
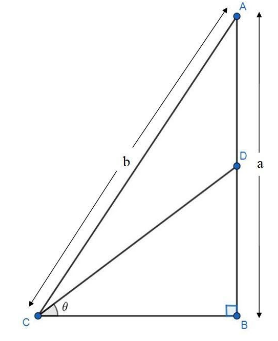
In the given figure, $AD = DB$ and $\angle B$ is a right angle. Determine:
${\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta $

Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint: Use the given data $AD = DB$ to find the length of $DB$ and apply the Pythagoras theorem in the triangle ABC to find $BC$. Use the length DB and BC to find the hypotenuse of the triangle BCD using Pythagoras theorem and then find the trigonometric ratios to approach the desired result.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have given that $AD = DB$ and $\angle B$ is a right angle.
We can use the given data,
$AB = a$
$AB$ can be break in two parts as $AD$ and $DB$, so it can be express as:
$AD + DB = a$
It is also given that $AD = DB$, so we have from the above equation:
$AD + AD = a$
$2AD = a$
$AD = \dfrac{a}{2}$
Thus, we have the conclusion that:
$AD = DB = \dfrac{a}{2}$.
Now, apply the Pythagoras theorem in the triangle $ABC$, then we have
$A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
Substitute the value of $AB = a$ and $AC = b$ into the equation, then we obtain
${b^2} = {a^2} + B{C^2}$
Solve the equation for the value of $BC$,
$ \Rightarrow B{C^2} = {b^2} - {a^2}$
$ \Rightarrow BC = \sqrt {{b^2} - {a^2}} $
Now, we have in the $\Delta BCD$:
Base $\left( {BC} \right) = \sqrt {{b^2} - {a^2}} $ and Perpendicular$\left( {BD} \right) = \dfrac{a}{2}$
Now, apply the Pythagoras theorem in $\Delta BCD$, so we have
$B{C^2} + B{D^2} = C{D^2}$
Substitute the value of $BC$ and $BD$ into the equation:
${\left( {\sqrt {{b^2} - {a^2}} } \right)^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{a}{2}} \right)^2} = C{D^2}$
$ \Rightarrow C{D^2} = {b^2} - {a^2} + \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{4}$
Simplify the equation:
$ \Rightarrow C{D^2} = \dfrac{{4{b^2} - 4{a^2} + {a^2}}}{4}$
\[ \Rightarrow C{D^2} = \dfrac{{4{b^2} - 3{a^2}}}{4}\]
\[ \Rightarrow CD = \dfrac{{\sqrt {4{b^2} - 3{a^2}} }}{2}\]
Now, we have in the $\Delta BCD$:
Base $\left( {BC} \right) = \sqrt {{b^2} - {a^2}} $ , Perpendicular $\left( {BD} \right) = \dfrac{a}{2}$ and the hypotenuse \[\left( {CD} \right) = \dfrac{{\sqrt {4{b^2} - 3{a^2}} }}{2}\]
Now, use the trigonometric ratio in $\Delta BCD$,
$\sin \theta = \dfrac{{BD}}{{CD}}$
Substitute the values of $BD$ and $CD$, so we have
$\sin \theta = \dfrac{{\dfrac{a}{2}}}{{\dfrac{{\sqrt {4{b^2} - 3{a^2}} }}{2}}}$
$\sin \theta = \dfrac{a}{{\sqrt {4{b^2} - 3{a^2}} }}$
Using the trigonometric ratio:
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{{BC}}{{CD}}$
Substitute the values of $BC$ and $CD$, so we have
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{b^2} - {a^2}} }}{{\dfrac{{\sqrt {4{b^2} - 3{a^2}} }}{2}}}$
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{{2\sqrt {{b^2} - {a^2}} }}{{\sqrt {4{b^2} - 3{a^2}} }}$
We have to find the value of ${\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta $, so substitute the value of $\sin \theta $ and $\cos \theta $ into the equation:
\[{\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = {\left( {\dfrac{a}{{\sqrt {4{b^2} - 3{a^2}} }}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{{2\sqrt {{b^2} - {a^2}} }}{{\sqrt {4{b^2} - 3{a^2}} }}} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{{4{b^2} - 3{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{4\left( {{b^2} - {a^2}} \right)}}{{4{b^2} - 3{a^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = \dfrac{{{a^2} + 4{b^2} - 4{a^2}}}{{4{b^2} - 3{a^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = \dfrac{{4{b^2} - 3{a^2}}}{{4{b^2} - 3{a^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1\]
Therefore, the value of \[{\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta \] is $1$.
