
In mammals, teeth are
-Only two sets, present throughout life.
-Embedded in the socket of jaw bones
-Different types.
These conditions are respectively referred to as:
A. Diphyodont, heterodont, thecodont
B. Diphyodont, thecodont, heterodont
C. Thecodont, diphyodont, heterodont
D. Thecodont, heterodont, diphyodont.
Answer
582k+ views
Hint: Teeth in mammals are calcified hard tissues present in the jaw. These structures function to shape to the jaw and masticate the food consumed. Teeth are of different types based on their arrangement, types and sets of teeth that develop through the life of individuals.
Complete step by step answer: The arrangement of teeth on the jaw bones is known as Dentition. There are three types of dentition. They are explained below.
Dentition based on morphology
There are two types of dentition based on the morphology of teeth. They are homodont and heterodont. Homodont animals have the same size and same shaped teeth. On the other hand, animals with teeth of different sizes and shapes are known as heterodont. For example, whales are homodont while humans are heterodont.
Heterodont dentition involves four types of teeth – incisors, canines, premolars and molars.
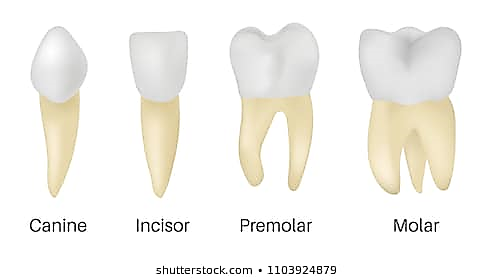
Fig: Heterodont dentition in human
Dentition based on the attachment of teeth
There are three dentition types based on attachment of teeth. Thecodont is the condition when teeth are attached to sockets on the jaw bone. Acrodont dentition refers to the condition where teeth are fused to the jaw bone. In Pleurodont dentition, instead of being fused, teeth are attached to the inner side of the jaw. Thecodont dentition is found in humans, acrodont in amphibians while pleurodont dentition is exhibited by Iguanas.
Dentition based on succession of teeth
Dentition based on replacement of teeth can be of three types – monophyodont, diphyodont and polyphyodont. Monophyodont animals have one set of teeth throughout their lifetime like marsupials and whales. Diphyodont dentition is a characteristic of humans, where one set of teeth are replaced by a second set. The first set is a temporary one while the second set is a permanent set. Polyphyodont dentition as in sharks is the condition where teeth are continuously replaced through life time.
Therefore, based on the above discussion, we can conclude that mammals have two sets of teeth throughout their lifetime, teeth that are placed in sockets of the jaw bone, differ morphologically and there are. These conditions are respectively known as Diphyodont, Thecodont and Heterodont.
Hence, option (b) is correct.
Note: Dentition is the arrangement of teeth on the jaw. Dentition of mammals is of heterodont, diphyodont and thecodont type. Since teeth structure and arrangement does not change extensively based on the outer environment of organisms, dentition study is very useful for archaeologists. Also, teeth are better preserved than bones, study of dentition allows us to know more about living populations across different timelines.
Complete step by step answer: The arrangement of teeth on the jaw bones is known as Dentition. There are three types of dentition. They are explained below.
Dentition based on morphology
There are two types of dentition based on the morphology of teeth. They are homodont and heterodont. Homodont animals have the same size and same shaped teeth. On the other hand, animals with teeth of different sizes and shapes are known as heterodont. For example, whales are homodont while humans are heterodont.
Heterodont dentition involves four types of teeth – incisors, canines, premolars and molars.

Fig: Heterodont dentition in human
Dentition based on the attachment of teeth
There are three dentition types based on attachment of teeth. Thecodont is the condition when teeth are attached to sockets on the jaw bone. Acrodont dentition refers to the condition where teeth are fused to the jaw bone. In Pleurodont dentition, instead of being fused, teeth are attached to the inner side of the jaw. Thecodont dentition is found in humans, acrodont in amphibians while pleurodont dentition is exhibited by Iguanas.
Dentition based on succession of teeth
Dentition based on replacement of teeth can be of three types – monophyodont, diphyodont and polyphyodont. Monophyodont animals have one set of teeth throughout their lifetime like marsupials and whales. Diphyodont dentition is a characteristic of humans, where one set of teeth are replaced by a second set. The first set is a temporary one while the second set is a permanent set. Polyphyodont dentition as in sharks is the condition where teeth are continuously replaced through life time.
Therefore, based on the above discussion, we can conclude that mammals have two sets of teeth throughout their lifetime, teeth that are placed in sockets of the jaw bone, differ morphologically and there are. These conditions are respectively known as Diphyodont, Thecodont and Heterodont.
Hence, option (b) is correct.
Note: Dentition is the arrangement of teeth on the jaw. Dentition of mammals is of heterodont, diphyodont and thecodont type. Since teeth structure and arrangement does not change extensively based on the outer environment of organisms, dentition study is very useful for archaeologists. Also, teeth are better preserved than bones, study of dentition allows us to know more about living populations across different timelines.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




