
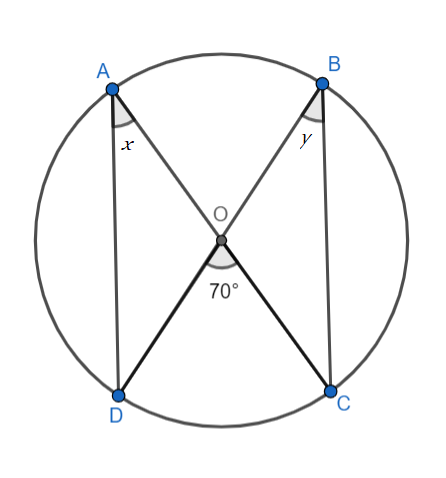
In the given figure, find the value of $x$ and $y$ where O is the centre of the circle.

Answer
614.4k+ views
Hint: In this question, we will use the central angle theorem on a given angle, that is ${{70}^{\circ }}$, to find the values of the angles $x$ and $y$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the given question we have a circle with centre $O$. Here four points $A,B,C$ and $D$ are marked on the circumference of the circle and are joined with the lines $AD,AC,BD,BC$.
Also given that, $\angle DOC={{70}^{\circ }}$
Now, in two-dimensional geometry, we have a central angle theorem. According to this theorem,
The central angle subtended by two points on a circumference of a circle is twice the inscribed angle subtended by these two points.
Now, In a given question, Point $D$ and $C$, which are points on the circle, subtended an angle $DOC$ on the centre of the circle.
Also, $\angle $$DAC$ is the angle formed by point $D$ and $C$ on the point $A$, which is on the circumference of the circle. Hence, $\angle DAC$ is inscribed angle subtended by point $D$ and $C$.
Therefore, by central angle theorem, $\angle DOC$ must be twice of the $\angle DAC$. That is,
$\angle DOC=2\angle DAC$
Dividing two from both sides of the equation, we get,
$\angle DAC=\dfrac{\angle DOC}{2}$
Putting value of $\angle DOC$ here, we get,
$\angle DAC=\dfrac{{{70}^{\circ }}}{2}={{35}^{\circ }}$
Similarly, $\angle DBC$ is the angle formed by point $D$ and $C$ on the point $B$, which is on the circumference of the circle. Hence, $\angle DBC$ is inscribed angle subtended by point $D$ and $C$.
Therefore, by central angle theorem, $\angle DOC$ must be twice of the $\angle DBC$. That is,
$\angle DOC=2\angle DBC$
Dividing two from both sides of the equation, we get,
$\angle DBC=\dfrac{\angle DOC}{2}$
Putting value of $\angle DOC$ here, we get,
$\angle DBC=\dfrac{{{70}^{\circ }}}{2}={{35}^{\circ }}$
Hence, the value of $x$ and $y$ are ${{35}^{\circ }}$.
Note: Alternative way to do this question is that you can use angle sum property as $\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta BOC$ are isosceles triangles.From the figure $\angle BOD$=${{180}^{\circ }}$ as it is linear pair So,then $\angle DOC$+$\angle COB$=${{180}^{\circ }}$ which gives $\angle COB$=${{110}^{\circ }}$ by angle sum property for $\Delta COB$ we get required answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the given question we have a circle with centre $O$. Here four points $A,B,C$ and $D$ are marked on the circumference of the circle and are joined with the lines $AD,AC,BD,BC$.
Also given that, $\angle DOC={{70}^{\circ }}$
Now, in two-dimensional geometry, we have a central angle theorem. According to this theorem,
The central angle subtended by two points on a circumference of a circle is twice the inscribed angle subtended by these two points.
Now, In a given question, Point $D$ and $C$, which are points on the circle, subtended an angle $DOC$ on the centre of the circle.
Also, $\angle $$DAC$ is the angle formed by point $D$ and $C$ on the point $A$, which is on the circumference of the circle. Hence, $\angle DAC$ is inscribed angle subtended by point $D$ and $C$.
Therefore, by central angle theorem, $\angle DOC$ must be twice of the $\angle DAC$. That is,
$\angle DOC=2\angle DAC$
Dividing two from both sides of the equation, we get,
$\angle DAC=\dfrac{\angle DOC}{2}$
Putting value of $\angle DOC$ here, we get,
$\angle DAC=\dfrac{{{70}^{\circ }}}{2}={{35}^{\circ }}$
Similarly, $\angle DBC$ is the angle formed by point $D$ and $C$ on the point $B$, which is on the circumference of the circle. Hence, $\angle DBC$ is inscribed angle subtended by point $D$ and $C$.
Therefore, by central angle theorem, $\angle DOC$ must be twice of the $\angle DBC$. That is,
$\angle DOC=2\angle DBC$
Dividing two from both sides of the equation, we get,
$\angle DBC=\dfrac{\angle DOC}{2}$
Putting value of $\angle DOC$ here, we get,
$\angle DBC=\dfrac{{{70}^{\circ }}}{2}={{35}^{\circ }}$
Hence, the value of $x$ and $y$ are ${{35}^{\circ }}$.
Note: Alternative way to do this question is that you can use angle sum property as $\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta BOC$ are isosceles triangles.From the figure $\angle BOD$=${{180}^{\circ }}$ as it is linear pair So,then $\angle DOC$+$\angle COB$=${{180}^{\circ }}$ which gives $\angle COB$=${{110}^{\circ }}$ by angle sum property for $\Delta COB$ we get required answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




