
In $C_{ 6 }H_{ 14 }$, the number of possible structural isomer is:
A. 3
B. 6
C. 4
D. 5
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: In this question to get the correct answer you have only one way that is to draw all the different structures possible with the chemical formula given in the question. Now try to figure out the answer by counting the number of isomers.
Complete step by step answer:
"Structural Isomers" are compounds that consist of the same number and kind of atoms, arranged in different structures.
Here the $C_{ 6 }H_{ 14 }$ compound is given to us. The name of this six-carbon compound is hexane.
Hexane has 5 structural isomers, which means we can arrange carbons in 5 different ways. We can name these compounds as,
n-hexane
2-methyl pentane
3-methyl pentane
2,2-dimethylbutane
2,3-dimethyl butane
Let’s looks at structures of these five compounds -
n-hexane
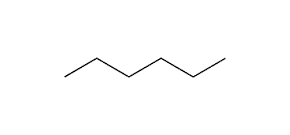
2-methyl pentane
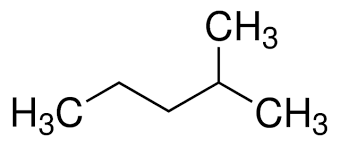
3-methyl pentane
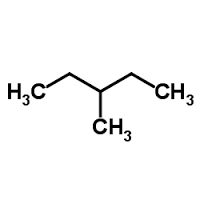
2,3-dimethyl butane
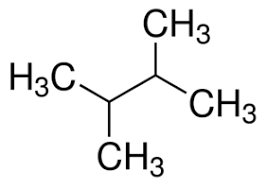
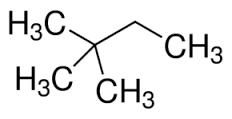
2,2-dimethylbutane
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option D.
Additional information: We should know that all alkanes are colorless. The boiling points of the various hexanes are somewhat similar and, as for other alkanes, are generally lower for the more branched forms.
Note: We can also classify these 5 isomers of hexane into two subtypes of structural isomers.
In chain isomers, the carbon atoms are connected in different orders. Example - n-hexane, 2,3-dimethyl butane, and 2-methyl pentane.
In position isomers, the carbon skeleton remains unchanged, but substituents are moved around. Example - (1) 2,3-dimethylbutane and 2,2-dimethylbutane (2) 3-methyl pentane and 2-methyl pentane
Complete step by step answer:
"Structural Isomers" are compounds that consist of the same number and kind of atoms, arranged in different structures.
Here the $C_{ 6 }H_{ 14 }$ compound is given to us. The name of this six-carbon compound is hexane.
Hexane has 5 structural isomers, which means we can arrange carbons in 5 different ways. We can name these compounds as,
n-hexane
2-methyl pentane
3-methyl pentane
2,2-dimethylbutane
2,3-dimethyl butane
Let’s looks at structures of these five compounds -
n-hexane

2-methyl pentane

3-methyl pentane

2,3-dimethyl butane

2,2-dimethylbutane

Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option D.
Additional information: We should know that all alkanes are colorless. The boiling points of the various hexanes are somewhat similar and, as for other alkanes, are generally lower for the more branched forms.
Note: We can also classify these 5 isomers of hexane into two subtypes of structural isomers.
In chain isomers, the carbon atoms are connected in different orders. Example - n-hexane, 2,3-dimethyl butane, and 2-methyl pentane.
In position isomers, the carbon skeleton remains unchanged, but substituents are moved around. Example - (1) 2,3-dimethylbutane and 2,2-dimethylbutane (2) 3-methyl pentane and 2-methyl pentane
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




