
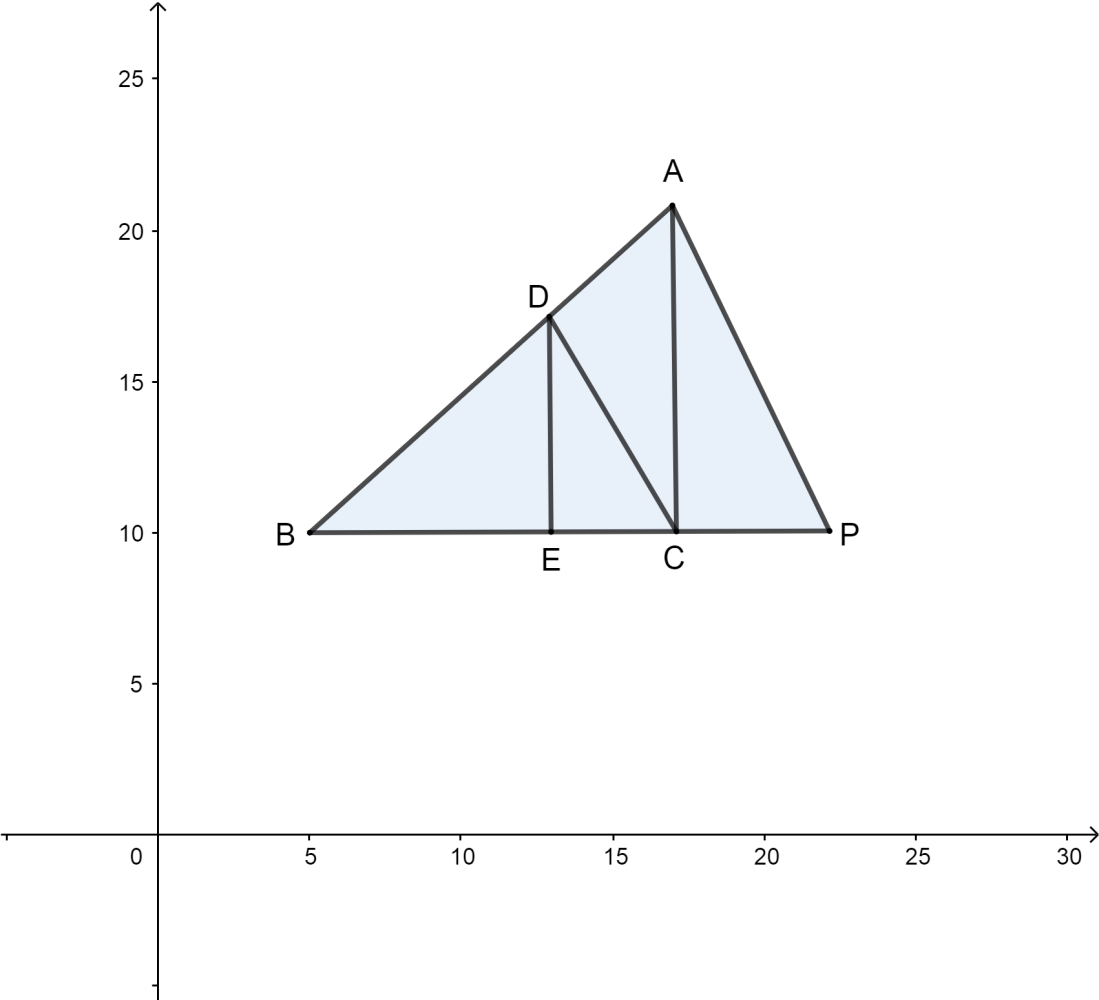
In the given figure $DE\parallel AC$ and $DC\parallel AP$then which of the following is true?
A. $BE\left( AD+CP \right)=B{{E}^{2}}$
B. $BE\times CP=EC\times BC$
C. $BC\times CP=EC\times BC$

Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: We will first write the basic proportionality theorem then we choose $\Delta BAC$ and apply the theorem on this triangle and find the equation of proportion and then we will again apply the theorem on $\Delta BAP$ and find another equation of proportion. Finally, we will compare this equation to get our answer.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, as we see that it is given that $DE\parallel AC$ and $DC\parallel AP$:
Now we know that according to the Basic Proportionality theorem that if a line is parallel to a side of a triangle that intersects the other sides into two distinct points, then the line divides those sides in proportion.
