrac{1}{b}:\dfrac{1}{c} = \dfrac{1}{1}:\dfrac{1}{2}:\dfrac{1}{3}$
(or) We can take L.C.M and by taking L.C.M, we get the value of miller indices as 6,3,2.
The value of h is 6.
The value of k is 3.
The value of l is 2.
We can represent the miller indices as $\left( {hkl} \right) = \left( {632} \right)$
Let us now calculate the interplanar spacing for orthorhombic crystals.
$\dfrac{1}{{{d_{hkl}}^2}} = \dfrac{4}{3}\left( {\dfrac{{{h^ + } + hk + {k^2}}}{{{a^2}}}} \right) + \left( {\dfrac{{{l^2}}}{{{c^2}}}} \right)$
Let us now substitute the values of a, c, h, k, and l to calculate the interplanar spacing.
$\dfrac{1}{{{d_{hkl}}^2}} = \dfrac{4}{3}\left( {\dfrac{{{{\left( 6 \right)}^2} + \left( 6 \right)\left( 2 \right) + {{\left( 2 \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( 1 \right)}^2}}}} \right) + \left( {\dfrac{{{{\left( 2 \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( 3 \right)}^2}}}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow $$\dfrac{1}{{{d_{hkl}}^2}} = \dfrac{{760}}{9}$
$ \Rightarrow $${d_{hkl}}^2 = \dfrac{9}{{760}}$
$ \Rightarrow $${d_{hkl}} = \dfrac{3}{{\sqrt {760} }}$
The inter-planar spacing is $\dfrac{3}{{\sqrt {760} }}$.
The plane is sketched as,

Note:
We have to know that in two dimensions there are two orthorhombic Bravais lattices: primitive rectangular and centered rectangular. In three dimensions, primitive orthorhombic, base-centered orthorhombic, body-centered orthorhombic, and face-centered orthorhombic are the four orthorhombic Bravais lattices.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




