
In the equation $P{V^\gamma } = {\text{constant}}$, the value of $\gamma $ is unity. Then the process is
A) Isothermal
B) Adiabatic
C) Isobaric
D) Irreversible.
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint:Heat absorbed or given out by the system even though at every stage the gas has the same temperature as that of the surrounding reservoir. This is possible because of the infinitesimal difference in temperature between the system and the surrounding.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that, $P{V^\gamma } = {\text{constant}}$
The value of$\gamma $ is unity that is, $\gamma = 1$
Then above equation becomes, $PV = {\text{constant}}$
The ideal gas equation for $n$moles of gas is, $PV = nRT$
As the temperature remains constant, along with mass of gas in this process.
That is $n$, $R$, $T$ are constants.
Then equation becomes,
$PV = {\text{constant}}$
$\therefore {P_1}{V_1} = {P_2}{V_2}$
This is the equation of the isothermal process.
A process in which a system undergoes physical changes in such a way that the temperature remains constant by the exchange of heat energy with the surrounding is known as isothermal process.
Additional information:
Consider a certain mass of a gas in a conducting cylinder fitted with a frictionless movable piston. The following conditions must be fulfilled to keep the temperature (for an isothermal process) constant.
-The cylinder and gas should be good conductors of heat.
-The cylinder should be in good thermal contact with surroundings.
-The surrounding should allow heat exchanges with the cylinder gas system keeping the temperature of gas essentially constant.
-The process should be quasi static.
-The process must be slow allowing sufficient time for the system to compensate for the changes, if any.
$P - V$ graph of an isothermal process is a rectangular hyperbola. This graph is called isotherm.
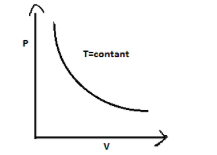
therefore Correct option is (A).
Note:In an isothermal process the internal energy remains constant.
For an ideal gas internal energy depends only on temperature. Thus, there is no change in the internal energy of an ideal gas in an isothermal process.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that, $P{V^\gamma } = {\text{constant}}$
The value of$\gamma $ is unity that is, $\gamma = 1$
Then above equation becomes, $PV = {\text{constant}}$
The ideal gas equation for $n$moles of gas is, $PV = nRT$
As the temperature remains constant, along with mass of gas in this process.
That is $n$, $R$, $T$ are constants.
Then equation becomes,
$PV = {\text{constant}}$
$\therefore {P_1}{V_1} = {P_2}{V_2}$
This is the equation of the isothermal process.
A process in which a system undergoes physical changes in such a way that the temperature remains constant by the exchange of heat energy with the surrounding is known as isothermal process.
Additional information:
Consider a certain mass of a gas in a conducting cylinder fitted with a frictionless movable piston. The following conditions must be fulfilled to keep the temperature (for an isothermal process) constant.
-The cylinder and gas should be good conductors of heat.
-The cylinder should be in good thermal contact with surroundings.
-The surrounding should allow heat exchanges with the cylinder gas system keeping the temperature of gas essentially constant.
-The process should be quasi static.
-The process must be slow allowing sufficient time for the system to compensate for the changes, if any.
$P - V$ graph of an isothermal process is a rectangular hyperbola. This graph is called isotherm.

therefore Correct option is (A).
Note:In an isothermal process the internal energy remains constant.
For an ideal gas internal energy depends only on temperature. Thus, there is no change in the internal energy of an ideal gas in an isothermal process.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




