
In contrast to annelids, the Platyhelminthes show
(a) Radial symmetry
(b) Presence of pseudocoel
(c) Bilateral symmetry
(d) Absence of body cavity
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: Both the annelids and Platyhelminthes are mostly aquatic and are equipped with well-developed musculature for support and movement. But the annelids have a special organization of its wall layers which gives it an edge over Platyhelminthes.
Complete answer:
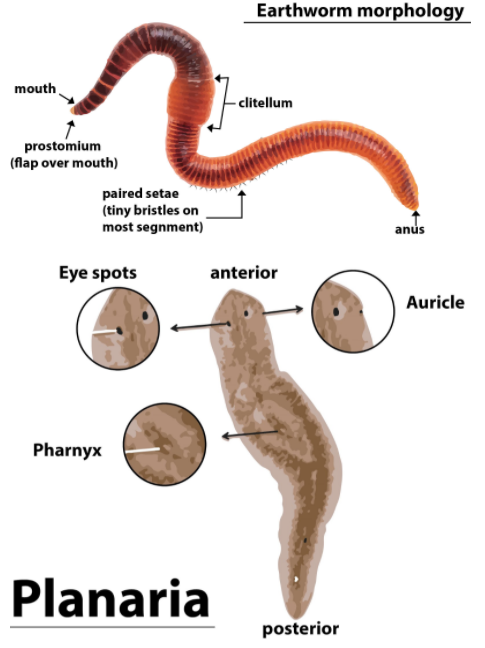
Phylum Annelida is a large phylum. Annelids are mostly known as ringworms or segmented worms. They are coelomate (body cavity) and triploblastic. They possess a bilaterally symmetrical body organization wherein a plane passing through their center divides them into two equal right and left halves. The Platyhelminthes are also bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic true multicellular organizations with a dorso-ventrally flattened body. They do not possess a body cavity and thus are acoelomate, unlike annelids that possess a true coelom and thus are coelomate.
Additional Information: -Annelids are metamerically segmented animals living in freshwater, seawater, or moist soil. Their digestive tract is also complete. Their characteristic feature is the external segmentation of their body into ring-like grooves called annuli.
-Flatworms are mostly parasites and thus they are devoid of the alimentary canal. They usually absorb the digested food of their host through their general body surface. E.g. Taenia solium. A blind sac body plan is exhibited by them.
-Phylum Ascehelminthes are the only phylum in the animal kingdom that are characterized by the presence of a false body cavity or pseudocoelom that is not lined by epithelium.
-Cnidarians are radially symmetrical, diploblastic, and multicellular organisms with a tissue grade of organization. They are aquatic with habitats ranging from freshwater to marine. They may exist in solitary forms or forming colonies. They may be free-swimming or sedentary. E.g. Hydra.
So, the correct answer is ‘Absence of body cavity.’
Note: In a blind sac body plan, an animal has a single pore which serves the dual function of ingestion as well egestion. That means food enters through an opening into a single cavity and after digestion, the undigested food is passed out from the same opening. Along with Platyhelminthes, Cnidarians also have a blind sac body plan.
Complete answer:
Phylum Annelida is a large phylum. Annelids are mostly known as ringworms or segmented worms. They are coelomate (body cavity) and triploblastic. They possess a bilaterally symmetrical body organization wherein a plane passing through their center divides them into two equal right and left halves. The Platyhelminthes are also bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic true multicellular organizations with a dorso-ventrally flattened body. They do not possess a body cavity and thus are acoelomate, unlike annelids that possess a true coelom and thus are coelomate.
Additional Information: -Annelids are metamerically segmented animals living in freshwater, seawater, or moist soil. Their digestive tract is also complete. Their characteristic feature is the external segmentation of their body into ring-like grooves called annuli.
-Flatworms are mostly parasites and thus they are devoid of the alimentary canal. They usually absorb the digested food of their host through their general body surface. E.g. Taenia solium. A blind sac body plan is exhibited by them.
-Phylum Ascehelminthes are the only phylum in the animal kingdom that are characterized by the presence of a false body cavity or pseudocoelom that is not lined by epithelium.
-Cnidarians are radially symmetrical, diploblastic, and multicellular organisms with a tissue grade of organization. They are aquatic with habitats ranging from freshwater to marine. They may exist in solitary forms or forming colonies. They may be free-swimming or sedentary. E.g. Hydra.
So, the correct answer is ‘Absence of body cavity.’
Note: In a blind sac body plan, an animal has a single pore which serves the dual function of ingestion as well egestion. That means food enters through an opening into a single cavity and after digestion, the undigested food is passed out from the same opening. Along with Platyhelminthes, Cnidarians also have a blind sac body plan.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




