
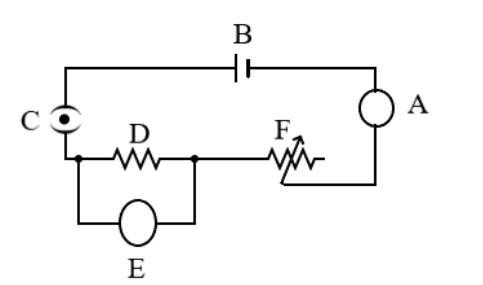
In the electric circuit shown in the figure, label the parts A, B, C, D, E and F. State the function of each part. Show in the diagram the direction of flow of current.

Answer
476.4k+ views
Hint: The functions of the circuit elements need to be stated out and in order to do this the circuit elements must be identified first. The role of each of the elements in the circuit must be mentioned and analyzed. The direction of flow of conventional current in the circuit is also required to be found with the help of the cell or the battery.
Complete answer:
The above problem revolves around the concept of a current circuit which involves the connection of many other devices or circuit elements that contribute to the working of the circuit as per the needs of the user. The above diagram shows a closed circuit to which various elements are connected and the reason why the circuit is closed is that, it provides a closed path for the flow of current produced from its source in the circuit as the flow of current requires a closed pathway for it to flow through all the circuit elements in the circuit.Since it can be seen that the above circuit diagram forms a closed circuit it can be concluded that current would efficiently flow through it.
Now, let us identify all the circuitry elements in the circuit labelled from A to F. In the given diagram the circuit elements of the circuit are identified using the standard symbols used to represent these devices or elements when drawing a circuit diagram. Each element can be represented by a symbol through which they are identified. Hence, the names of the circuit elements from A to F in this order are:
A – Ammeter
B – Cell
C – Key
D – Resistor
E – Voltmeter
F – Rheostat
We now state the function of each circuit element that would each have its contribution to the working of the circuit and the flow of current through the circuit. The function of each of these circuit elements named from A to F are:
Ammeter: Ammeter is a device that measures current, that is, the amount of current that flows through the circuit is accurately measured by it and it is always connected in series to the circuit in order to measure the current. This is because the current in the circuit remains the same throughout in a series connection and hence when connected in series the entire amount of current can be easily detected rather than measuring only a part of the current when it gets split at any junction for example.
Cell: The Cell is the source or the supply for the production of direct current in the circuit. It is because of the connection of these circuit elements that the circuit produces current from which the current flows through all the other elements of the circuit. The cell is an essential circuitry element as every circuit requires either a cell or a battery in order for the circuit to function because the source or the origin of the current is rather from this element. Each cell has a positive and a negative terminal which represents the higher and the lower potential of the cell respectively and hence the voltage or the potential difference is produced. Every cell has its own internal resistance.
Key: A key is a small device that is connected to the circuit in order to control the direction or the pathway of the current in certain circumstances and its main role is to function like a switch wherein when the key is plugged in the circuit is closed and the current starts to flow through the circuit and when the key is unplugged then then the circuit is open and hence no current flows. This is similar to the on and off state of a switch and hence only when the key is plugged in will the circuit function.
Resistor: Resistor is a device that restricts or hinders the flow of current and hence plays a role in controlling the current in the circuit. It is a means by which the current produced is limited in order to avoid the damage of certain devices if large amounts of current flow through them. By definition, a resistor is a device which opposes the flow of current in order to limit it. It can also be known as a load.
Voltmeter: A voltmeter is a device that measures the voltage in the circuit and is always connected in parallel to the device through which the voltage needs to be measured as the potential difference between the two ends of the device through which voltage needs to be measured is recorded. In the above circuit diagram the voltmeter is connected in parallel to the resistor and hence the potential difference or the voltage drop across it is measured in this case.
Rheostat:This is known as a variable resistor which is also a resistor and which also has the same function as that of the resistor but in this case the resistor value can be chosen as per the circuit's needs so as to correspondingly vary the amount of current flowing through the circuit. The resistance can be chosen in accordance to the user’s choice.
