
In laminar flow,
A) The velocity of the fluid at each point changes periodically
B) The velocity of the fluid at each point changes throughout its flow.
C) The relative velocity of the fluid at each point with respect to each other remains constant throughout its flow.
D) The velocity of the fluid at each point remains constant throughout its flow.
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: If the velocity of the flow at each point in space remains constant with time, the flow is said to be steady. If the velocity of the fluid at a point changes with time the flow is called unsteady flow. Beyond a certain velocity called critical velocity, a steady flow becomes non steady.
Complete step by step answer:
If a fluid flows such that its velocity at a point is always the same in magnitude and direction, the fluid is said to have streamline flow. Streamline flow is also known as steady flow or orderly flow or laminar flow.
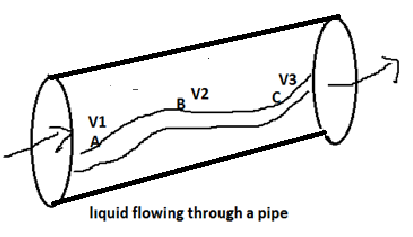
Consider a liquid flowing through a pipe of the shape. A particle of the liquid possesses velocity ${v_1}$ at A and ${v_2}$ at B and ${v_3}$ at C. as the liquid flows, different particles will pass through points A,B and C. if it so happens that all the particles will have velocity ${v_1}$when they reach A, velocity ${v_2}$ when they reach B and velocity ${v_3}$ when they reach C, then the flow of the liquid is orderly and is called streamline flow.
A streamline or laminar is a straight or curved path such that tangent to it at a point gives the direction of flow of liquid at that point. For example the path ABC is streamline. Two streamlines cannot cross because; there is only one direction of flow at every point. If a liquid flows in a tube or pipe of uniform cross sectional area, all the streamlines will be parallel to the axis of the tube.
From these observations we can say, in laminar flow, the velocity of the fluid at each point remains constant throughout its flow.
$\therefore $ Correct option is (D).
Note:
-A streamline flow is not necessarily an ideal flow.
-A streamline flow not necessarily an incompressible flow.
-Generally in fluid dynamics we assume that the flow is steady, incompressible and non-viscous. Such a fluid is called an ideal fluid.
Complete step by step answer:
If a fluid flows such that its velocity at a point is always the same in magnitude and direction, the fluid is said to have streamline flow. Streamline flow is also known as steady flow or orderly flow or laminar flow.

Consider a liquid flowing through a pipe of the shape. A particle of the liquid possesses velocity ${v_1}$ at A and ${v_2}$ at B and ${v_3}$ at C. as the liquid flows, different particles will pass through points A,B and C. if it so happens that all the particles will have velocity ${v_1}$when they reach A, velocity ${v_2}$ when they reach B and velocity ${v_3}$ when they reach C, then the flow of the liquid is orderly and is called streamline flow.
A streamline or laminar is a straight or curved path such that tangent to it at a point gives the direction of flow of liquid at that point. For example the path ABC is streamline. Two streamlines cannot cross because; there is only one direction of flow at every point. If a liquid flows in a tube or pipe of uniform cross sectional area, all the streamlines will be parallel to the axis of the tube.
From these observations we can say, in laminar flow, the velocity of the fluid at each point remains constant throughout its flow.
$\therefore $ Correct option is (D).
Note:
-A streamline flow is not necessarily an ideal flow.
-A streamline flow not necessarily an incompressible flow.
-Generally in fluid dynamics we assume that the flow is steady, incompressible and non-viscous. Such a fluid is called an ideal fluid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




