
In prokaryotes, the ribosomes binding site on mRNA is called
(a)Hogness sequence
(b)Shine- Dalgarno sequence
(c)Prinbow sequence
(d)TATA- box
Answer
573.6k+ views
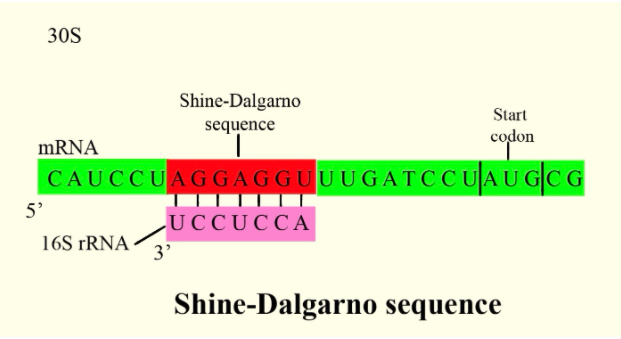
Hint: In prokaryotes, the ribosomes binding site (RBS) on the mRNA is present in the 5' UTR region. It is made up of purine bases. In Escherichia coli, a sequence i.e AGGAGG contains six-base consensus, e.g the sequence is AGGAGGU, while the shorter GAGG dominates in the E. coli virus T4 early genes.
Complete answer:
In bacterial and archaeal messenger RNA, a ribosomal binding site is present which is located around 8 bases upstream of the start codon AUG is called the Shine–Dalgarno (SD) sequence which is common in bacteria, but rarer in archaea, also present in some chloroplast and mitochondrial transcripts. To initiate protein synthesis the RNA sequence helps recruit the ribosome to the messenger RNA (mRNA) by aligning the ribosome with the start codon and as dictated by the codons, tRNA may add amino acids in sequence moving downstream from the translational start site after alignment.
Shine and Dalgarno showed by using a method developed by Hunt that the nucleotide tract at the 3' end of E. coli 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is pyrimidine-rich and has the specific sequence YACCUCCUUA, they proposed that these ribosomal nucleotides recognize the complementary purine-rich sequence AGGAGGU, which is found upstream of the start codon AUG in several mRNAs found in viruses that affect E. coli. It is confirmed by many studies that base pairing between the SD sequence in mRNA and the 3' end of 16S rRNA is of prime importance for the initiation of translation by bacterial ribosomes. The scientists Dalgarno and Shine, in 1973 proposed that in eukaryotes, in the termination of protein synthesis, the 3'-end of the small 18S rRNA may play a role by complementary base pairing with termination codons and this came from their observation that the 3' terminal sequences of 18S rRNA from Drosophila melanogaster, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and rabbit cells are identical: GAUCAUUA -3'OH. It is proved that this nucleotide tract played an important role in the cell as the conservation of this sequence between such distantly related eukaryotes.
Additional Information: 1) Australian scientists John Shine and Lynn Dalgarno proposed the Shine–Dalgarno sequence.
2) Shine and Dalgarno also proposed in 1974, a similar role for the 3' end of 16S rRNA in recognizing termination triplets in E.coli based on complementarity relationships between the E.coli termination codons and 3'-terminal UUA-OH in 16S rRNA.
3) This Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence enables the initiation of protein synthesis by aligning the ribosome with the start codon. It just simply put genes are read in groups of three letters but you need to let the ribosome know where to start.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Shine- Dalgarno sequence’.
Note: If Shine–Dalgarno sequence got any mutations, The translation in prokaryotes can reduce or increase and this change is due to a reduced or increased mRNA-ribosome pairing efficiency, and also translation can be restored with the help of the compensatory mutations in the 3'-terminal 16S rRNA sequence.
Complete answer:
In bacterial and archaeal messenger RNA, a ribosomal binding site is present which is located around 8 bases upstream of the start codon AUG is called the Shine–Dalgarno (SD) sequence which is common in bacteria, but rarer in archaea, also present in some chloroplast and mitochondrial transcripts. To initiate protein synthesis the RNA sequence helps recruit the ribosome to the messenger RNA (mRNA) by aligning the ribosome with the start codon and as dictated by the codons, tRNA may add amino acids in sequence moving downstream from the translational start site after alignment.
Shine and Dalgarno showed by using a method developed by Hunt that the nucleotide tract at the 3' end of E. coli 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is pyrimidine-rich and has the specific sequence YACCUCCUUA, they proposed that these ribosomal nucleotides recognize the complementary purine-rich sequence AGGAGGU, which is found upstream of the start codon AUG in several mRNAs found in viruses that affect E. coli. It is confirmed by many studies that base pairing between the SD sequence in mRNA and the 3' end of 16S rRNA is of prime importance for the initiation of translation by bacterial ribosomes. The scientists Dalgarno and Shine, in 1973 proposed that in eukaryotes, in the termination of protein synthesis, the 3'-end of the small 18S rRNA may play a role by complementary base pairing with termination codons and this came from their observation that the 3' terminal sequences of 18S rRNA from Drosophila melanogaster, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and rabbit cells are identical: GAUCAUUA -3'OH. It is proved that this nucleotide tract played an important role in the cell as the conservation of this sequence between such distantly related eukaryotes.
Additional Information: 1) Australian scientists John Shine and Lynn Dalgarno proposed the Shine–Dalgarno sequence.
2) Shine and Dalgarno also proposed in 1974, a similar role for the 3' end of 16S rRNA in recognizing termination triplets in E.coli based on complementarity relationships between the E.coli termination codons and 3'-terminal UUA-OH in 16S rRNA.
3) This Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence enables the initiation of protein synthesis by aligning the ribosome with the start codon. It just simply put genes are read in groups of three letters but you need to let the ribosome know where to start.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Shine- Dalgarno sequence’.

Note: If Shine–Dalgarno sequence got any mutations, The translation in prokaryotes can reduce or increase and this change is due to a reduced or increased mRNA-ribosome pairing efficiency, and also translation can be restored with the help of the compensatory mutations in the 3'-terminal 16S rRNA sequence.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