In order to determine the direction of flow of current we first need to look at the manner in which the cell is connected. Current is defined as the flow of charge or electrons and this flow of electrons occurs from the negative terminal of the cell, that is, the electrons are produced from the negative terminal of the cell and get collected at the positive terminal of the cell. The direction of conventional current is always said to be in the direction opposite to the direction of flow of electrons and hence the direction of current is from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the cell. This can be seen in the diagram below where the arrows indicate the current direction:
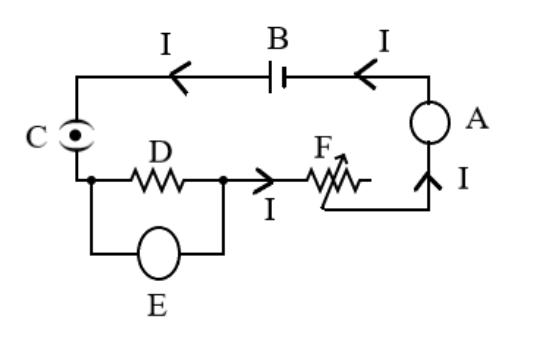
Note: In the given diagram the circuit element labelled as D can also be identified to be a load that is applied to the circuit which controls the flow of current which is also correct.A load is a device that can not only refer to a resistance but also refers to a collection or a combination of electrical components which tend to hinder the flow of current.
Complete answer:
The above problem revolves around the concept of a current circuit which involves the connection of many other devices or circuit elements that contribute to the working of the circuit as per the needs of the user. The above diagram shows a closed circuit to which various elements are connected and the reason why the circuit is closed is that, it provides a closed path for the flow of current produced from its source in the circuit as the flow of current requires a closed pathway for it to flow through all the circuit elements in the circuit.Since it can be seen that the above circuit diagram forms a closed circuit it can be concluded that current would efficiently flow through it.
Now, let us identify all the circuitry elements in the circuit labelled from A to F. In the given diagram the circuit elements of the circuit are identified using the standard symbols used to represent these devices or elements when drawing a circuit diagram. Each element can be represented by a symbol through which they are identified. Hence, the names of the circuit elements from A to F in this order are:
A – Ammeter
B – Cell
C – Key
D – Resistor
E – Voltmeter
F – Rheostat
We now state the function of each circuit element that would each have its contribution to the working of the circuit and the flow of current through the circuit. The function of each of these circuit elements named from A to F are:
Ammeter: Ammeter is a device that measures current, that is, the amount of current that flows through the circuit is accurately measured by it and it is always connected in series to the circuit in order to measure the current. This is because the current in the circuit remains the same throughout in a series connection and hence when connected in series the entire amount of current can be easily detected rather than measuring only a part of the current when it gets split at any junction for example.
Cell: The Cell is the source or the supply for the production of direct current in the circuit. It is because of the connection of these circuit elements that the circuit produces current from which the current flows through all the other elements of the circuit. The cell is an essential circuitry element as every circuit requires either a cell or a battery in order for the circuit to function because the source or the origin of the current is rather from this element. Each cell has a positive and a negative terminal which represents the higher and the lower potential of the cell respectively and hence the voltage or the potential difference is produced. Every cell has its own internal resistance.
Key: A key is a small device that is connected to the circuit in order to control the direction or the pathway of the current in certain circumstances and its main role is to function like a switch wherein when the key is plugged in the circuit is closed and the current starts to flow through the circuit and when the key is unplugged then then the circuit is open and hence no current flows. This is similar to the on and off state of a switch and hence only when the key is plugged in will the circuit function.
Resistor: Resistor is a device that restricts or hinders the flow of current and hence plays a role in controlling the current in the circuit. It is a means by which the current produced is limited in order to avoid the damage of certain devices if large amounts of current flow through them. By definition, a resistor is a device which opposes the flow of current in order to limit it. It can also be known as a load.
Voltmeter: A voltmeter is a device that measures the voltage in the circuit and is always connected in parallel to the device through which the voltage needs to be measured as the potential difference between the two ends of the device through which voltage needs to be measured is recorded. In the above circuit diagram the voltmeter is connected in parallel to the resistor and hence the potential difference or the voltage drop across it is measured in this case.
Rheostat:This is known as a variable resistor which is also a resistor and which also has the same function as that of the resistor but in this case the resistor value can be chosen as per the circuit's needs so as to correspondingly vary the amount of current flowing through the circuit. The resistance can be chosen in accordance to the user’s choice.
In order to determine the direction of flow of current we first need to look at the manner in which the cell is connected. Current is defined as the flow of charge or electrons and this flow of electrons occurs from the negative terminal of the cell, that is, the electrons are produced from the negative terminal of the cell and get collected at the positive terminal of the cell. The direction of conventional current is always said to be in the direction opposite to the direction of flow of electrons and hence the direction of current is from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the cell. This can be seen in the diagram below where the arrows indicate the current direction:

Note: In the given diagram the circuit element labelled as D can also be identified to be a load that is applied to the circuit which controls the flow of current which is also correct.A load is a device that can not only refer to a resistance but also refers to a collection or a combination of electrical components which tend to hinder the flow of current.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




