
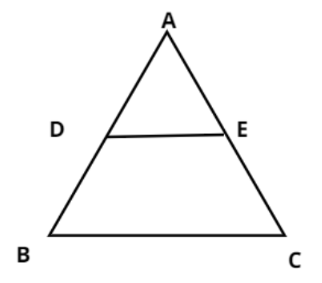
In the figure D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively of a $\vartriangle ABC$ such that ${\text{DE||BC}}$ and divides $\vartriangle ABC$ into two parts, equal in area, find $\dfrac{{BD}}{{AB}}$.

Answer
620.7k+ views
Hint: In this problem we have been with a triangle ABC such that the line segment DE inside this triangle is parallel to BC. So BCED forms a trapezium now and it is given that this DE divides this triangle into two equal areas. Thus use the respective formula for area of triangle and area of trapezium along with triangle congruence postulates to reach the answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given that the area of triangle ADE is equal to the area of trapezium BCED.
$ \Rightarrow {\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ADE} \right) = {\text{Area}}\left( {{\text{trapezium BCED}}} \right)$
Now add area of triangle ADE both sides we have
$ \Rightarrow {\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ADE} \right) + {\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ADE} \right) = {\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ADE} \right) + {\text{Area}}\left( {{\text{trapezium BCED}}} \right)$
In above equation R.H.S part is the total area of triangle ABC
\[ \Rightarrow 2{\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ADE} \right) = {\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ABC} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ADE} \right)}}{{{\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ABC} \right)}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\] …………………. (1)
Now in triangle ADE and in triangle ABC we have
$\angle ADE = \angle B$ [$\because DE||BC{\text{ & }}\angle ADE = \angle B$ (Corresponding angles)]
And, $\angle A = \angle A$ [common angle]
Therefore \[{\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ADE} \right) \approx {\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ABC} \right)\] (similar triangles)
Therefore according the property of similar triangles
$\dfrac{{AD}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{{AE}}{{AC}} = \dfrac{{DE}}{{BC}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ADE} \right)}}{{{\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ABC} \right)}}} $
Now from equation (1) we have
$\dfrac{{AD}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{{AE}}{{AC}} = \dfrac{{DE}}{{BC}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{1}{2}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
$ \Rightarrow AD = \dfrac{{AB}}{{\sqrt 2 }}$……………………………. (2)
Now from figure we can say that
$BD = AB - AD$
Now from equation (2)
$BD = AB - AD = AB - \dfrac{{AB}}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{BD}}{{AB}} = 1 - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$.
So, this is the required ratio of BD to AB.
Thus, this is the required answer.
Note: Whenever we face such types of geometry questions the key point is to understand the diagrammatic representation of the data provided in the question. Having a good understanding of various triangle congruence postulates like ASA, AAA, SSS along with formulas of various sections like triangle and trapezium always helps in getting on the right track to reach the answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given that the area of triangle ADE is equal to the area of trapezium BCED.
$ \Rightarrow {\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ADE} \right) = {\text{Area}}\left( {{\text{trapezium BCED}}} \right)$
Now add area of triangle ADE both sides we have
$ \Rightarrow {\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ADE} \right) + {\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ADE} \right) = {\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ADE} \right) + {\text{Area}}\left( {{\text{trapezium BCED}}} \right)$
In above equation R.H.S part is the total area of triangle ABC
\[ \Rightarrow 2{\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ADE} \right) = {\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ABC} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ADE} \right)}}{{{\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ABC} \right)}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\] …………………. (1)
Now in triangle ADE and in triangle ABC we have
$\angle ADE = \angle B$ [$\because DE||BC{\text{ & }}\angle ADE = \angle B$ (Corresponding angles)]
And, $\angle A = \angle A$ [common angle]
Therefore \[{\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ADE} \right) \approx {\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ABC} \right)\] (similar triangles)
Therefore according the property of similar triangles
$\dfrac{{AD}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{{AE}}{{AC}} = \dfrac{{DE}}{{BC}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ADE} \right)}}{{{\text{Area}}\left( {\Delta ABC} \right)}}} $
Now from equation (1) we have
$\dfrac{{AD}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{{AE}}{{AC}} = \dfrac{{DE}}{{BC}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{1}{2}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
$ \Rightarrow AD = \dfrac{{AB}}{{\sqrt 2 }}$……………………………. (2)
Now from figure we can say that
$BD = AB - AD$
Now from equation (2)
$BD = AB - AD = AB - \dfrac{{AB}}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{BD}}{{AB}} = 1 - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$.
So, this is the required ratio of BD to AB.
Thus, this is the required answer.
Note: Whenever we face such types of geometry questions the key point is to understand the diagrammatic representation of the data provided in the question. Having a good understanding of various triangle congruence postulates like ASA, AAA, SSS along with formulas of various sections like triangle and trapezium always helps in getting on the right track to reach the answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




