
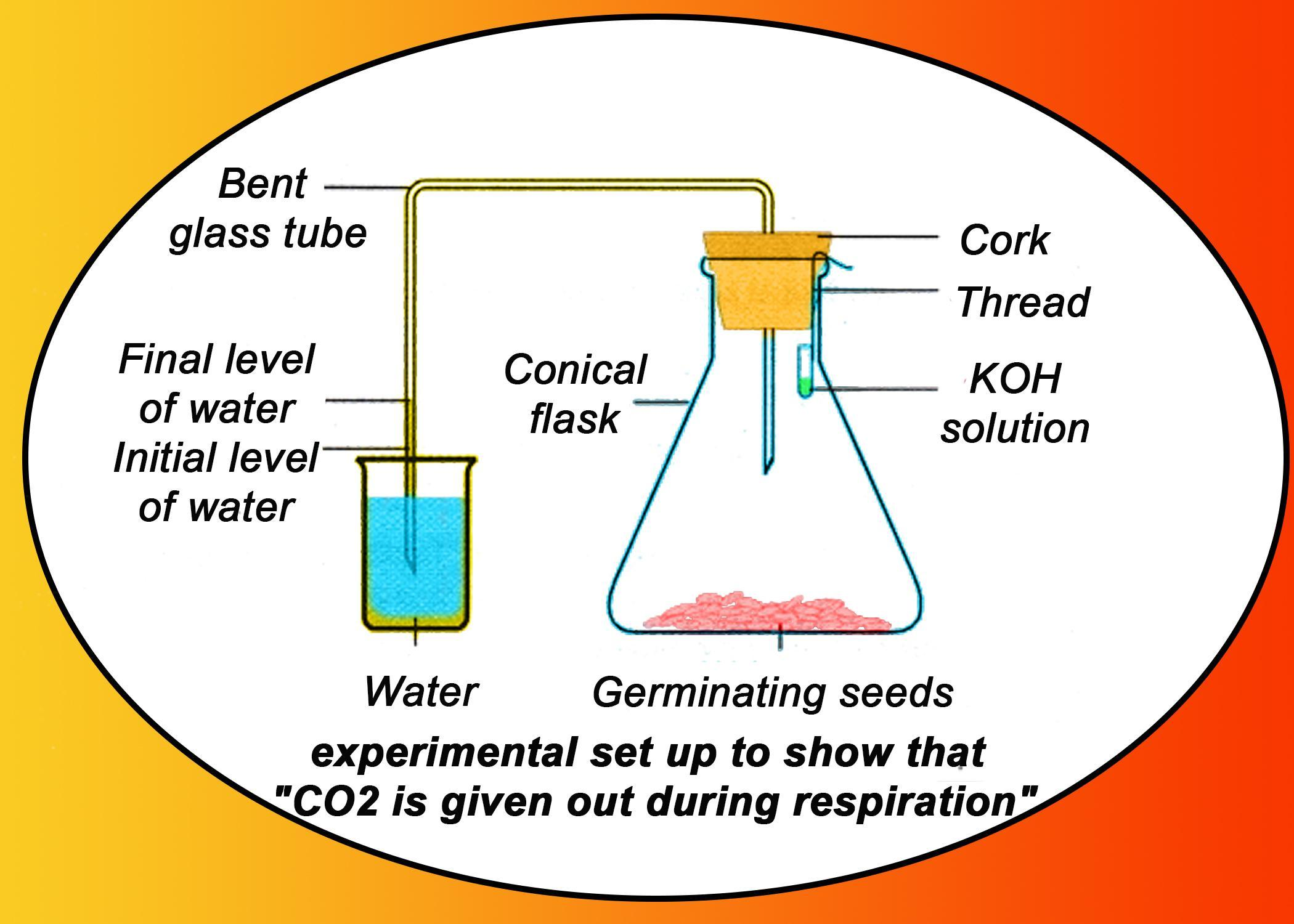
In the experimental set up to show that "Carbon dioxide is given out during respiration", name the substance taken in the small test tube kept in the conical flask. State its function and the consequence of its use.
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: The substance that is taken in the small test tube is an inorganic compound and is commonly called as caustic potash. It is a colorless solid and comes under the category of a strong base. Its molar mass is 56.1056 g/mol.
Complete answer:
In the experiment in which Carbon dioxide is given out during respiration, KOH solution or pallets are taken in a tube and placed within the conical flask, KOH absorbs the carbon dioxide and it prevents the carbon dioxide from being utilized by the plant for the method of photosynthesis.
Additional Information: Photosynthesis- The method by which green plants and certain other organisms transform light energy into energy. During photosynthesis, light energy is captured and is further used by the plant to convert water, Carbon dioxide, and minerals into oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds. As you know that the photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the method always starts when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centers that contain green chlorophyll pigments.
In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they're embedded within the cell wall. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is employed to take out electrons from suitable substances, like water, producing oxygen gas. The hydrogen which was available as was removed by the splitting of water is employed within the creation of two further compounds, these compounds are reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and ATP (ATP), the "energy currency" of cells.
Note: Plants use carbon dioxide from the surrounding environment to produce sugars such as glucose and oxygen, which can later be utilized as a source of energy by the plants.
Complete answer:
In the experiment in which Carbon dioxide is given out during respiration, KOH solution or pallets are taken in a tube and placed within the conical flask, KOH absorbs the carbon dioxide and it prevents the carbon dioxide from being utilized by the plant for the method of photosynthesis.
Additional Information: Photosynthesis- The method by which green plants and certain other organisms transform light energy into energy. During photosynthesis, light energy is captured and is further used by the plant to convert water, Carbon dioxide, and minerals into oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds. As you know that the photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the method always starts when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centers that contain green chlorophyll pigments.

In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they're embedded within the cell wall. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is employed to take out electrons from suitable substances, like water, producing oxygen gas. The hydrogen which was available as was removed by the splitting of water is employed within the creation of two further compounds, these compounds are reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and ATP (ATP), the "energy currency" of cells.
Note: Plants use carbon dioxide from the surrounding environment to produce sugars such as glucose and oxygen, which can later be utilized as a source of energy by the plants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




