
In benzene all \[C - C\] bond length between all carbon atoms are equal because of:
A.Tautomerism
B.\[S{p^2}\] hybridisation
C.Isomerism
D.Resonance
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: Benzene is an organic molecule. It is a resonance hybrid of various canonical structures. Resonance is the delocalization of electrons. Electron delocalization can stabilize benzene.
Complete step by step answer:
Benzene is an organic molecule having the molecular formula \[{C_6}{H_6}\] . The structure of benzene is given below.

All the carbon atoms are \[S{p^2}\] hybridised. These \[S{p^2}\] hybrid orbitals are arranged in a triangular planar fashion. One of the unhybridized p orbital will remain perpendicular to the above plane. Each C atom will use two of the \[S{p^2}\] hybridized orbital and form 2 \[C - C\] sigma bonds by \[s{p^2} - s{p^2}\] head-on overlap. The remaining \[S{p^2}\] orbital is used to form a sigma bond by overlap with the 1s orbital of hydrogen. There will be 6 \[C - C\] sigma bonds that form the sides of the hexagon. All the \[C - C - C\] bond angles will be \[120^\circ \] .
According to the resonance concept, benzene is a resonance hybrid of the following structures.
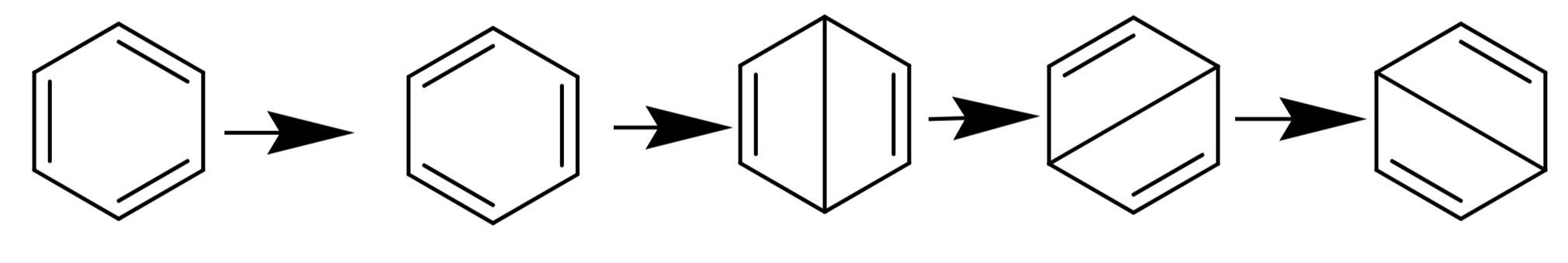
The resonance explains the unusual stability of benzene. The resonance hybrid will have a lower energy than the contributing structures. The resonance energy of benzene is -150.5 kJ/mol.
The six mutually parallel unhybridized p orbitals will stand perpendicular to the hexagonal carbon ring and overlap sideways above and below the plane of the ring. Due to the delocalization of pi electrons all the carbon-carbon bonds of benzene have the same length.
Note: All the six carbon-carbon bonds in benzene have equal length. It is greater than carbon-carbon double bond length and lower than carbon-carbon single bond length. Carbon-carbon bond length in benzene is 1.39 angstrom. In contrast to alkenes benzene undergo substitution reactions rather than additional reactions. There are two resonance structures for benzene; these are kekule and dewar structures. Kekule structure has some limitations. It could not explain the remarkable stability of benzene towards strong oxidants like \[KMn{O_4}\] .
Complete step by step answer:
Benzene is an organic molecule having the molecular formula \[{C_6}{H_6}\] . The structure of benzene is given below.

All the carbon atoms are \[S{p^2}\] hybridised. These \[S{p^2}\] hybrid orbitals are arranged in a triangular planar fashion. One of the unhybridized p orbital will remain perpendicular to the above plane. Each C atom will use two of the \[S{p^2}\] hybridized orbital and form 2 \[C - C\] sigma bonds by \[s{p^2} - s{p^2}\] head-on overlap. The remaining \[S{p^2}\] orbital is used to form a sigma bond by overlap with the 1s orbital of hydrogen. There will be 6 \[C - C\] sigma bonds that form the sides of the hexagon. All the \[C - C - C\] bond angles will be \[120^\circ \] .
According to the resonance concept, benzene is a resonance hybrid of the following structures.

The resonance explains the unusual stability of benzene. The resonance hybrid will have a lower energy than the contributing structures. The resonance energy of benzene is -150.5 kJ/mol.
The six mutually parallel unhybridized p orbitals will stand perpendicular to the hexagonal carbon ring and overlap sideways above and below the plane of the ring. Due to the delocalization of pi electrons all the carbon-carbon bonds of benzene have the same length.
Note: All the six carbon-carbon bonds in benzene have equal length. It is greater than carbon-carbon double bond length and lower than carbon-carbon single bond length. Carbon-carbon bond length in benzene is 1.39 angstrom. In contrast to alkenes benzene undergo substitution reactions rather than additional reactions. There are two resonance structures for benzene; these are kekule and dewar structures. Kekule structure has some limitations. It could not explain the remarkable stability of benzene towards strong oxidants like \[KMn{O_4}\] .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




