
In complementary gene interaction genotypic ratio is
$
A.9:7 \\
B.9:3:31 \\
C.12:3:1 \\
D.1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1 \\
$
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: Complementary genes is a group of genes that complement to or contribute to a single characteristic where both genes can mask the effect of the other.
Complete answer
Complementary genes:- Two independent parts of genes, which interact to produce a trait together, but each dominant gene alone does not show its effects, are called complementary genes.
Example: when white flowered sweet peas are crossed they produce plants with purple flower F1 plants on inbreeding or self-fertilization give F2 generation in a ratio of a purple flowered to 7 white flowered plants.
Explanation:- Two pairs of genes located in different chromosomes regulate the flower colour in their varieties of sweet peas. One dominant gene, say C, controls the synthesis of the raw material for the purple pigment and another dominant gene, say E, controls the formation of an enzyme that converts the raw material into purple pigment.
At least one C gene and one E gene must be present to produce purple flowers; the absence of any one or both results in white flowers.
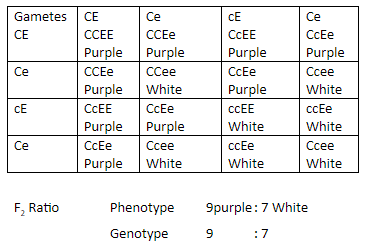
A cross between two white flowered varieties, one is genotypically ccEE and the other CCee. The former lack genes for the formation of the raw material, and the latter lack genes for the formation of enzymes needed to change the raw material into the final pigment. Hence both are white coloured. The absence of any one or both results in white flowers.
In CcEE and CCee, former lacks the gene for the formation of the raw material and latter lacks the gene for the formation of enzymes needed to change the raw material into the final pigment. Hence both are white coloured.
Hence in F1 generation, all are phenotypically purple, as they carry a gene for the raw material as well as a gene for the enzyme required to convert the raw material into the pigment.
In F2 generation of these cross between two purple-flowered plants of F1 generation, the Phenotypic ratio is $9:7$ i.e. $9$ purple flowered plants and $7$ white flowered plants.
But the genotypic ratio is $ \to $
$1$ CCEE Raw material $ + $ Enzyme
$2$ CCEe Raw material $ + $ Enzyme
$2$ CcEE Raw material $ + $ Enzyme
$4$ CcEe Raw material $ + $ Enzyme
$1$ CCee Only raw material
$2$ Ccee Only raw material
$1$ ccEE only Enzyme
$2$ ccEe only Enzyme
$1$ ccee No raw material, No Enzyme
Hence, genotypic ratio is $1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1.$
The correct option is ‘D’, $1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1.$
Note:Several varieties of white flowered sweet peas (Lathyrus odoratus) are known and a cross between most of these varieties yield only white flowered plants. However, a cross between two particular white flowered varieties produces plants with purple flowers. F2 generation in the ratio of $9:7$ and genotypic ratio $1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1.$
Complete answer
Complementary genes:- Two independent parts of genes, which interact to produce a trait together, but each dominant gene alone does not show its effects, are called complementary genes.
Example: when white flowered sweet peas are crossed they produce plants with purple flower F1 plants on inbreeding or self-fertilization give F2 generation in a ratio of a purple flowered to 7 white flowered plants.
Explanation:- Two pairs of genes located in different chromosomes regulate the flower colour in their varieties of sweet peas. One dominant gene, say C, controls the synthesis of the raw material for the purple pigment and another dominant gene, say E, controls the formation of an enzyme that converts the raw material into purple pigment.
At least one C gene and one E gene must be present to produce purple flowers; the absence of any one or both results in white flowers.

A cross between two white flowered varieties, one is genotypically ccEE and the other CCee. The former lack genes for the formation of the raw material, and the latter lack genes for the formation of enzymes needed to change the raw material into the final pigment. Hence both are white coloured. The absence of any one or both results in white flowers.
In CcEE and CCee, former lacks the gene for the formation of the raw material and latter lacks the gene for the formation of enzymes needed to change the raw material into the final pigment. Hence both are white coloured.
Hence in F1 generation, all are phenotypically purple, as they carry a gene for the raw material as well as a gene for the enzyme required to convert the raw material into the pigment.
In F2 generation of these cross between two purple-flowered plants of F1 generation, the Phenotypic ratio is $9:7$ i.e. $9$ purple flowered plants and $7$ white flowered plants.
But the genotypic ratio is $ \to $
$1$ CCEE Raw material $ + $ Enzyme
$2$ CCEe Raw material $ + $ Enzyme
$2$ CcEE Raw material $ + $ Enzyme
$4$ CcEe Raw material $ + $ Enzyme
$1$ CCee Only raw material
$2$ Ccee Only raw material
$1$ ccEE only Enzyme
$2$ ccEe only Enzyme
$1$ ccee No raw material, No Enzyme
Hence, genotypic ratio is $1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1.$
The correct option is ‘D’, $1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1.$
Note:Several varieties of white flowered sweet peas (Lathyrus odoratus) are known and a cross between most of these varieties yield only white flowered plants. However, a cross between two particular white flowered varieties produces plants with purple flowers. F2 generation in the ratio of $9:7$ and genotypic ratio $1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1.$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




