
In $\text{Fe}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{5}}$, the $\text{Fe}-\text{C}$ bond possess:
A. $\pi $ character only
B. both $\pi $ and $\sigma $ characters
C. ionic character
D. $\sigma $ character only
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: The $\text{Fe}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{5}}$ compound forms metal-carbonyl bonds with each other. The structure of this compound is the same as others but the bonding is different. This bonding involves the d-orbitals and antibonding orbitals of the metal atom.
Complete step by step answer:
- In $\text{Fe}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{5}}$, there are same ligands which is $\text{CO}$ so, $\text{Fe}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{5}}$ is a homoleptic carbonyl compound. Such compounds are formed by most of the transition metals or d-block elements and they have simple and well defined structures. The shape of the compound is trigonal bi-pyramidal. The IUPAC name of the compound is Pentacarbonyliron $\left( 0 \right)$. The structure is
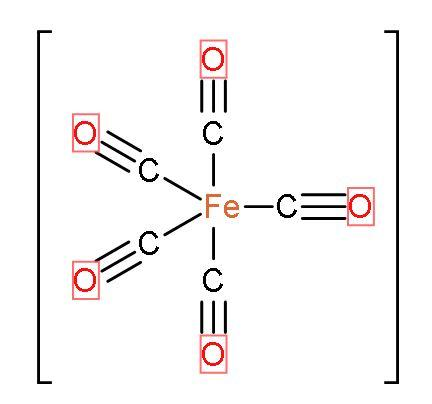
Let us discuss the special type of bonding in $\text{Fe}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{5}}$:
The special type of bonding is named as ‘synergic bonding’. The ligand $\left( \text{CO} \right)$ donates its lone pair of electrons to the vacant orbitals of the central metal atom which is an iron atom and forms the sigma-bond with it. As the iron atom also possesses some electrons in its d-orbitals. The configuration of iron is $1{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{2}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{2}{{\text{p}}^{6}}\text{3}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{3}{{\text{p}}^{6}}\text{4}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{3}{{\text{d}}^{6}}$ or $\begin{matrix}
\uparrow \downarrow & \uparrow & \uparrow & \uparrow & \uparrow \\
\end{matrix}$.
It back donates these electrons to the molecular orbitals of the ligand forming a $\pi $-bond. The $\text{M}-\text{C}$ $\pi $ bond is formed by the donation of electrons from a filled d-orbital of metal into the vacant antibonding ${{\pi }^{*}}$ orbital of carbon monoxide. The bonding looks like
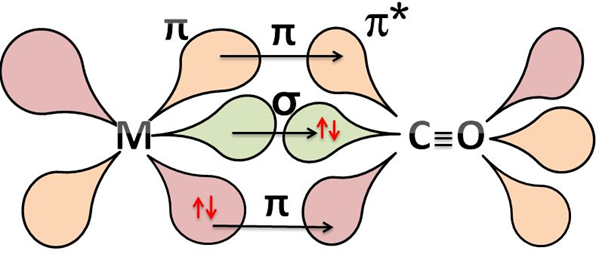
This creates a synergic effect between the metal to ligand which strengthens the bond between $\text{CO}$ and the metal. The metal-carbon bond in metal carbonyls possesses both $\sigma $ and $\pi $ character.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: One important point to keep in mind is that the metal atom donates its electron pairs to the antibonding MO of $\text{CO}$, so the $\text{CO}$ bond is weakened by this synergic bonding which leads to a larger $\text{CO}$ bond length in the complex.
Complete step by step answer:
- In $\text{Fe}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{5}}$, there are same ligands which is $\text{CO}$ so, $\text{Fe}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{5}}$ is a homoleptic carbonyl compound. Such compounds are formed by most of the transition metals or d-block elements and they have simple and well defined structures. The shape of the compound is trigonal bi-pyramidal. The IUPAC name of the compound is Pentacarbonyliron $\left( 0 \right)$. The structure is

Let us discuss the special type of bonding in $\text{Fe}{{\left( \text{CO} \right)}_{5}}$:
The special type of bonding is named as ‘synergic bonding’. The ligand $\left( \text{CO} \right)$ donates its lone pair of electrons to the vacant orbitals of the central metal atom which is an iron atom and forms the sigma-bond with it. As the iron atom also possesses some electrons in its d-orbitals. The configuration of iron is $1{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{2}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{2}{{\text{p}}^{6}}\text{3}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{3}{{\text{p}}^{6}}\text{4}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{3}{{\text{d}}^{6}}$ or $\begin{matrix}
\uparrow \downarrow & \uparrow & \uparrow & \uparrow & \uparrow \\
\end{matrix}$.
It back donates these electrons to the molecular orbitals of the ligand forming a $\pi $-bond. The $\text{M}-\text{C}$ $\pi $ bond is formed by the donation of electrons from a filled d-orbital of metal into the vacant antibonding ${{\pi }^{*}}$ orbital of carbon monoxide. The bonding looks like

This creates a synergic effect between the metal to ligand which strengthens the bond between $\text{CO}$ and the metal. The metal-carbon bond in metal carbonyls possesses both $\sigma $ and $\pi $ character.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: One important point to keep in mind is that the metal atom donates its electron pairs to the antibonding MO of $\text{CO}$, so the $\text{CO}$ bond is weakened by this synergic bonding which leads to a larger $\text{CO}$ bond length in the complex.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




