
In endospermic seed, the cotyledons are
A)Fleshy
B)Leathery
C)Papery
D)Green
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: A small embryonic plant that is enclosed inside a seed coat is known as a seed. A seed ripens and is present in all gymnosperms and angiosperms plants. A seed consists of three parts- an embryo, a cotyledon (supply of nutrients for the embryo), and a seed coat.
Complete answer:
-Embryo is having the structures known as Cotyledons in seed plants. It is the central portion of a seed embryo to which the immature shoot is known as epicotyl and the immature roots known as the radical are attached.
-Cotyledons are the flattened seed leaves. A single cotyledon is present in monocots while two cotyledons are present in dicots, hence they are named as monocots and dicots, respectively.
-In dicots, Cotyledons provide as a storage tissue and are very well developed, whereas scutellum is a small structure in monocots.
-Classification of plants depends on the number of cotyledons present in the embryo. In the Monocot plant, the embryo has one cotyledon and in the dicot plant embryo has two cotyledons.
Seed Subdivision
On the basis of endosperm, seeds are classified into two types:
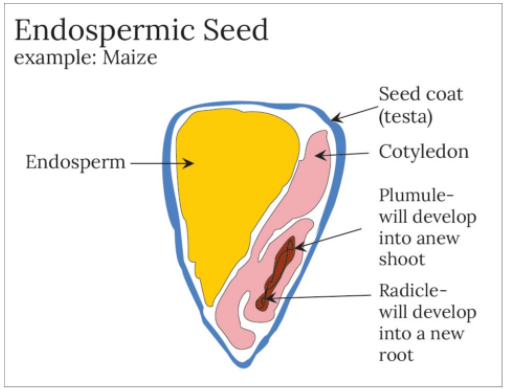
1)Albuminous/Endospermic seeds: It is large, thick, and fleshy and serves as the food source for the developing embryo. It has thin and membranous Cotyledons. Its function is to absorb food from the endosperm and transfer it to the growing embryo.
E.g. Dicot endospermic seeds are Poppy, Custard apple, Muskmelon, Fenugreek, and Monocot endospermic seeds are Cereals, Millets, Palm, Onion, etc.
2)Exalbuminous/Non-endospermic seeds: The cotyledons become thick and fleshy as it stores the food.
E.g. Dicot non-endospermic seeds are Gram, pea, Mango, Mustard, Soybean, and Monocot non-endospermic seeds are Orchid, Amorphophallus, etc.
Additional Information: -Monocotyledons consist of the embryo having one cotyledon or seed leaf and dicotyledons consist of the embryo having two cotyledons or seed leaf and in gymnosperms consist of two or more cotyledons.
-The embryonic root is known as radicle and the embryonic shoot is known as plumule. Epicotyl is the point of attachment of the cotyledons above the embryonic stem and below it is hypocotyl.
-The stored food starts as the tissue in angiosperms known as endosperm generally acquired from the parent plant through double fertilization.
-The triploid endosperm has a rich amount of oil or starch and proteins. The female gametophyte is the food storage tissue in gymnosperms (a haploid tissue).
-The seeds attached to the seed coat by appendages. The seed coat differs with the kind of seed it is attached. For the dispersal of seed, appendages are very helpful. Some of the appendages are Hilum, Aril, Hair, and Wings.
So, the correct answer is “fleshy”.
Note: -Endosperm develops from the endosperm nuclei which is formed by the two polar nuclei and one sperm nuclei. It stores food for the developing embryo.
-The mature ovule is nothing but the embryo comprises an embryonic plant with food storage and bordering by a protective coat and gives rise to a plant similar to that of its mother.
-The plant comprises plumule, radical, and cotyledon. The cotyledons without the plumule and radical is known as the primary axis.
Complete answer:
-Embryo is having the structures known as Cotyledons in seed plants. It is the central portion of a seed embryo to which the immature shoot is known as epicotyl and the immature roots known as the radical are attached.
-Cotyledons are the flattened seed leaves. A single cotyledon is present in monocots while two cotyledons are present in dicots, hence they are named as monocots and dicots, respectively.
-In dicots, Cotyledons provide as a storage tissue and are very well developed, whereas scutellum is a small structure in monocots.
-Classification of plants depends on the number of cotyledons present in the embryo. In the Monocot plant, the embryo has one cotyledon and in the dicot plant embryo has two cotyledons.
Seed Subdivision
On the basis of endosperm, seeds are classified into two types:
1)Albuminous/Endospermic seeds: It is large, thick, and fleshy and serves as the food source for the developing embryo. It has thin and membranous Cotyledons. Its function is to absorb food from the endosperm and transfer it to the growing embryo.
E.g. Dicot endospermic seeds are Poppy, Custard apple, Muskmelon, Fenugreek, and Monocot endospermic seeds are Cereals, Millets, Palm, Onion, etc.
2)Exalbuminous/Non-endospermic seeds: The cotyledons become thick and fleshy as it stores the food.
E.g. Dicot non-endospermic seeds are Gram, pea, Mango, Mustard, Soybean, and Monocot non-endospermic seeds are Orchid, Amorphophallus, etc.
Additional Information: -Monocotyledons consist of the embryo having one cotyledon or seed leaf and dicotyledons consist of the embryo having two cotyledons or seed leaf and in gymnosperms consist of two or more cotyledons.
-The embryonic root is known as radicle and the embryonic shoot is known as plumule. Epicotyl is the point of attachment of the cotyledons above the embryonic stem and below it is hypocotyl.
-The stored food starts as the tissue in angiosperms known as endosperm generally acquired from the parent plant through double fertilization.
-The triploid endosperm has a rich amount of oil or starch and proteins. The female gametophyte is the food storage tissue in gymnosperms (a haploid tissue).
-The seeds attached to the seed coat by appendages. The seed coat differs with the kind of seed it is attached. For the dispersal of seed, appendages are very helpful. Some of the appendages are Hilum, Aril, Hair, and Wings.
So, the correct answer is “fleshy”.
Note: -Endosperm develops from the endosperm nuclei which is formed by the two polar nuclei and one sperm nuclei. It stores food for the developing embryo.
-The mature ovule is nothing but the embryo comprises an embryonic plant with food storage and bordering by a protective coat and gives rise to a plant similar to that of its mother.
-The plant comprises plumule, radical, and cotyledon. The cotyledons without the plumule and radical is known as the primary axis.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




