
Why in terms of structure and bonding, does $ - 2 - $ ene exist as two geometric isomers whereas $ - 1 - $ ene does not?
Answer
490.8k+ views
Hint: Geometrical isomerism is a type of configurational isomerism where difference of orientation of substituents is observed in the spatial dimension. Geometrical isomerism is shown by the compounds which possess double bonds in their structure.
Complete answer:
Geometrical isomers are further categorized on the basis of arrangement of substituents with each other. If the side substituents around the double bond are on the same side, then is it known as “cis” isomers. If the side substituents are present in different locations around the double bond is known as ‘’trans” isomers.
Cis-trans isomers comes under the category of stereoisomers because molecular formula of the compound remains same but the orientation of substituents varies in three-dimensional space.
In compound but $ - 2 - $ ene, from the structure of compound we see that double bond is present at $ {2^{nd}} $ position in the compound. We can draw the geometrical isomers of but $ - 2 - $ ene which are expressed as:
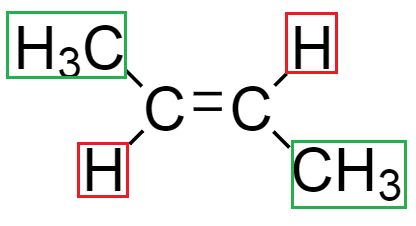
From the above structure, we see that in the diagram $ \left( 1 \right) $ , both the methyl groups around the double bond are in opposite directions. Hence, it is known as trans isomers.
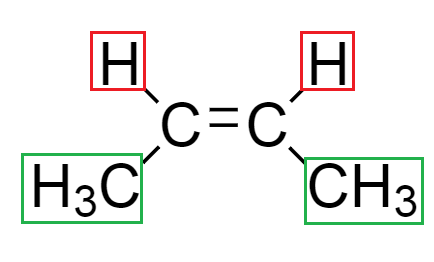
From the above structure, we see that in the diagram $ \left( 2 \right) $ , both the methyl groups around the double bond are in the same direction. Hence, it is known as cis isomers.
In compound but $ - 1 - $ ene, from the structure of compound we see that double bond is present at $ {1^{st}} $ position in the compound. We can draw the geometrical isomers of but $ - 1 - $ ene which are expressed as:
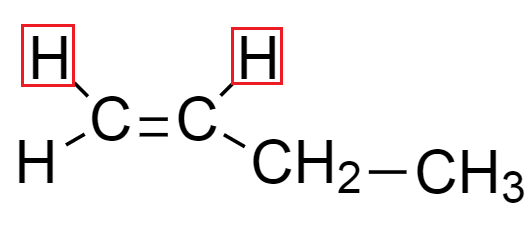
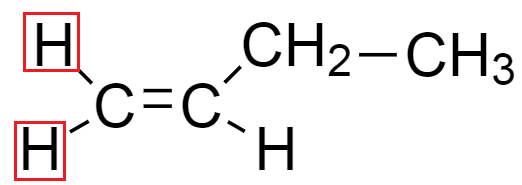
From the above structure we see that hydrogen atoms in both the diagrams are on the same side because terminal carbon contains both the substituents which are identical. Hence, only one isomer is possible in but $ - 1 - $ ene.
Note:
Physical and chemical properties of cis-trans isomers vary from each other like melting point is high in the case of trans molecule than cis molecule, boiling point of cis isomers are higher than trans isomers. HPLC method is employed for the separation of cis and trans isomers.
Complete answer:
Geometrical isomers are further categorized on the basis of arrangement of substituents with each other. If the side substituents around the double bond are on the same side, then is it known as “cis” isomers. If the side substituents are present in different locations around the double bond is known as ‘’trans” isomers.
Cis-trans isomers comes under the category of stereoisomers because molecular formula of the compound remains same but the orientation of substituents varies in three-dimensional space.
In compound but $ - 2 - $ ene, from the structure of compound we see that double bond is present at $ {2^{nd}} $ position in the compound. We can draw the geometrical isomers of but $ - 2 - $ ene which are expressed as:

From the above structure, we see that in the diagram $ \left( 1 \right) $ , both the methyl groups around the double bond are in opposite directions. Hence, it is known as trans isomers.

From the above structure, we see that in the diagram $ \left( 2 \right) $ , both the methyl groups around the double bond are in the same direction. Hence, it is known as cis isomers.
In compound but $ - 1 - $ ene, from the structure of compound we see that double bond is present at $ {1^{st}} $ position in the compound. We can draw the geometrical isomers of but $ - 1 - $ ene which are expressed as:


From the above structure we see that hydrogen atoms in both the diagrams are on the same side because terminal carbon contains both the substituents which are identical. Hence, only one isomer is possible in but $ - 1 - $ ene.
Note:
Physical and chemical properties of cis-trans isomers vary from each other like melting point is high in the case of trans molecule than cis molecule, boiling point of cis isomers are higher than trans isomers. HPLC method is employed for the separation of cis and trans isomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




