
In the following reactions, the major products (A) and (C) are respectively
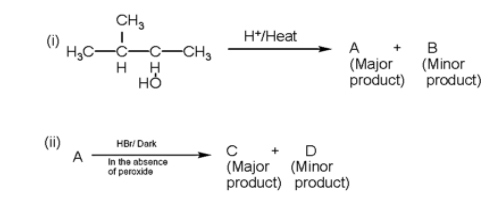

Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: The stability of the carbocation is important in predicting the stability of the molecule. The stability order of the carbocation is tertiary carbocation ˃ secondary carbocation ˃ primary carbocation.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
- In the given question, two reactions are given in which we have to find the major product of the reaction.
- Firstly, we will write the first reaction in which firstly the hydroxyl ion will be released due to bond breakage due to heat and a secondary carbocation will be formed.
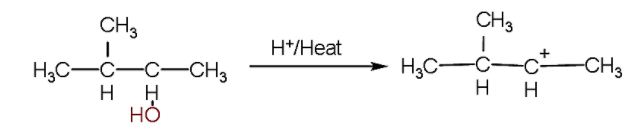
- Now, as we know, secondary carbocation is less stable than the tertiary carbocation because more alkyl groups are attached with the tertiary carbocation which tends to increase the electron density at the carbocation.
- Now, we will rearrange the position of carbocation by the method of 1,2 hydride shift in which the position of hydrogen atom changes as shown below:
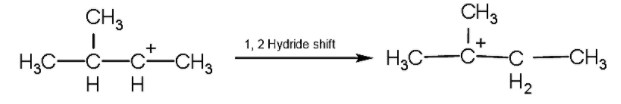
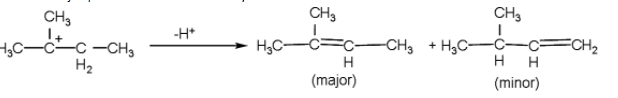
- Now, after the formation of the tertiary carbocation, the hydrogen atom will be released from the adjacent carbon due to which the pi- the bond will be formed.
-And the major product formed is 2-methyl but -2-ene.
-Now, in the second reaction, the compound A is the 2-methyl but -2-ene which undergoes anti- Markovnikov reaction.
-In Anti - Markovnikov reaction, the negatively charged element goes to that carbon atom which has the maximum number of the alkyl group.
-So, here firstly the pi - the bond will break and the addition of the bromine will take place through Anti - Markovnikov rule.
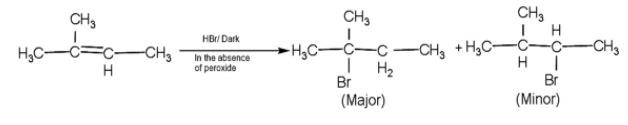
- Here, the bromine attached to the tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary.
Therefore, the major product A and C are 2-methyl but -2-ene and 2-methyl 2-Bromobutane.
Note: The Anti - markovnikov rule is applicable only in the presence of hydrogen bromide and peroxide. If peroxide is absent in the reaction the negatively charged group attaches through electrophilic addition mechanism.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
- In the given question, two reactions are given in which we have to find the major product of the reaction.
- Firstly, we will write the first reaction in which firstly the hydroxyl ion will be released due to bond breakage due to heat and a secondary carbocation will be formed.

- Now, as we know, secondary carbocation is less stable than the tertiary carbocation because more alkyl groups are attached with the tertiary carbocation which tends to increase the electron density at the carbocation.
- Now, we will rearrange the position of carbocation by the method of 1,2 hydride shift in which the position of hydrogen atom changes as shown below:

- Now, after the formation of the tertiary carbocation, the hydrogen atom will be released from the adjacent carbon due to which the pi- the bond will be formed.
-And the major product formed is 2-methyl but -2-ene.

-Now, in the second reaction, the compound A is the 2-methyl but -2-ene which undergoes anti- Markovnikov reaction.
-In Anti - Markovnikov reaction, the negatively charged element goes to that carbon atom which has the maximum number of the alkyl group.
-So, here firstly the pi - the bond will break and the addition of the bromine will take place through Anti - Markovnikov rule.

- Here, the bromine attached to the tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary.
Therefore, the major product A and C are 2-methyl but -2-ene and 2-methyl 2-Bromobutane.
Note: The Anti - markovnikov rule is applicable only in the presence of hydrogen bromide and peroxide. If peroxide is absent in the reaction the negatively charged group attaches through electrophilic addition mechanism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




