
In complex hydrides, hydride ions act as ligands and are coordinated to metal ions. These hydrides are good reducing agents. Which of the following hydrides is not a complex hydride?
(A) $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$
(B) $NaB{{H}_{4}}$
(C) ${{(Al{{H}_{3}})}_{n}}$
(D) $LiB{{H}_{4}}$
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: Draw the structure of the options given above. It is important to know that hydride ligand shares 2 electrons with the metal atom, so the central metal atom should have the charge to balance out the remaining charges present due to ligands and outer sphere ions.
Complete step by step answer:
Chemical compounds that consist of an array of anions or neutral molecules that are bound to a central atom via coordinate covalent bonds are called coordination compounds. Coordination compounds are also referred to as coordination complexes.
The neutral molecules or ions that are bound to the central atom are referred to as ligands or complexing agents. They act as Lewis base and donate electron pairs to transition metal ion thus a dative bond is formed between ligands and the transition metal ion. Hence these compounds are coordination complexes.
We will now draw the structure of the compounds given in options and try to identify the coordination compounds based on the explanation given above.
(A)
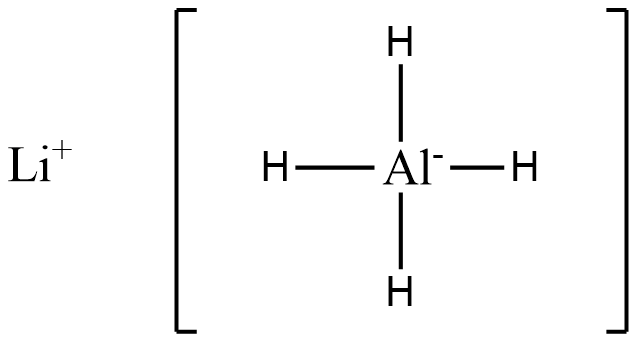
In the above structure we see that 4 hydride ions donate lone pairs of electrons to the central metal atom, Al. Hence (A) is a complex hydride.
(B)
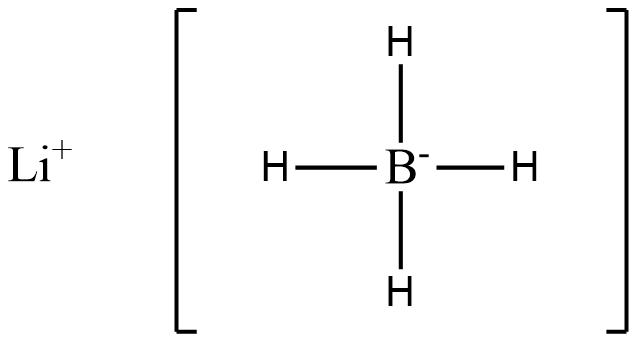
In the above structure we see that 4 hydride ions donate lone pairs of electrons to the central metal atom, B. Hence (B) is a complex hydride.
(C) ${{(Al{{H}_{3}})}_{n}}$ is a polymer of aluminium hydride. Hence (C) is not a complex hydride.
(D)
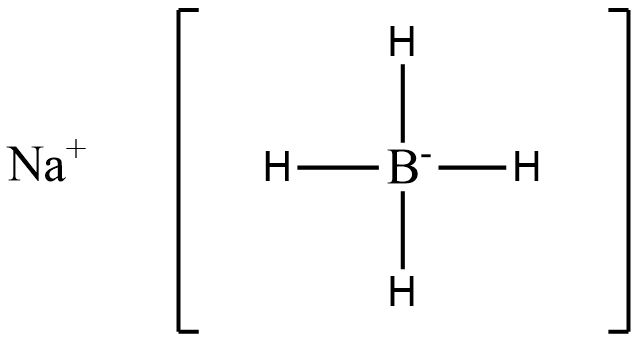
In the above structure we see that 4 hydride ions donate lone pairs of electrons to the central metal atom, B. Hence (D) is a complex hydride.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The stability of a complex compound is explained using the crystal field theory.
-The Crystal Field Theory (CFT) is a model for the bonding interaction between transition metal atoms and ligands.
-It describes the attraction between the positive charge of the metal cation and negative charge on the non-bonding electrons of the ligand.
-When the ligands approach the central metal ion, the degeneracy of electronic orbitals (usually d or f orbitals) are broken due to the static electric field produced by the surrounding charge distribution.
Complete step by step answer:
Chemical compounds that consist of an array of anions or neutral molecules that are bound to a central atom via coordinate covalent bonds are called coordination compounds. Coordination compounds are also referred to as coordination complexes.
The neutral molecules or ions that are bound to the central atom are referred to as ligands or complexing agents. They act as Lewis base and donate electron pairs to transition metal ion thus a dative bond is formed between ligands and the transition metal ion. Hence these compounds are coordination complexes.
We will now draw the structure of the compounds given in options and try to identify the coordination compounds based on the explanation given above.
(A)

In the above structure we see that 4 hydride ions donate lone pairs of electrons to the central metal atom, Al. Hence (A) is a complex hydride.
(B)

In the above structure we see that 4 hydride ions donate lone pairs of electrons to the central metal atom, B. Hence (B) is a complex hydride.
(C) ${{(Al{{H}_{3}})}_{n}}$ is a polymer of aluminium hydride. Hence (C) is not a complex hydride.
(D)

In the above structure we see that 4 hydride ions donate lone pairs of electrons to the central metal atom, B. Hence (D) is a complex hydride.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The stability of a complex compound is explained using the crystal field theory.
-The Crystal Field Theory (CFT) is a model for the bonding interaction between transition metal atoms and ligands.
-It describes the attraction between the positive charge of the metal cation and negative charge on the non-bonding electrons of the ligand.
-When the ligands approach the central metal ion, the degeneracy of electronic orbitals (usually d or f orbitals) are broken due to the static electric field produced by the surrounding charge distribution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




