
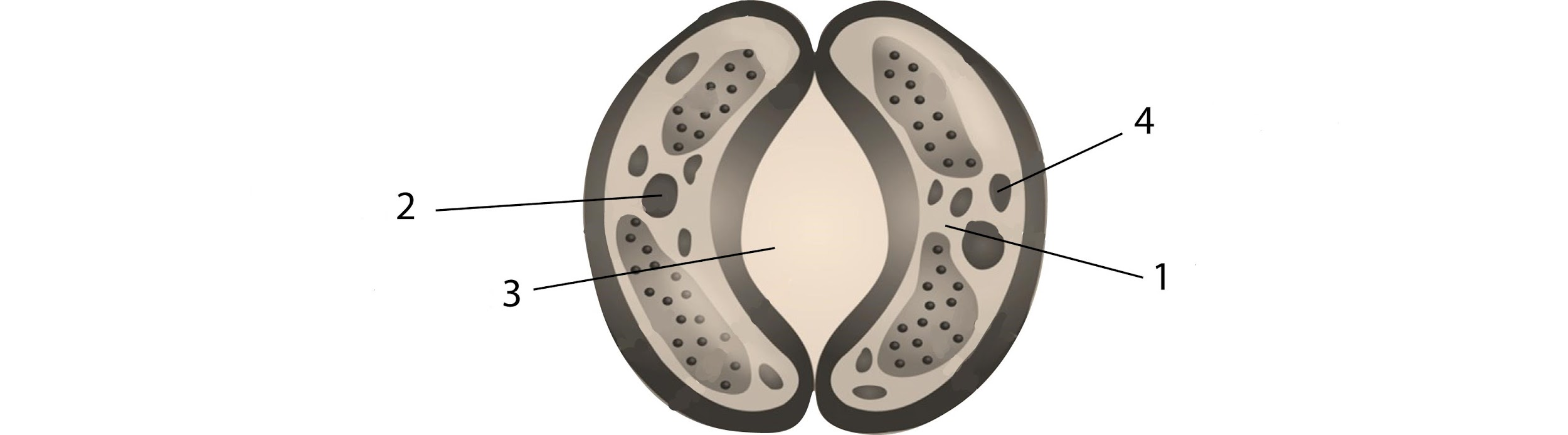
In the above sketch of the stomatal apparatus, parts 1,2,3 and 4 were labeled differently by four students. The correct labeling is:
(a) I- Guard cell, II-Stoma, III-Starch granules, IV-Nucleus
(b) I- Cytoplasm, II-Nucleus, III-Stoma, IV-Chloroplast
(c) I- Guard cell, II-Starch, III-Nucleus, IV-Stoma
(d) I- Cytoplasm, II-Chloroplast, III-Stoma, IV-Nucleus

Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: Stomata are specialized epidermal structures whose primary function is the gaseous exchange between the plant’s internal tissues and the atmosphere. Loss of water in the form of water vapors also takes place in the process of stomatal transpiration.
Complete answer:
Stomata are minute pores generally present on leaf epidermis. Each stoma is bordered by two specialized green epidermal cells called guard cells, which are generally kidney-shaped or bean-shaped. Like any other normal cell, they also have rich cytoplasm and a single nucleus. Chloroplasts are also present in them. Guard cells, also, surrounded by specialized epidermal cells called subsidiary cells or accessory cells.
Additional Information: Guard cells surround the stomata and in return get surrounded by two to four subsidiary cells. They are connected to the subsidiary cells via plasmodesmata. They are the only epidermal cells with chloroplasts. Apart from containing chloroplast, they also possess small vacuoles and also store starch. The guard cells have inner thickened walls while outer thin walls. Radial micellation is also a characteristic feature of guard cells where the cellulose microfibrils radiate around the circumference of the stomatal pore. They are crucial in regulating the stomatal apertures and thus can control the rate of carbon dioxide uptake and water loss. Both these factors can influence photosynthesis and water status of the plant respectively. The guard cells owing to their small size get easily influenced by turgor changes, which, in turn, leads to the opening and closing of the stomata.
So, the correct answer is ‘I- Cytoplasm, II-Nucleus, III-Stoma, IV-Chloroplast’.
Note: -Two types of stomata can be observed in nature- Scotoactive stomata and Photoactive stomata. Photoactive stomata are the one which opens only during the day and closes during the night. This is the most common type of stomata found in mesophytic plants.
-Scotoactive stomata are the kind of stomata which opens during night time and inactive i.e closed during day time. It is an adaptation in xerophytic plants that live in a water-scarce habitat such as deserts. Closure of stomata during the day helps xerophytic plants to conserve water by avoiding the loss of water via transpiration. But the closure of stomata also means no exchange of gases. This is compensated by the opening of stomata during night time when sunlight is absent and thus water loss is minimized to its lowest possibility.
Complete answer:
Stomata are minute pores generally present on leaf epidermis. Each stoma is bordered by two specialized green epidermal cells called guard cells, which are generally kidney-shaped or bean-shaped. Like any other normal cell, they also have rich cytoplasm and a single nucleus. Chloroplasts are also present in them. Guard cells, also, surrounded by specialized epidermal cells called subsidiary cells or accessory cells.
Additional Information: Guard cells surround the stomata and in return get surrounded by two to four subsidiary cells. They are connected to the subsidiary cells via plasmodesmata. They are the only epidermal cells with chloroplasts. Apart from containing chloroplast, they also possess small vacuoles and also store starch. The guard cells have inner thickened walls while outer thin walls. Radial micellation is also a characteristic feature of guard cells where the cellulose microfibrils radiate around the circumference of the stomatal pore. They are crucial in regulating the stomatal apertures and thus can control the rate of carbon dioxide uptake and water loss. Both these factors can influence photosynthesis and water status of the plant respectively. The guard cells owing to their small size get easily influenced by turgor changes, which, in turn, leads to the opening and closing of the stomata.
So, the correct answer is ‘I- Cytoplasm, II-Nucleus, III-Stoma, IV-Chloroplast’.
Note: -Two types of stomata can be observed in nature- Scotoactive stomata and Photoactive stomata. Photoactive stomata are the one which opens only during the day and closes during the night. This is the most common type of stomata found in mesophytic plants.
-Scotoactive stomata are the kind of stomata which opens during night time and inactive i.e closed during day time. It is an adaptation in xerophytic plants that live in a water-scarce habitat such as deserts. Closure of stomata during the day helps xerophytic plants to conserve water by avoiding the loss of water via transpiration. But the closure of stomata also means no exchange of gases. This is compensated by the opening of stomata during night time when sunlight is absent and thus water loss is minimized to its lowest possibility.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