Note: The Pythagoras theorem says that when one of the angles of the triangle is a right angle then the square of the hypotenuse of the triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the perpendicular and base of the triangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have given that $AD = DB$ and $\angle B$ is a right angle.
We can use the given data,
$AB = a$
$AB$ can be break in two parts as $AD$ and $DB$, so it can be express as:
$AD + DB = a$
It is also given that $AD = DB$, so we have from the above equation:
$AD + AD = a$
$2AD = a$
$AD = \dfrac{a}{2}$
Thus, we have the conclusion that:
$AD = DB = \dfrac{a}{2}$.
Now, apply the Pythagoras theorem in the triangle $ABC$, then we have
$A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
Substitute the value of $AB = a$ and $AC = b$ into the equation, then we obtain
${b^2} = {a^2} + B{C^2}$
Solve the equation for the value of $BC$,
$ \Rightarrow B{C^2} = {b^2} - {a^2}$
$ \Rightarrow BC = \sqrt {{b^2} - {a^2}} $
Now, we have in the $\Delta BCD$:
Base $\left( {BC} \right) = \sqrt {{b^2} - {a^2}} $ and Perpendicular$\left( {BD} \right) = \dfrac{a}{2}$
Now, apply the Pythagoras theorem in $\Delta BCD$, so we have
$B{C^2} + B{D^2} = C{D^2}$
Substitute the value of $BC$ and $BD$ into the equation:
${\left( {\sqrt {{b^2} - {a^2}} } \right)^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{a}{2}} \right)^2} = C{D^2}$
$ \Rightarrow C{D^2} = {b^2} - {a^2} + \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{4}$
Simplify the equation:
$ \Rightarrow C{D^2} = \dfrac{{4{b^2} - 4{a^2} + {a^2}}}{4}$
\[ \Rightarrow C{D^2} = \dfrac{{4{b^2} - 3{a^2}}}{4}\]
\[ \Rightarrow CD = \dfrac{{\sqrt {4{b^2} - 3{a^2}} }}{2}\]
Now, we have in the $\Delta BCD$:
Base $\left( {BC} \right) = \sqrt {{b^2} - {a^2}} $ , Perpendicular $\left( {BD} \right) = \dfrac{a}{2}$ and the hypotenuse \[\left( {CD} \right) = \dfrac{{\sqrt {4{b^2} - 3{a^2}} }}{2}\]
Now, use the trigonometric ratio in $\Delta BCD$,
$\sin \theta = \dfrac{{BD}}{{CD}}$
Substitute the values of $BD$ and $CD$, so we have
$\sin \theta = \dfrac{{\dfrac{a}{2}}}{{\dfrac{{\sqrt {4{b^2} - 3{a^2}} }}{2}}}$
$\sin \theta = \dfrac{a}{{\sqrt {4{b^2} - 3{a^2}} }}$
Using the trigonometric ratio:
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{{BC}}{{CD}}$
Substitute the values of $BC$ and $CD$, so we have
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{b^2} - {a^2}} }}{{\dfrac{{\sqrt {4{b^2} - 3{a^2}} }}{2}}}$
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{{2\sqrt {{b^2} - {a^2}} }}{{\sqrt {4{b^2} - 3{a^2}} }}$
We have to find the value of ${\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta $, so substitute the value of $\sin \theta $ and $\cos \theta $ into the equation:
\[{\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = {\left( {\dfrac{a}{{\sqrt {4{b^2} - 3{a^2}} }}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{{2\sqrt {{b^2} - {a^2}} }}{{\sqrt {4{b^2} - 3{a^2}} }}} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{{4{b^2} - 3{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{4\left( {{b^2} - {a^2}} \right)}}{{4{b^2} - 3{a^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = \dfrac{{{a^2} + 4{b^2} - 4{a^2}}}{{4{b^2} - 3{a^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = \dfrac{{4{b^2} - 3{a^2}}}{{4{b^2} - 3{a^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1\]
Therefore, the value of \[{\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta \] is $1$.
Note: The Pythagoras theorem says that when one of the angles of the triangle is a right angle then the square of the hypotenuse of the triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the perpendicular and base of the triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




