
In the following reaction \[{\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + HCl }} \to {\text{ MnC}}{{\text{l}}_{{\text{2
}}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O + C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\]
Find
-Substance reduced
-Substance oxidized
-Oxidizing agent
-Reducing agent
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: Assign the oxidation number to all atoms. Oxidation is the loss of electrons while reduction is the gain of electrons. The substance which helps other species to get reduced and itself get oxidized is known as a reducing agent. While substance that helps other species to get oxidised and itself get reduced is known as oxidising agent
Complete Step by step answer: he redox reaction given to us is:
\[{\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + HCl }} \to {\text{ MnC}}{{\text{l}}_{{\text{2 }}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O + C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\]
Using the oxidation number rules we can calculate the oxidation number of all atoms in the given reaction as follows:
The oxidation number of oxygen is always -2 except in peroxide. In peroxide oxidation number of oxygen is -1.
Using this rule we can determine the oxidation number of \[{\text{Mn}}\] in [{\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ }}\].
Oxidation number of \[{\text{O}}\] =-2
So, Oxidation number of \[{\text{Mn}}\] in \[{\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ }}\]= +4
Oxidation number of hydrogen is always +1 except in metal hydride it is -1.
Oxidation number of chlorine is -1 in most of the compounds.
Oxidation number of \[{\text{H}}\] in \[{\text{HCl }}\] = +1
So, oxidation number of \[{\text{Cl}}\] in \[{\text{HCl }}\] = -1
As oxidation number of \[{\text{Cl}}\]is -1 so oxidation number of \[{\text{Mn}}\] in \[{\text{MnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] is +2.
Oxidation number of \[{\text{H}}\] in \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\] is +1 and oxidation number of \[{\text{O }}\]is -2.
Oxidation number of an element is zero so oxidation number of \[{\text{Cl}}\] in \[{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] is 0.
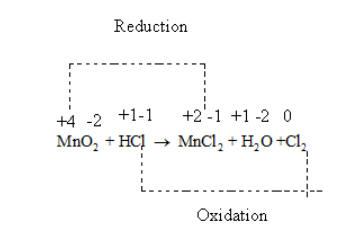
Thus, in the given reaction \[{\text{Mn}}\] is getting reduced from +4 to +2 and \[{\text{Cl}}\] is getting oxidised from -1 to 0.
So,
The substance reduce is\[{\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]
The substance oxidised is\[{\text{HCl }}\].
The substance that is reduced acts as an oxidising agent while a substance that is oxidised acts as a reducing agent.
Hence, Oxidising agent = \[{\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]
Reducing agent = \[{\text{HCl }}\]
Note: In the given reaction\[{\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] is getting reduced and oxidised \[{\text{HCl }}\] so act as oxidising agent. While \[{\text{HCl }}\]is getting oxidised and reduced \[{\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]so act as reducing agent. To determine the species getting oxidised and reduced it is important to assign the oxidation number correctly.
Complete Step by step answer: he redox reaction given to us is:
\[{\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + HCl }} \to {\text{ MnC}}{{\text{l}}_{{\text{2 }}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O + C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\]
Using the oxidation number rules we can calculate the oxidation number of all atoms in the given reaction as follows:
The oxidation number of oxygen is always -2 except in peroxide. In peroxide oxidation number of oxygen is -1.
Using this rule we can determine the oxidation number of \[{\text{Mn}}\] in [{\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ }}\].
Oxidation number of \[{\text{O}}\] =-2
So, Oxidation number of \[{\text{Mn}}\] in \[{\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ }}\]= +4
Oxidation number of hydrogen is always +1 except in metal hydride it is -1.
Oxidation number of chlorine is -1 in most of the compounds.
Oxidation number of \[{\text{H}}\] in \[{\text{HCl }}\] = +1
So, oxidation number of \[{\text{Cl}}\] in \[{\text{HCl }}\] = -1
As oxidation number of \[{\text{Cl}}\]is -1 so oxidation number of \[{\text{Mn}}\] in \[{\text{MnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] is +2.
Oxidation number of \[{\text{H}}\] in \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\] is +1 and oxidation number of \[{\text{O }}\]is -2.
Oxidation number of an element is zero so oxidation number of \[{\text{Cl}}\] in \[{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] is 0.

Thus, in the given reaction \[{\text{Mn}}\] is getting reduced from +4 to +2 and \[{\text{Cl}}\] is getting oxidised from -1 to 0.
So,
The substance reduce is\[{\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]
The substance oxidised is\[{\text{HCl }}\].
The substance that is reduced acts as an oxidising agent while a substance that is oxidised acts as a reducing agent.
Hence, Oxidising agent = \[{\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]
Reducing agent = \[{\text{HCl }}\]
Note: In the given reaction\[{\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] is getting reduced and oxidised \[{\text{HCl }}\] so act as oxidising agent. While \[{\text{HCl }}\]is getting oxidised and reduced \[{\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]so act as reducing agent. To determine the species getting oxidised and reduced it is important to assign the oxidation number correctly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




