
In $C{H_3}COOH$ molecule, the $C - C$ bond is formed by:
A. $s{p^3} - s{p^3}$overlap
B. $s{p^2} - s{p^2}$ overlap
C. $s{p^3} - s{p^2}$ overlap
D. $s{p^3} - sp$ overlap
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: Acetic acid also known as ethanoic acid is an organic compound with chemical formula $C{H_3}COOH$. The functional group present in this compound is carboxylic acid i.e. $ - COOH$.
Complete answer
In acetic acid, we have two carbon atoms,4 hydrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms. Hybridisation is known as intermixing of atomic orbitals. These atomic orbitals must have the same energy and after the recombination their orbitals will lead to the making of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals are having equivalent energy. The total number of hybrid orbitals must be equal to the sum of all intermixing orbitals.
In $sp$ hybridisation, one $s$ orbital and one $p$ orbitals will mix to form another two hybrid orbitals which are equivalent in same size and energy. This $sp$ hybridisation is diagonal in shape. And it contains a $50\% $$s$ and $50\% $ $p$ orbitals. In $s{p^2}$hybridisation, one ${\rm{s}}$ orbital and two \[p\]orbitals will mix to form three hybrid orbitals which are equivalent in same size and energy. This $s{p^2}$ hybridisation is trigonal planar in shape. In $s{p^3}$ hybridisation one ${\rm{s}}$ orbital and three $p$ orbitals will mix to form another four hybrid orbitals which is equivalent in size and energy. This $s{p^3}$ hybridisation is tetrahedral in shape.
In case of ethanoic acid, the carbon of methyl group combines with three hydrogen atoms and one adjacent carbon. In case of carbon $2p$ is the valence subshell and hydrogen has $1s$ valence subshell. So, there will be four $s - p$ hybrid orbitals. So, the hybridisation of methyl carbon will be $s{p^3}$.While in case of carboxylate carbon atom carbon forms three $s - p$ hybrid orbitals. So, the hybridisation of carbon in the carboxylate group will be $s{p^2}$. The structure of $C{H_3}COOH$ showing these hybridisations is shown below.
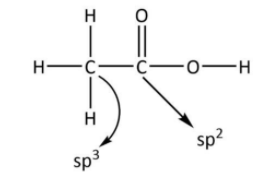
Hence, the $C - C$ bond is formed by $s{p^3} - s{p^2}$overlap.
Hence, option C is correct.
Note
The examples of molecules with $sp$hybridisation will be carbon dioxide, Beryllium chloride etc. And the examples of molecules with $s{p^2}$hybridisation is boron trifluoride, ethylene. And the examples of molecules with $s{p^3}$hybridisation will be methane, ethane etc.
Complete answer
In acetic acid, we have two carbon atoms,4 hydrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms. Hybridisation is known as intermixing of atomic orbitals. These atomic orbitals must have the same energy and after the recombination their orbitals will lead to the making of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals are having equivalent energy. The total number of hybrid orbitals must be equal to the sum of all intermixing orbitals.
In $sp$ hybridisation, one $s$ orbital and one $p$ orbitals will mix to form another two hybrid orbitals which are equivalent in same size and energy. This $sp$ hybridisation is diagonal in shape. And it contains a $50\% $$s$ and $50\% $ $p$ orbitals. In $s{p^2}$hybridisation, one ${\rm{s}}$ orbital and two \[p\]orbitals will mix to form three hybrid orbitals which are equivalent in same size and energy. This $s{p^2}$ hybridisation is trigonal planar in shape. In $s{p^3}$ hybridisation one ${\rm{s}}$ orbital and three $p$ orbitals will mix to form another four hybrid orbitals which is equivalent in size and energy. This $s{p^3}$ hybridisation is tetrahedral in shape.
In case of ethanoic acid, the carbon of methyl group combines with three hydrogen atoms and one adjacent carbon. In case of carbon $2p$ is the valence subshell and hydrogen has $1s$ valence subshell. So, there will be four $s - p$ hybrid orbitals. So, the hybridisation of methyl carbon will be $s{p^3}$.While in case of carboxylate carbon atom carbon forms three $s - p$ hybrid orbitals. So, the hybridisation of carbon in the carboxylate group will be $s{p^2}$. The structure of $C{H_3}COOH$ showing these hybridisations is shown below.

Hence, the $C - C$ bond is formed by $s{p^3} - s{p^2}$overlap.
Hence, option C is correct.
Note
The examples of molecules with $sp$hybridisation will be carbon dioxide, Beryllium chloride etc. And the examples of molecules with $s{p^2}$hybridisation is boron trifluoride, ethylene. And the examples of molecules with $s{p^3}$hybridisation will be methane, ethane etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




