
In glycolysis, during oxidation, electrons are removed by -
(a)ATP
(b)Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate
(c)${ NAD }^{ + }$
(d)Molecular oxygen
Answer
560.4k+ views
Hint: The process of glycolysis occurs in every living cell of the body. It occurs in ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. During oxidizing reaction, an oxidizing agent accepts electrons and reduces itself in the step catalyzed by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Complete answer:
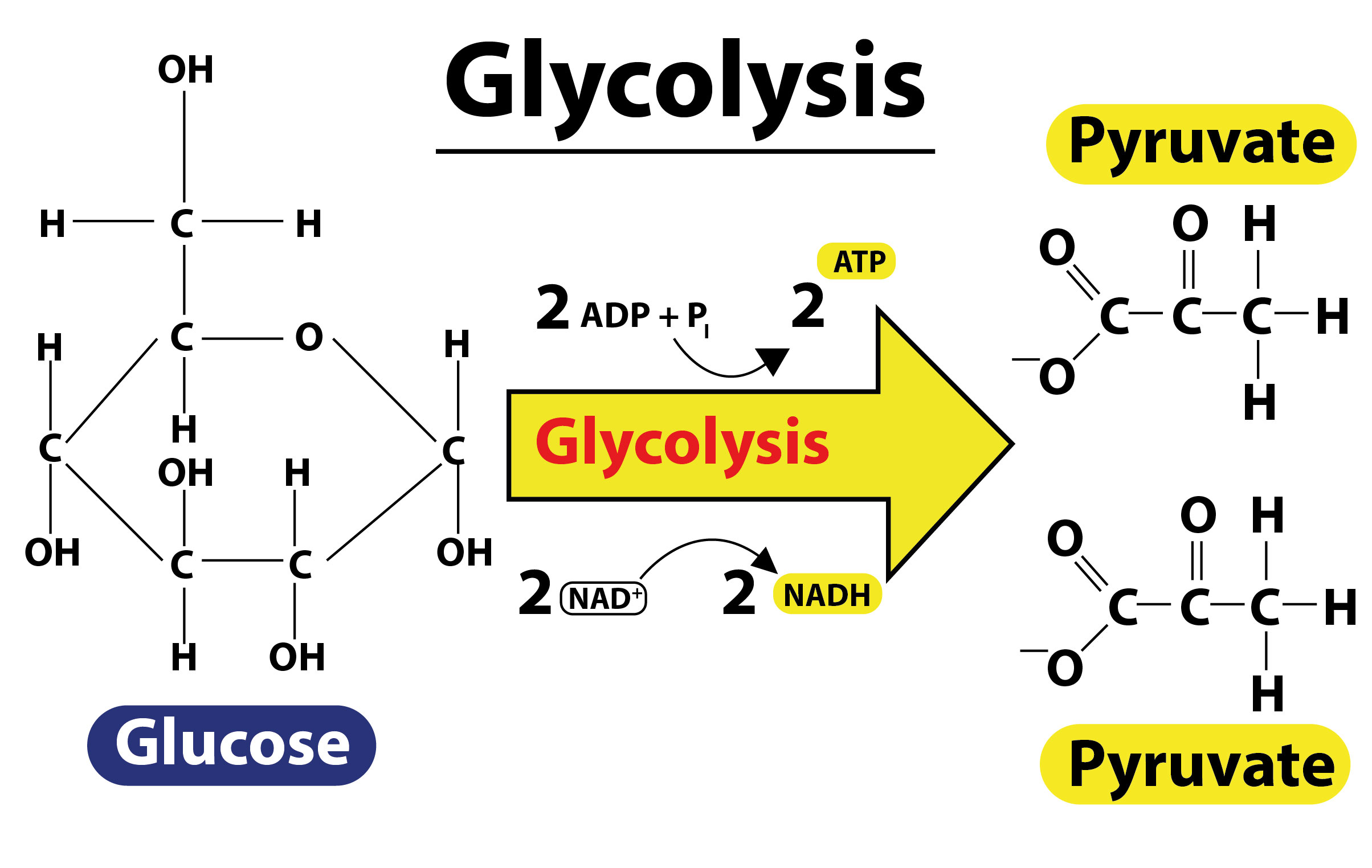
- Glycolysis is the first step in respiration of living cells. It is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose to pyruvate through ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
- In the oxidation reaction, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is oxidized, resulting in the removal of a pair of electrons by ${ NAD }^{ + }$ and the addition of a phosphate group to form 1,3-diphosphoglyceric acid.
- ${ NAD }^{ + }$ is thus an oxidizing agent which reduces itself by accepting electrons and forming NADH.
- The reaction is given as ${ NAD }^{ + }\quad +\quad { P }_{ i }\quad \overset { Glyceraldehyde\quad 3-phosphate\quad dehydrogenase }{ \longrightarrow } \quad NADH\quad +\quad { H }^{ + }$. As denoted, the reaction is catalyzed by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Additional Information:
- In glycolysis, one molecule of glucose produces four ATP, two NADH, and two pyruvate molecules.
- Although four ATP molecules are formed, two molecules of ATP are already used in the first half of glycolysis, thus the net gain is two ATP molecules.
- The two pyruvate molecules formed are further used in starting the Krebs/Citric acid cycle.
So, the correct answer is ‘${ NAD }^{ + }$’.
Note: - Red blood cells, or erythrocytes, are solely reliant on glycolysis as a source of energy because they do not have mitochondria.
- The enzymes involved in glycolysis are rate limiting steps and are needed in sufficient quantities for the reactions to continue.
Complete answer:
- Glycolysis is the first step in respiration of living cells. It is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose to pyruvate through ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
- In the oxidation reaction, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is oxidized, resulting in the removal of a pair of electrons by ${ NAD }^{ + }$ and the addition of a phosphate group to form 1,3-diphosphoglyceric acid.
- ${ NAD }^{ + }$ is thus an oxidizing agent which reduces itself by accepting electrons and forming NADH.
- The reaction is given as ${ NAD }^{ + }\quad +\quad { P }_{ i }\quad \overset { Glyceraldehyde\quad 3-phosphate\quad dehydrogenase }{ \longrightarrow } \quad NADH\quad +\quad { H }^{ + }$. As denoted, the reaction is catalyzed by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Additional Information:
- In glycolysis, one molecule of glucose produces four ATP, two NADH, and two pyruvate molecules.
- Although four ATP molecules are formed, two molecules of ATP are already used in the first half of glycolysis, thus the net gain is two ATP molecules.
- The two pyruvate molecules formed are further used in starting the Krebs/Citric acid cycle.

So, the correct answer is ‘${ NAD }^{ + }$’.
Note: - Red blood cells, or erythrocytes, are solely reliant on glycolysis as a source of energy because they do not have mitochondria.
- The enzymes involved in glycolysis are rate limiting steps and are needed in sufficient quantities for the reactions to continue.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




