
In Iberis amara and Alyssum, the inflorescence is
(a) Spike
(b) Raceme
(c) Corymb
(d) Catkin
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: The inflorescence of the plant is a bunch or group of flowers organized on a stem that is formed from a major branch or by an elaborate organization of branches. It is an evolved segment of the shoot in plants in which bare seeds and flowers are produced.
Complete answer:
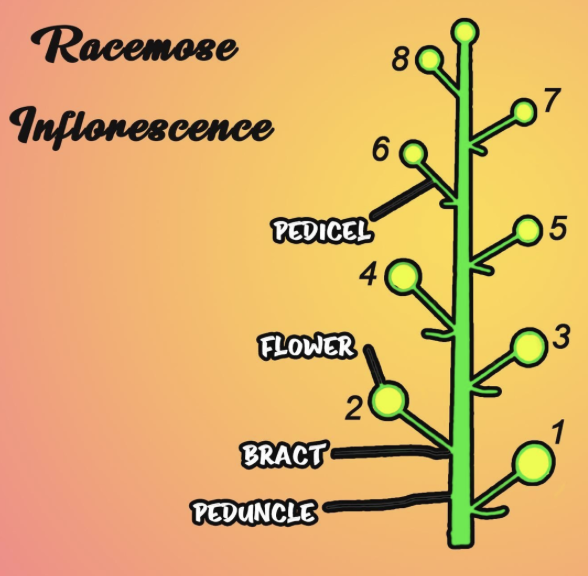
In Iberis amara and Alyssum, the inflorescence is the raceme. An unbranched, undefined class of inflorescence carrying pedicellate flowers with small floral stalks known as the pedicels through its axis is known as a raceme. Racemes which are indeterminate inflorescences where the flowers that came first are near the base and the fresh flowers are formed as the shoot develops.
Additional information:
Spike: The unbranched, undefined inflorescence, close to raceme inflorescence but have sessile flowers that are bound directly and does not have stalks. Justicia adhatoda and prickly chaff flowers are common examples.
Catkin: Catkin also known as ament is very close to a spike or raceme inflorescence but with intermediate bracts so distinct as to cover the flowers till pollination occurs. Some common examples are willow, alder, and birch.
Corymb: Corymb is a type of inflorescence where the flowers are developed in a particular way that the outer ones are formed on the lengthy pedicels than the innermost ones, making all flowers come to the same level.
So, the correct answer is ‘Raceme’.
Note:
- The corymb inflorescence has a flat top that looks like an umbel and sometimes has a branching part which looks like a panicle. Corymb structure has flowers which are parallel, intermediate, flat, and convex sometimes.
- The raceme inflorescence is also known as a panicle that has branching on the main axis. Mustard and radish are some common examples that show raceme inflorescence.
- The name corymb is taken from the Greek language, where the word korymbos means "group of flowers or fruit"
Complete answer:
In Iberis amara and Alyssum, the inflorescence is the raceme. An unbranched, undefined class of inflorescence carrying pedicellate flowers with small floral stalks known as the pedicels through its axis is known as a raceme. Racemes which are indeterminate inflorescences where the flowers that came first are near the base and the fresh flowers are formed as the shoot develops.
Additional information:
Spike: The unbranched, undefined inflorescence, close to raceme inflorescence but have sessile flowers that are bound directly and does not have stalks. Justicia adhatoda and prickly chaff flowers are common examples.

Catkin: Catkin also known as ament is very close to a spike or raceme inflorescence but with intermediate bracts so distinct as to cover the flowers till pollination occurs. Some common examples are willow, alder, and birch.
Corymb: Corymb is a type of inflorescence where the flowers are developed in a particular way that the outer ones are formed on the lengthy pedicels than the innermost ones, making all flowers come to the same level.
So, the correct answer is ‘Raceme’.
Note:
- The corymb inflorescence has a flat top that looks like an umbel and sometimes has a branching part which looks like a panicle. Corymb structure has flowers which are parallel, intermediate, flat, and convex sometimes.
- The raceme inflorescence is also known as a panicle that has branching on the main axis. Mustard and radish are some common examples that show raceme inflorescence.
- The name corymb is taken from the Greek language, where the word korymbos means "group of flowers or fruit"
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




