
In animals, meiotic division occurs during gamete formation. This gametic meiosis results in
(a)Haplontic life cycle
(b)Diplontic life cycle
(c)Diplohaplontic life cycle
(d)None of the above
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: The life cycle in which meiosis is "gametic" includes the multicellular diploid stage. It is found in gymnosperm and angiosperm. Diplonts are classified as organisms that undergo such a life cycle. Some examples include few parabasalids in excavations and in opisthokonts, certain ascomycetes.
Complete answer:
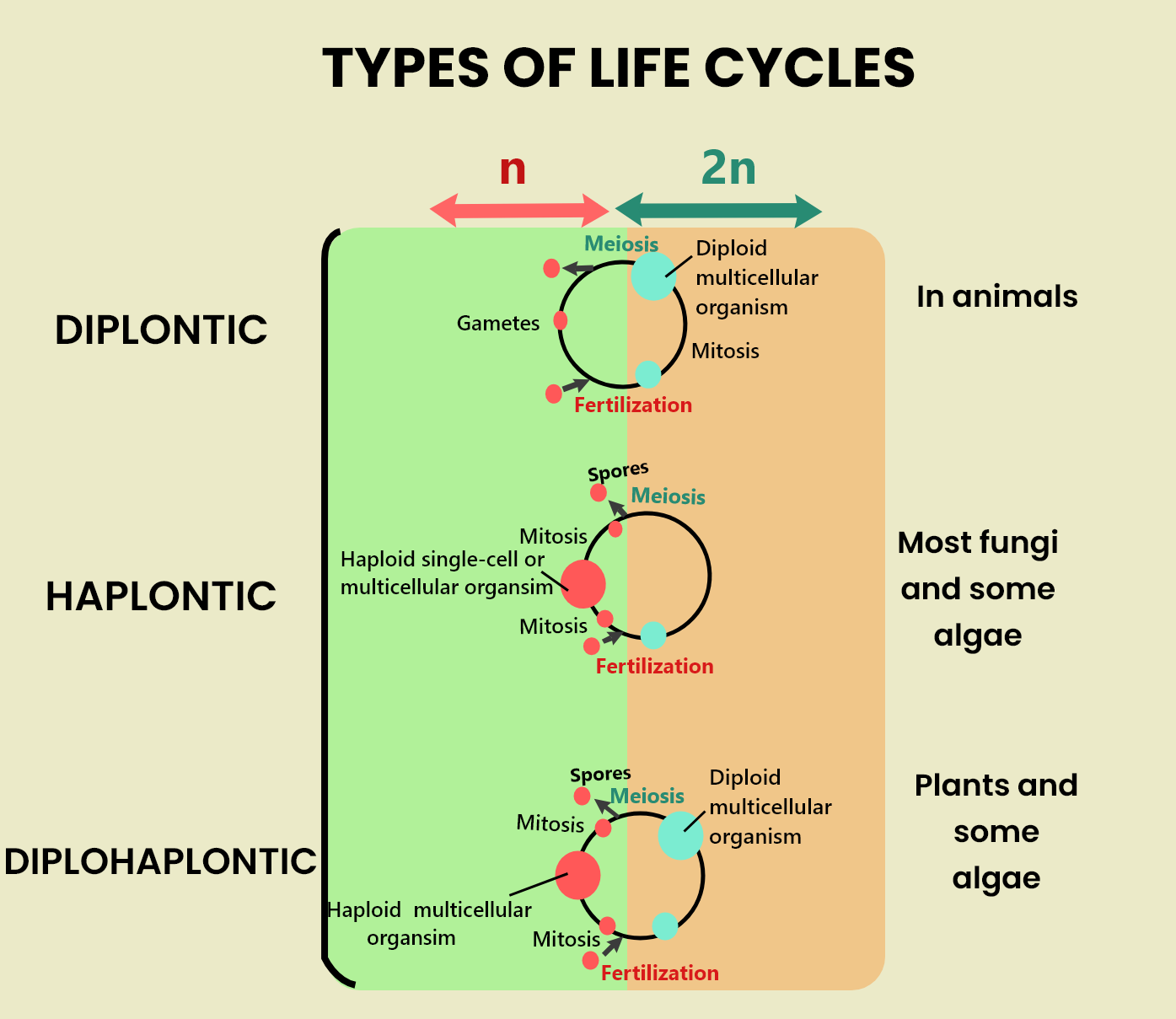
Meiosis takes place during the formation of gametes (gametogenesis) in most animals. This is known as gametic meiosis. A diploid zygote is produced when two gametes combine in fertilization.
The diplontic life cycle is a result of gametic meiosis.
In gametic meiosis, the zygote divides mitotically to produce a multicellular diploid organism or a group of more unicellular diploid cells, instead of dividing meiotically immediately to produce haploid cells. To produce haploid cells or gametes, cells from the diploid individuals then undergo meiosis. As in many leaves, haploid cells can divide again (by mitosis) to form more haploid cells, but the haploid phase is not the predominant phase of the life cycle. Mitosis occurs only in the diploid process in most diplonts, i.e. gametes typically develop rapidly and fuse to create diploid zygotes.
Additional Information:
In the phase of the diplontic life cycle:
-The sporophyte is noticeable.
-Green algae such as Cladophora glomerata, acetabularia in archaeplastida, and ciliates in alveolates are some examples of diplonts.
The zygote undergoes meiosis in the haplontic cycle and gametophyte is the dominant step.
A period in which multicellular diploid and haploid phases occur is the haplodiplontic life cycle (also referred to as the diplohaplontic, diplobiontic, or dibiontic life cycle). Meiosis is "sporic" here.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Diplontic life cycle’.
Note: Life cycles involving sexual reproduction require alternating phases of haploid (n) and diploid (2n), i.e. a ploidy transition is involved. Meiosis must occur to return from a diploid phase to a haploid phase. There are 3 types of cycles with respect to shifts in ploidy: haplontic, diplontic, and diplohaplontic life cycles.
Complete answer:
Meiosis takes place during the formation of gametes (gametogenesis) in most animals. This is known as gametic meiosis. A diploid zygote is produced when two gametes combine in fertilization.
The diplontic life cycle is a result of gametic meiosis.
In gametic meiosis, the zygote divides mitotically to produce a multicellular diploid organism or a group of more unicellular diploid cells, instead of dividing meiotically immediately to produce haploid cells. To produce haploid cells or gametes, cells from the diploid individuals then undergo meiosis. As in many leaves, haploid cells can divide again (by mitosis) to form more haploid cells, but the haploid phase is not the predominant phase of the life cycle. Mitosis occurs only in the diploid process in most diplonts, i.e. gametes typically develop rapidly and fuse to create diploid zygotes.
Additional Information:
In the phase of the diplontic life cycle:
-The sporophyte is noticeable.
-Green algae such as Cladophora glomerata, acetabularia in archaeplastida, and ciliates in alveolates are some examples of diplonts.
The zygote undergoes meiosis in the haplontic cycle and gametophyte is the dominant step.
A period in which multicellular diploid and haploid phases occur is the haplodiplontic life cycle (also referred to as the diplohaplontic, diplobiontic, or dibiontic life cycle). Meiosis is "sporic" here.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Diplontic life cycle’.
Note: Life cycles involving sexual reproduction require alternating phases of haploid (n) and diploid (2n), i.e. a ploidy transition is involved. Meiosis must occur to return from a diploid phase to a haploid phase. There are 3 types of cycles with respect to shifts in ploidy: haplontic, diplontic, and diplohaplontic life cycles.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




