
In animals, the first stage of glucose breakdown is
(a)Krebs Cycle
(b)Glycolysis
(c)Oxidative Phosphorylation
(d)Electron transport chain
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: The first stage of the glucose breakdown would mean the end products would be released energy and some byproduct molecules. Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration would require a particular pathway to break down glucose to provide energy.
Complete answer:
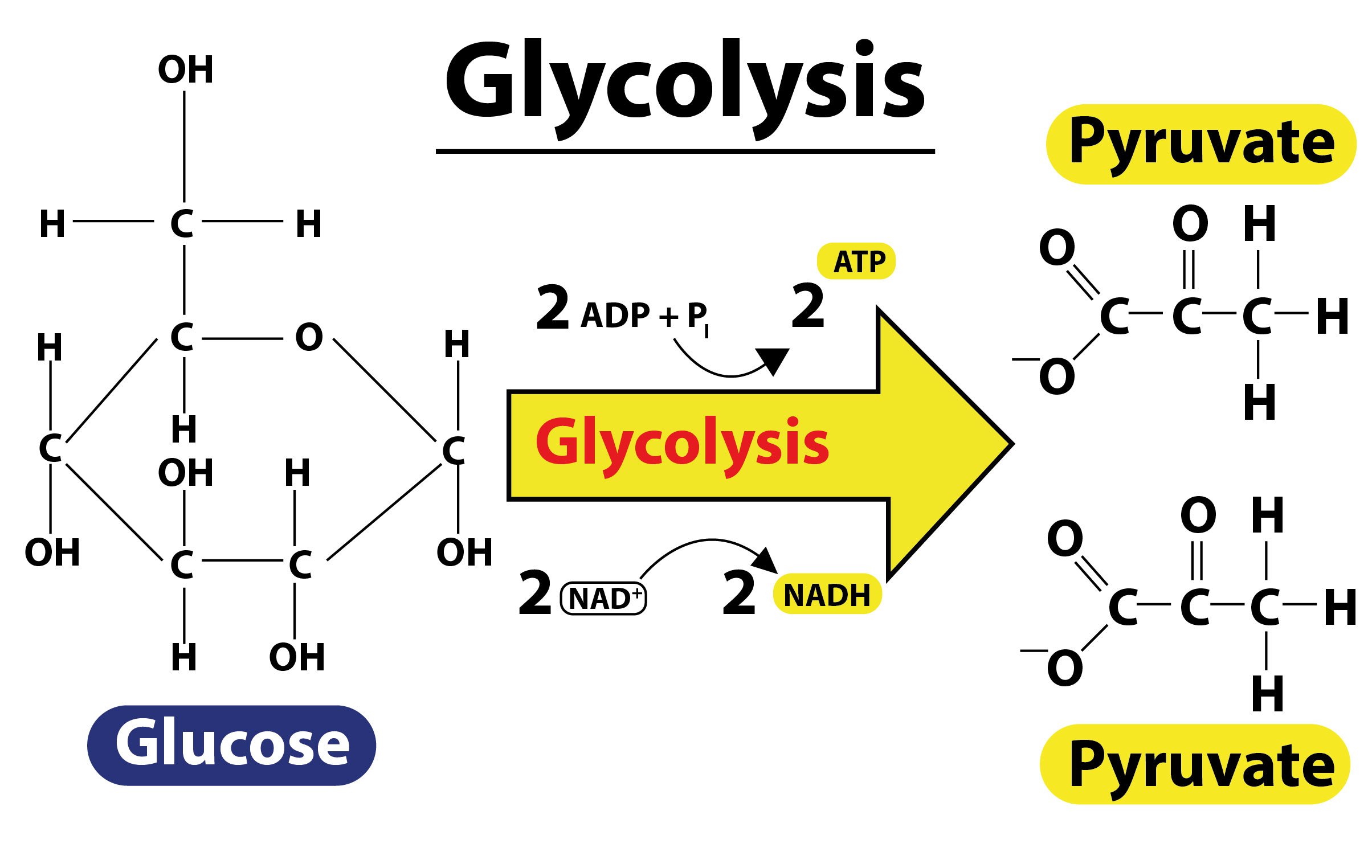
- The first stage of glucose breakdown in animals is known as glycolysis. The name is derived from the words glucose which is an older name of glucose and lysis which means ‘to break’.
- This pathway occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic cells. Hence, this pathway is oxygen-independent.
- This occurs in all living organisms and occurs in the cytosol of most of them. Here, glucose undergoes partial oxidation to form two molecules of pyruvate. The free energy released is used to form high-energy molecules ATP and NADH.
Additional Information:
- The most common form of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP) pathway. Other forms include various fermentative pathways and the Entner-Doudoroff pathway.
- There are ten enzyme-catalyzed steps and the end product, pyruvate, is transported to the mitochondria.
- The pathway is divided into two phases, the energy-requiring phase, and the energy-releasing phase.
- Glycolysis converts one six-carbon molecule of glucose to two three-carbon molecules of pyruvate. The other products formed are two molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADH.
So, the correct answer is ‘Glycolysis’.
Note: - The overall steps of aerobic respiration are $Glycolysis\quad \longrightarrow \quad Pyruvate\quad metabolism\quad \longrightarrow \quad Kreb's\quad cycle\quad \longrightarrow \quad Electron\quad transport\quad chain$
- Other molecules such as fructose and galactose can also be converted into intermediates in the pathway. The intermediates formed in this pathway may be used in other reactions, not just in glycolysis itself. For example, DHAP (dihydroxyacetone phosphate) is a source of the glycerol that can combine with fatty acids to form fats.
Complete answer:
- The first stage of glucose breakdown in animals is known as glycolysis. The name is derived from the words glucose which is an older name of glucose and lysis which means ‘to break’.
- This pathway occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic cells. Hence, this pathway is oxygen-independent.
- This occurs in all living organisms and occurs in the cytosol of most of them. Here, glucose undergoes partial oxidation to form two molecules of pyruvate. The free energy released is used to form high-energy molecules ATP and NADH.
Additional Information:
- The most common form of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP) pathway. Other forms include various fermentative pathways and the Entner-Doudoroff pathway.
- There are ten enzyme-catalyzed steps and the end product, pyruvate, is transported to the mitochondria.
- The pathway is divided into two phases, the energy-requiring phase, and the energy-releasing phase.
- Glycolysis converts one six-carbon molecule of glucose to two three-carbon molecules of pyruvate. The other products formed are two molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADH.
So, the correct answer is ‘Glycolysis’.

Note: - The overall steps of aerobic respiration are $Glycolysis\quad \longrightarrow \quad Pyruvate\quad metabolism\quad \longrightarrow \quad Kreb's\quad cycle\quad \longrightarrow \quad Electron\quad transport\quad chain$
- Other molecules such as fructose and galactose can also be converted into intermediates in the pathway. The intermediates formed in this pathway may be used in other reactions, not just in glycolysis itself. For example, DHAP (dihydroxyacetone phosphate) is a source of the glycerol that can combine with fatty acids to form fats.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