So if we see that in $\Delta BAC$ , $DE\parallel AC$ where $AC$ is the side of the triangle and $DE$ is parallel to it so according to the above theorem it will intersect the other two sides that are $BA\text{ and }BC$ and divide them in proportion as follows:
$\dfrac{BE}{EC}=\dfrac{BD}{AD}\text{ }.............\text{Equation 1}\text{.}$
Similarly, we see that in $\Delta BAP$ , $DC\parallel AP$ where $AP$ is the side of the triangle and $DE$ is parallel to it so according to the basic proportionality theorem it will intersect the other two sides that are $BA\text{ and }BP$ and divide them in proportion as follows:
$\dfrac{BD}{DA}=\dfrac{BC}{CP}\text{ }.............\text{Equation 2}\text{.}$
Now both the equations have $\dfrac{BD}{AD}$ terms therefore we will equate them:
Hence from equation 1 and 2 we have: $\dfrac{BE}{EC}=\dfrac{BC}{CP}$
We will now cross multiply and we will get: $BE\times CP=BC\times EC$ .
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note:
The basic Proportionality theorem was introduced by a famous Greek Mathematician, Thales, therefore, it is also called Thales Theorem. Also, be aware that which triangle you choose as for this theorem to apply the line should be parallel to one of the sides of the triangle. As far as option $A$ is concerned, we have $BE\left( AD+CP \right)=B{{E}^{2}}$ when we rearrange it we will get: $\left( AD+CP \right)=\dfrac{B{{E}^{2}}}{BE}\Rightarrow \left( AD+CP \right)=BE$ , as we cannot deduce this from equation 1 and equation 2 this option will be rejected. Similarly, in option $C$, we have $BC\times CP=EC\times BC$ , we will cancel $BC$ from both sides and therefore, we will get: \[CP=EC\] , which is not true as seen from equation 1 and equation 2. Hence this option will be rejected as well.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, as we see that it is given that $DE\parallel AC$ and $DC\parallel AP$:
Now we know that according to the Basic Proportionality theorem that if a line is parallel to a side of a triangle that intersects the other sides into two distinct points, then the line divides those sides in proportion.
So if we see that in $\Delta BAC$ , $DE\parallel AC$ where $AC$ is the side of the triangle and $DE$ is parallel to it so according to the above theorem it will intersect the other two sides that are $BA\text{ and }BC$ and divide them in proportion as follows:
$\dfrac{BE}{EC}=\dfrac{BD}{AD}\text{ }.............\text{Equation 1}\text{.}$
Similarly, we see that in $\Delta BAP$ , $DC\parallel AP$ where $AP$ is the side of the triangle and $DE$ is parallel to it so according to the basic proportionality theorem it will intersect the other two sides that are $BA\text{ and }BP$ and divide them in proportion as follows:
$\dfrac{BD}{DA}=\dfrac{BC}{CP}\text{ }.............\text{Equation 2}\text{.}$
Now both the equations have $\dfrac{BD}{AD}$ terms therefore we will equate them:
Hence from equation 1 and 2 we have: $\dfrac{BE}{EC}=\dfrac{BC}{CP}$
We will now cross multiply and we will get: $BE\times CP=BC\times EC$ .
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note:
The basic Proportionality theorem was introduced by a famous Greek Mathematician, Thales, therefore, it is also called Thales Theorem. Also, be aware that which triangle you choose as for this theorem to apply the line should be parallel to one of the sides of the triangle. As far as option $A$ is concerned, we have $BE\left( AD+CP \right)=B{{E}^{2}}$ when we rearrange it we will get: $\left( AD+CP \right)=\dfrac{B{{E}^{2}}}{BE}\Rightarrow \left( AD+CP \right)=BE$ , as we cannot deduce this from equation 1 and equation 2 this option will be rejected. Similarly, in option $C$, we have $BC\times CP=EC\times BC$ , we will cancel $BC$ from both sides and therefore, we will get: \[CP=EC\] , which is not true as seen from equation 1 and equation 2. Hence this option will be rejected as well.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




