
In root, what structure increases surface area for the absorption of water and minerals from the soil?
Answer
481.2k+ views
Hint: The root is a part of the plant, which grows downwards. During seed germination, the radicle is the first organ to come out, which elongates to form the taproot. The main root of the plant is also known as the primary root. It gives off lateral branches, forming tertiary roots and secondary roots. All the roots form the root system. Root tip, root hair, root cap, and root apical meristem are parts of a root.
Complete answer
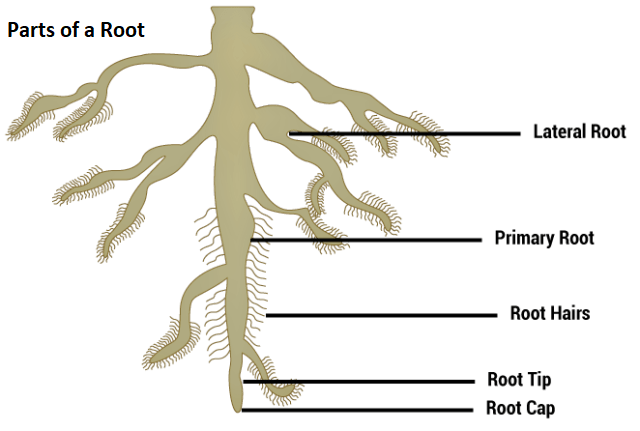
Fig: Root System
Root hairs are the structures which increase the surface area of absorption of water and minerals. They are delicate and very fine, thread-like structures, which arise from the region of maturation of the root. In origin, they are exogenous. They are unicellular structures, which are developed from the epidermis of the root. The major function of root hairs is the increase in the surface area of absorption of minerals and water from the soil.
The root hairs are suitable for absorption of water from the soil because of the following reasons:
1. The root hairs possess a large surface area. An increase in the surface area leads to greater absorption.
2. Each root hair possesses a semi-permeable membrane.
3. Root hair consists of a solution (cell sap) of a higher concentration than the surrounding soil water.
4. Roots possess hair-like projections called root hairs, which protrude from their surface. The root hairs aid the plant absorb more nutrients and water as they enhance the available surface area. Through the root hairs, the roots of many plants possess a mycorrhizal relationship with the fungi for greater absorption.
Note:
Root provides the proper anchorage to the plants. It transports the absorbed water and minerals to the stem via the xylem. It stores reserve food material. It is involved in the synthesis of plant growth regulators. It performs special physiological functions like storage of food, assimilation, sucking food from the host, absorption of atmospheric moisture, gaseous exchange, and climbing.
Complete answer

Fig: Root System
Root hairs are the structures which increase the surface area of absorption of water and minerals. They are delicate and very fine, thread-like structures, which arise from the region of maturation of the root. In origin, they are exogenous. They are unicellular structures, which are developed from the epidermis of the root. The major function of root hairs is the increase in the surface area of absorption of minerals and water from the soil.
The root hairs are suitable for absorption of water from the soil because of the following reasons:
1. The root hairs possess a large surface area. An increase in the surface area leads to greater absorption.
2. Each root hair possesses a semi-permeable membrane.
3. Root hair consists of a solution (cell sap) of a higher concentration than the surrounding soil water.
4. Roots possess hair-like projections called root hairs, which protrude from their surface. The root hairs aid the plant absorb more nutrients and water as they enhance the available surface area. Through the root hairs, the roots of many plants possess a mycorrhizal relationship with the fungi for greater absorption.
Note:
Root provides the proper anchorage to the plants. It transports the absorbed water and minerals to the stem via the xylem. It stores reserve food material. It is involved in the synthesis of plant growth regulators. It performs special physiological functions like storage of food, assimilation, sucking food from the host, absorption of atmospheric moisture, gaseous exchange, and climbing.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




