
In the chemical compound \[{C_2}{H_2}\] , how many pairs of electrons are shared between the two carbon atoms?
Answer
548.1k+ views
Hint: The acetylene or ethyne having the molecular formula \[{C_2}{H_2}\] shows the covalent bond between each of the atoms. The covalent bonds are formed between two atoms or ions where the sharing of electrons takes place between the electron pairs. They are also called a molecular bond. The forces of attraction/repulsion between two atoms (when they share a bond pair/ electron paid) are known as a covalent bond.
Complete step-by-step answer:The “covalence” word was termed by the scientist named Irving Langmuir, which states about the number of electron pairs shared by the neighbour atoms. Generally, carbon exhibits such kinds of compounds. The pair of electrons that share the two atoms which are extended around the nuclei of atoms leading to create a molecule.
Depending upon the sharing of electrons they are classified into different categories:
Single covalent bond
Double covalent bond
Triple covalent bond
In the case of \[{C_2}{H_2}\] compound \[2\] pairs of electrons are shared between the two carbon atoms. This forms the triple covalent bond.
Let’s see what is triple covalent bonds,
Triple covalent bond: The three electron pairs share between the two participating atoms and form a triple covalent bond. It is represented as two dashes \[( \equiv )\]. The triple covalent bonds are stronger than the single bond. This type is the least stable.
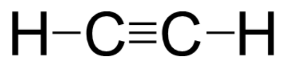
For example, Nitrogen (\[{N_2}\]) molecule has two nitrogen atoms with five valence electrons each and forms three electron pairs for octet completion. Each nitrogen atom shares its two electrons and forms a triple bond.
\[N \equiv N\]
Note: Single covalent bond: The electron pair shared between the two atoms, then such bonds are referred to be a single covalent bond. It is represented by a single dash \[( - )\] . These kinds of bonds have less density and are weaker than double and triple bonds, even though they are single covalent bonds.
For example, Methane ( \[C{H_4}\] ) is one example, where each hydrogen is sharing its electron with carbon and forming a single covalent bond. Where hydrogen and carbon are sharing one electron and completing their octet of methane (\[C{H_4}\] ) molecule.
Double covalent bond: The two-electron pairs share between the two participating atoms and form a double covalent bond. It is represented as two dashes \[( = )\] . The double covalent bonds are stronger than the single bond. This type is less stable.
For example, a Carbon dioxide (\[C{O_2}\]) molecule has two oxygen atoms with four valence electrons and one carbon atom with six valence electrons. Each oxygen atom shares its two electrons with carbon and forms a double bond.
\[O = C = O\]
Complete step-by-step answer:The “covalence” word was termed by the scientist named Irving Langmuir, which states about the number of electron pairs shared by the neighbour atoms. Generally, carbon exhibits such kinds of compounds. The pair of electrons that share the two atoms which are extended around the nuclei of atoms leading to create a molecule.
Depending upon the sharing of electrons they are classified into different categories:
Single covalent bond
Double covalent bond
Triple covalent bond
In the case of \[{C_2}{H_2}\] compound \[2\] pairs of electrons are shared between the two carbon atoms. This forms the triple covalent bond.
Let’s see what is triple covalent bonds,
Triple covalent bond: The three electron pairs share between the two participating atoms and form a triple covalent bond. It is represented as two dashes \[( \equiv )\]. The triple covalent bonds are stronger than the single bond. This type is the least stable.
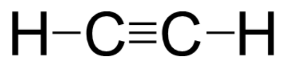
For example, Nitrogen (\[{N_2}\]) molecule has two nitrogen atoms with five valence electrons each and forms three electron pairs for octet completion. Each nitrogen atom shares its two electrons and forms a triple bond.
\[N \equiv N\]
Note: Single covalent bond: The electron pair shared between the two atoms, then such bonds are referred to be a single covalent bond. It is represented by a single dash \[( - )\] . These kinds of bonds have less density and are weaker than double and triple bonds, even though they are single covalent bonds.
For example, Methane ( \[C{H_4}\] ) is one example, where each hydrogen is sharing its electron with carbon and forming a single covalent bond. Where hydrogen and carbon are sharing one electron and completing their octet of methane (\[C{H_4}\] ) molecule.
Double covalent bond: The two-electron pairs share between the two participating atoms and form a double covalent bond. It is represented as two dashes \[( = )\] . The double covalent bonds are stronger than the single bond. This type is less stable.
For example, a Carbon dioxide (\[C{O_2}\]) molecule has two oxygen atoms with four valence electrons and one carbon atom with six valence electrons. Each oxygen atom shares its two electrons with carbon and forms a double bond.
\[O = C = O\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




