
In most green algae, pyrenoids, the storage bodies are located in................
A) Chloroplasts
B) Mitochondria
C) Cytoplasm
D)nucleus
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Green algae are phototrophic organisms. They strictly live in aqueous environment. They have carbon dioxide fixing enzymes.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, we must know about the structure of green algae.
>Green algae are the photoautotrophic eukaryotic organisms which strictly live in aqueous environment. The green algae are unicellular and colonial organisms which have one or more flagella. They have a well defined nucleus and cytoplasm. The cell wall contains cellulose and they store carbohydrate as starch. Most of them reproduce asexually by fission and sexually by alternation of generations. Green algae have two types of chloroplast a and b giving them bright green colour and also have accessory pigments like beta carotene and xanthophylls. Pyrenoids are subcellular microcompartments present in the chloroplast of hornworts. It was first described by Vaucher. Its main function is it is the centre of carbon dioxide fixation. It maintains a carbon dioxide rich environment around photosynthetic enzymes. It is the centre for active transport of bicarbonate from extracellular environment to chloroplast membrane and thylakoid.
>Mitochondria- It is the powerhouse of the cell. They have mitochondria with flat cristae.
>Nucleus- Green algae have a very well defined nucleus. The nucleus contains the genetic material.
>Cytoplasm –Cytoplasm comprises all the organelles. Nucleus, chloroplast, mitochondria are present in the cytoplasm.
Thus the correct answer is (A) Pyrenoids are located in Chloroplasts.
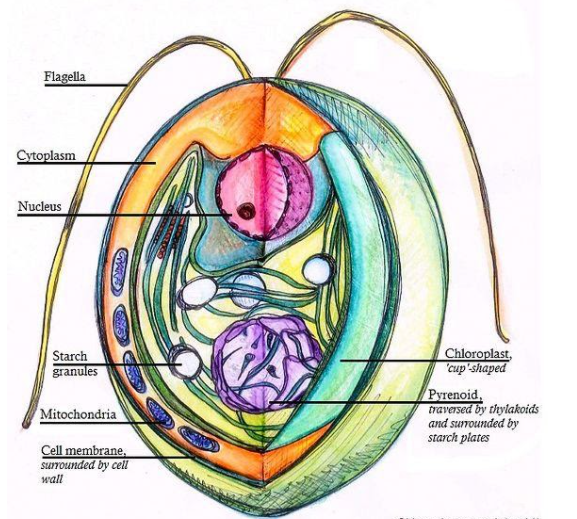
Note: Green algae belong to kingdom plantae but lack a well differentiated body. They have two types of pigments chlorophyll a and b. Some green algae have pyrenoids in the chloroplast which are the important centre for fixing carbon dioxide.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, we must know about the structure of green algae.
>Green algae are the photoautotrophic eukaryotic organisms which strictly live in aqueous environment. The green algae are unicellular and colonial organisms which have one or more flagella. They have a well defined nucleus and cytoplasm. The cell wall contains cellulose and they store carbohydrate as starch. Most of them reproduce asexually by fission and sexually by alternation of generations. Green algae have two types of chloroplast a and b giving them bright green colour and also have accessory pigments like beta carotene and xanthophylls. Pyrenoids are subcellular microcompartments present in the chloroplast of hornworts. It was first described by Vaucher. Its main function is it is the centre of carbon dioxide fixation. It maintains a carbon dioxide rich environment around photosynthetic enzymes. It is the centre for active transport of bicarbonate from extracellular environment to chloroplast membrane and thylakoid.
>Mitochondria- It is the powerhouse of the cell. They have mitochondria with flat cristae.
>Nucleus- Green algae have a very well defined nucleus. The nucleus contains the genetic material.
>Cytoplasm –Cytoplasm comprises all the organelles. Nucleus, chloroplast, mitochondria are present in the cytoplasm.
Thus the correct answer is (A) Pyrenoids are located in Chloroplasts.

Note: Green algae belong to kingdom plantae but lack a well differentiated body. They have two types of pigments chlorophyll a and b. Some green algae have pyrenoids in the chloroplast which are the important centre for fixing carbon dioxide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




