
In embryo sac, n, 2n, 3n conditions are found respectively in
(a) egg, antipodal, and endosperm
(b) nucleus, endosperm, and egg
(c) antipodal, zygote and endosperm
(d) endosperm, nucleus, and egg
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: The first part of the answer provides nourishment to the egg cells. The second part of the answer is the immediate product of fertilization in an organism. The third part of the answer provides nourishment to the embryo.
Complete answer:
In embryo sac, n, 2n, 3n conditions are found respectively in antipodal, zygote, and endosperm. In a majority of flowering plants, one of the megaspores remains functional while the other three degenerate. Only the functional megaspore then develops into the female gametophyte or ‘embryo sac’.
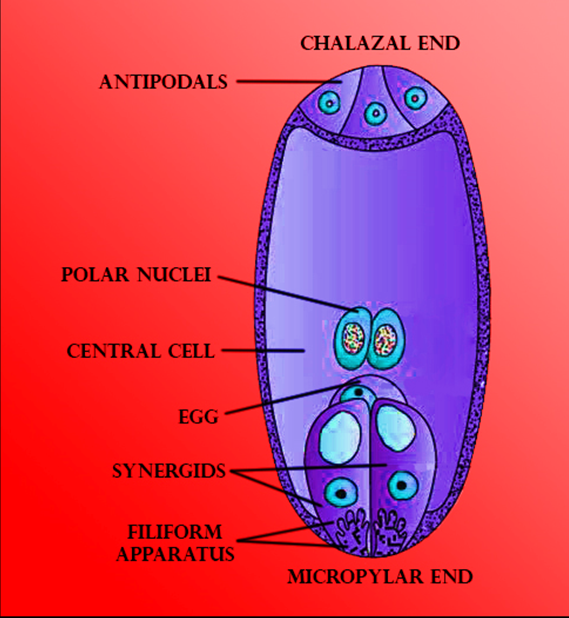
When we observe the distribution of cells inside the embryo sac, we come to know that:
- There is a large central cell.
- At the micropylar end, 3 cells are grouped together to form an egg apparatus. The egg apparatus, in turn, consists of two synergids and one ‘egg cell’.
- Three cells at the chalazal end are together called ‘antipodals’. They are haploid.
Now, during double fertilization one of the male gametes moves towards the egg cell and fuses with its nucleus thus completing the ‘syngamy’. This results in the formation of a diploid cell, which is named as ‘zygote’.
While the other male gamete moves towards the two polar nuclei located in the central cell. Here, a fusion occurs among them to form a triploid ‘primary endosperm nucleus’ (PEN). As this process involves the fusion of three haploid nuclei, it is called ‘triple fusion’.
So, the correct answer is, ‘antipodal, zygote, and endosperm’.
Note:
-Each ovule has one or two protective envelopes. These are called integuments.
-Integuments encircle the nucellus from all the sides except at the tip where a small opening called the ‘micropyle’ is organized.
-Opposite the micropylar end, is the ‘chalaza’. It represents the basal part of the ovule.
-Since two types of fusions, syngamy and triple fusion take place in an embryo sac the whole phenomenon is termed ‘double fertilization’. This event is unique to flowering plants.
Complete answer:
In embryo sac, n, 2n, 3n conditions are found respectively in antipodal, zygote, and endosperm. In a majority of flowering plants, one of the megaspores remains functional while the other three degenerate. Only the functional megaspore then develops into the female gametophyte or ‘embryo sac’.

When we observe the distribution of cells inside the embryo sac, we come to know that:
- There is a large central cell.
- At the micropylar end, 3 cells are grouped together to form an egg apparatus. The egg apparatus, in turn, consists of two synergids and one ‘egg cell’.
- Three cells at the chalazal end are together called ‘antipodals’. They are haploid.
Now, during double fertilization one of the male gametes moves towards the egg cell and fuses with its nucleus thus completing the ‘syngamy’. This results in the formation of a diploid cell, which is named as ‘zygote’.
While the other male gamete moves towards the two polar nuclei located in the central cell. Here, a fusion occurs among them to form a triploid ‘primary endosperm nucleus’ (PEN). As this process involves the fusion of three haploid nuclei, it is called ‘triple fusion’.
So, the correct answer is, ‘antipodal, zygote, and endosperm’.
Note:
-Each ovule has one or two protective envelopes. These are called integuments.
-Integuments encircle the nucellus from all the sides except at the tip where a small opening called the ‘micropyle’ is organized.
-Opposite the micropylar end, is the ‘chalaza’. It represents the basal part of the ovule.
-Since two types of fusions, syngamy and triple fusion take place in an embryo sac the whole phenomenon is termed ‘double fertilization’. This event is unique to flowering plants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




