
In the diagram of T.S. monocot leaf, identify labellings a, b, c, d with their functions.
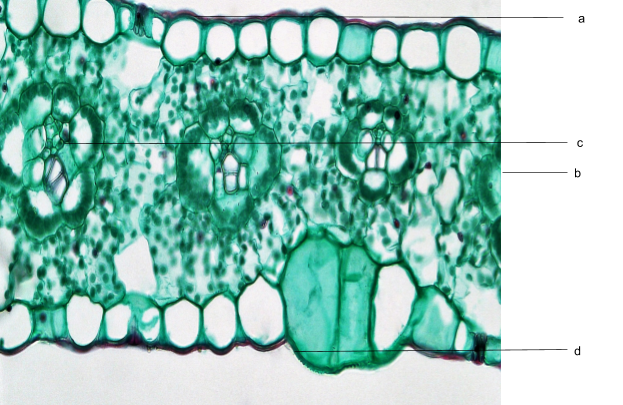
a-Motor action , b-Photosynthesis , c- Conduction , d-Transpiration
a-Motor action , b-Conduction , c-Photosynthesis , d-Transpiration
a-Transpiration , b-Photosynthesis , c-Conduction , d-Transpiration
a-Transpiration , b-Conduction , c-Photosynthesis, d-Motor action

Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: Monocot leaves are the leaves that appear on plants made from single-cotyledon seeds such as maize, rice, grass, wheat, etc. Monocot leaves are said to be isobilateral leaves, as both leaves have the same coloration on the surface. As with parallel ventilation, the leaves are normally ribboned.
Complete answer:
There is an upper and lower surface on the leaves of flowering plants, with the upper surface usually facing away from the ground and the lower surface facing it.
Monocot and dicot leaves each have an outer, waxy layer called the cuticle that protects the upper and lower epidermis dermal tissue. The cuticle covers and allows the leaf to hold water. The leaf is also covered by the epidermis, which is situated under the cuticle.
In gas exchange, it also plays a key role, since it includes pores called stomata. Stomata are also present to some degree in the stem and flowers of the plant, but they are mainly a characteristic of the leaves.
The region between the leaf's upper and lower epidermis is filled by a form of ground tissue called mesophyll. There are several chloroplasts in the mesophyll cells, organelles that conduct photosynthesis, converting light, water, and carbon dioxide into sugar that can be broken down by the plant to produce energy. The primary by-product of photosynthesis is oxygen, which is excellent for species such as humans that use oxygen to breathe.
In leaves, all vascular tissue types have a significant role to play. The xylem takes up water from the roots and dissolved minerals, and when doing photosynthesis, the cells in the mesophyll use the water. Via transpiration, the release of water vapour through the stomata, excess water is expelled. The phloem takes the photosynthesis-generated dissolved sugars to the stem and roots of the plant to be used or deposited.
In the diagram a – represents – trichomes – motor action, b-represents mesophyll - photosynthesis and c-xylem – conduction, d-represents stomata – transpiration.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A)
Note: On the upper and lower sides of the leaf, monocot leaves have stomata, and their veins run parallel to one another. There are also bulliform cells in monocot leaves. It is assumed that these huge, bubble-like cells located just beneath the epidermis, help the leaf bend or fold.
Complete answer:
There is an upper and lower surface on the leaves of flowering plants, with the upper surface usually facing away from the ground and the lower surface facing it.
Monocot and dicot leaves each have an outer, waxy layer called the cuticle that protects the upper and lower epidermis dermal tissue. The cuticle covers and allows the leaf to hold water. The leaf is also covered by the epidermis, which is situated under the cuticle.
In gas exchange, it also plays a key role, since it includes pores called stomata. Stomata are also present to some degree in the stem and flowers of the plant, but they are mainly a characteristic of the leaves.
The region between the leaf's upper and lower epidermis is filled by a form of ground tissue called mesophyll. There are several chloroplasts in the mesophyll cells, organelles that conduct photosynthesis, converting light, water, and carbon dioxide into sugar that can be broken down by the plant to produce energy. The primary by-product of photosynthesis is oxygen, which is excellent for species such as humans that use oxygen to breathe.
In leaves, all vascular tissue types have a significant role to play. The xylem takes up water from the roots and dissolved minerals, and when doing photosynthesis, the cells in the mesophyll use the water. Via transpiration, the release of water vapour through the stomata, excess water is expelled. The phloem takes the photosynthesis-generated dissolved sugars to the stem and roots of the plant to be used or deposited.
In the diagram a – represents – trichomes – motor action, b-represents mesophyll - photosynthesis and c-xylem – conduction, d-represents stomata – transpiration.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A)
Note: On the upper and lower sides of the leaf, monocot leaves have stomata, and their veins run parallel to one another. There are also bulliform cells in monocot leaves. It is assumed that these huge, bubble-like cells located just beneath the epidermis, help the leaf bend or fold.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




