
In the figure, the parts marked A, B, and C are sequentially.
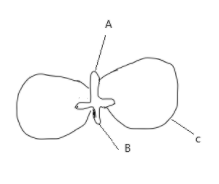
A) Plumule, Radicle, and Cotyledon
B) Radicle, Plumule, Cotyledon
C) Plumule, Cotyledon and Radicle
D) Radicle, Cotyledon and Plumule

Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint:The arrangement of vascular tissue and presence of a number of cotyledons is involved in the classification of plants into monocot and dicot. Monocot means presence of single cotyledons and more than one cotyledon is dicot.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, we have to know details about dicotyledonous plants. A cotyledon within a seed is the embryo part. Often the cotyledons may become the seedlings first leaves when the germination of seed takes place or during the beginning of its growth. Botanists use as classification means the number of cotyledons found in the seed. Monocots are the seeds that have cotyledons and the dicots have two cotyledons. Prior to the germination process the cotyledons formed during embryogenesis with the shoot and the roots of the plants. The cotyledons in the dicot plants have photosynthetic functions like leaves. It is the first part that emerged from the ground. Some of the cotyledons last for some days after they come out of the soil and some take a long period of time to grow. The plants like guava, sunflower, papaya, rose, tamarinds, mango, radish, castor, etc are a dicot plant that means they bear two cotyledons.
Now, the dicot seeds are covered with a seed coat. The seed coat consists of two layers; the outer testa and inner tegmen. Hilum is a scar found in the seed coat that involves the developing seeds attached to the fruit. There is a small pore found above the hilum that is termed as micropyle. The cotyledons are fleshy and they serve as the reservoir of food for the embryo. At last, the two ends of the embryo axis are the radical and the plumules. Therefore, in the given diagram, A is labeled as plumule, B as radical, and C as the cotyledon.
Thus, the correct option is ‘A’ Plumule, Radicle, and Cotyledon.
Note:In monocot seed the embryos possess a large cotyledon termed as scutellum like in rice, corn, and wheat. The scutellum is shield shaped and found laterally towards the axis of the embryo. It comprises a shoot tip and plumules that are covered by a sheath termed as coleoptile.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, we have to know details about dicotyledonous plants. A cotyledon within a seed is the embryo part. Often the cotyledons may become the seedlings first leaves when the germination of seed takes place or during the beginning of its growth. Botanists use as classification means the number of cotyledons found in the seed. Monocots are the seeds that have cotyledons and the dicots have two cotyledons. Prior to the germination process the cotyledons formed during embryogenesis with the shoot and the roots of the plants. The cotyledons in the dicot plants have photosynthetic functions like leaves. It is the first part that emerged from the ground. Some of the cotyledons last for some days after they come out of the soil and some take a long period of time to grow. The plants like guava, sunflower, papaya, rose, tamarinds, mango, radish, castor, etc are a dicot plant that means they bear two cotyledons.
Now, the dicot seeds are covered with a seed coat. The seed coat consists of two layers; the outer testa and inner tegmen. Hilum is a scar found in the seed coat that involves the developing seeds attached to the fruit. There is a small pore found above the hilum that is termed as micropyle. The cotyledons are fleshy and they serve as the reservoir of food for the embryo. At last, the two ends of the embryo axis are the radical and the plumules. Therefore, in the given diagram, A is labeled as plumule, B as radical, and C as the cotyledon.
Thus, the correct option is ‘A’ Plumule, Radicle, and Cotyledon.
Note:In monocot seed the embryos possess a large cotyledon termed as scutellum like in rice, corn, and wheat. The scutellum is shield shaped and found laterally towards the axis of the embryo. It comprises a shoot tip and plumules that are covered by a sheath termed as coleoptile.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




