
: In the following common emitter configuration an n-p-n transistor with current gain \[\beta = 100\] is used. The output voltage of the amplifier will be:
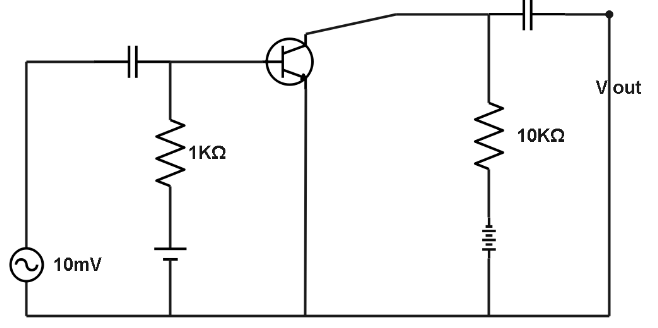
A. $10\,mV$
B. $0.1\,V$
C. $1.0\,V$
D. $10\,V$

Answer
497.1k+ views
Hint:The configuration in which the emitter is connected between collector and base is called a C-E (common emitter) configuration. Here we will apply the formula of current which is defined as the ratio of collector current to base current and then putting into the equation we will get the required answer.
Formula used:
$\beta = \dfrac{{iC}}{{iB}} = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{{V_i}}}$
Where, $\beta $ is the current gain, $iC$ is the current flowing into the collector terminal, $iB$ is the current flowing into the base terminal, ${V_0}$ is the output voltage and ${V_i}$ is the input voltage.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that, voltage gain is the product of current gain and resistance gain i.e.,
${\text{Voltage gain}} = \beta \times \dfrac{{{R_o}}}{{{R_i}}}$
According to the question,
$\beta = 100$
$\Rightarrow {R_o} = 10$
$\Rightarrow {R_i} = 1$
Now putting the value in above formula,
${\text{Voltage gain}} = 100 \times \dfrac{{10}}{1}$
And we know that voltage gain is $\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{{V_i}}}$ .
So,
$\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{{V_i}}} = 100 \times \dfrac{{10}}{1} \\
\Rightarrow {V_0} = 1000 \times 10 \times {10^{ - 3}} $
As $(10mV = 10 \times {10^{ - 3}}V)$
$\therefore {V_0} = 10V$
So, the output voltage of the amplifier is $10\,V$.
Hence, the correct option is D.
Note:NPN transistors most preferred over PNP transistors due to the following reasons:
Carrier Mobility:The majority carriers in NPN transistors are electrons unlike in PNP transistors where the majority charge carriers are holes. Electrons move far more easily than holes within the crystal lattice. As a result, they have higher mobility and operate faster providing a much better level of performance.
Negative Grounding: Over the years, a negative ground has become standard and the polarity of NPN transistors means that the basic transistor configurations operate with a negative ground.
Formula used:
$\beta = \dfrac{{iC}}{{iB}} = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{{V_i}}}$
Where, $\beta $ is the current gain, $iC$ is the current flowing into the collector terminal, $iB$ is the current flowing into the base terminal, ${V_0}$ is the output voltage and ${V_i}$ is the input voltage.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that, voltage gain is the product of current gain and resistance gain i.e.,
${\text{Voltage gain}} = \beta \times \dfrac{{{R_o}}}{{{R_i}}}$
According to the question,
$\beta = 100$
$\Rightarrow {R_o} = 10$
$\Rightarrow {R_i} = 1$
Now putting the value in above formula,
${\text{Voltage gain}} = 100 \times \dfrac{{10}}{1}$
And we know that voltage gain is $\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{{V_i}}}$ .
So,
$\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{{V_i}}} = 100 \times \dfrac{{10}}{1} \\
\Rightarrow {V_0} = 1000 \times 10 \times {10^{ - 3}} $
As $(10mV = 10 \times {10^{ - 3}}V)$
$\therefore {V_0} = 10V$
So, the output voltage of the amplifier is $10\,V$.
Hence, the correct option is D.
Note:NPN transistors most preferred over PNP transistors due to the following reasons:
Carrier Mobility:The majority carriers in NPN transistors are electrons unlike in PNP transistors where the majority charge carriers are holes. Electrons move far more easily than holes within the crystal lattice. As a result, they have higher mobility and operate faster providing a much better level of performance.
Negative Grounding: Over the years, a negative ground has become standard and the polarity of NPN transistors means that the basic transistor configurations operate with a negative ground.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




