
In Mammalian kidney,iHenle'siloop is present in
A. Cortex
B. Caput epididymis
C. Medulla
D. Ureter
Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: It is also considered as the inner zone of the kidney. It divides into a few conical masses projecting into the calyces. It is a long U-shaped portion of the tubule that conducts urine within each nephron of the kidney of reptiles, birds, and mammals.
Complete answer:
The renal tubule starts with a double-wall cup-like shape structure called Bowman's capsule, which encloses the glomerulus. The glomerulus with Bowman's capsule is called the Malpighian body or renal corpuscle. The tubule continues to form a tightly coiled network of the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT).
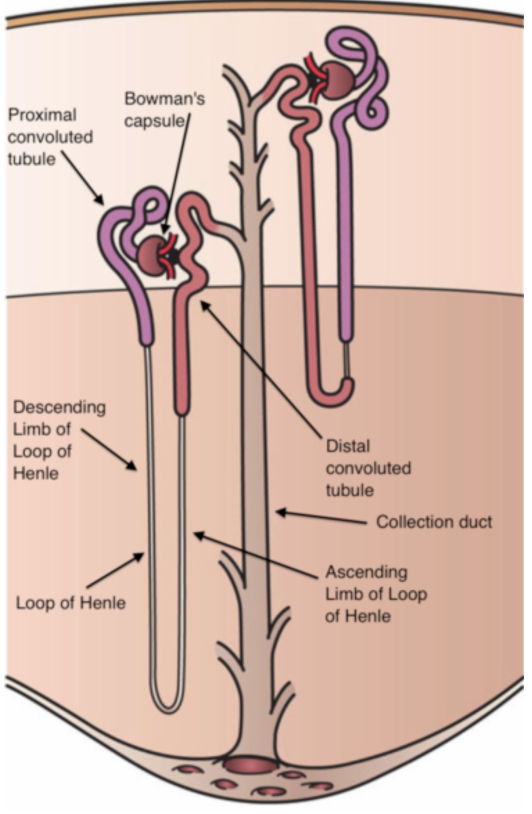
A Henle hairpin loop is the next part of the tubule, which has a descending branch and an ascending branch. The distal alveolar tubule (DCT) continues as a highly coiled ascending limb.
Additional information: The transport of ions along the nephron is essential for the reabsorption of sodium and water, the maintenance of plasma volume and blood pressure, and urine production. Henle's loop contributes to the absorption of about 25% of the filtered sodium and can be managed by diuretic therapy. . The Henle loop plays an important role in urinary concentration, which by contributing to the generation of hypertonic medullary interstitium in a process called countercurrent multiplication, it also aids in the reabsorption of calcium ions and magnesium ions.
So, the correct option is ‘Medulla’.
Note: The loop of the Henle descends from the cortex or spinal cord, which depends on the length of the henle at the renal papilla. The loop of Henle contains three main segments: descending thin member, ascending thin member, and ascending thick member. About $15\% - 25\%$ of the filtered NaCl is reabsorbed through the LoH, mainly through the thick ascendant.
Complete answer:
The renal tubule starts with a double-wall cup-like shape structure called Bowman's capsule, which encloses the glomerulus. The glomerulus with Bowman's capsule is called the Malpighian body or renal corpuscle. The tubule continues to form a tightly coiled network of the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT).

A Henle hairpin loop is the next part of the tubule, which has a descending branch and an ascending branch. The distal alveolar tubule (DCT) continues as a highly coiled ascending limb.
Additional information: The transport of ions along the nephron is essential for the reabsorption of sodium and water, the maintenance of plasma volume and blood pressure, and urine production. Henle's loop contributes to the absorption of about 25% of the filtered sodium and can be managed by diuretic therapy. . The Henle loop plays an important role in urinary concentration, which by contributing to the generation of hypertonic medullary interstitium in a process called countercurrent multiplication, it also aids in the reabsorption of calcium ions and magnesium ions.
So, the correct option is ‘Medulla’.
Note: The loop of the Henle descends from the cortex or spinal cord, which depends on the length of the henle at the renal papilla. The loop of Henle contains three main segments: descending thin member, ascending thin member, and ascending thick member. About $15\% - 25\%$ of the filtered NaCl is reabsorbed through the LoH, mainly through the thick ascendant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




