
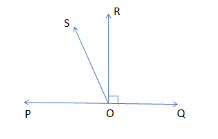
In the given figure, POQ is a line. Ray OR is perpendicular to the line PQ. OS is another ray lying between rays OP and OR. Prove that $ \angle ROS=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \angle QOS-\angle POS \right) $ .

Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: First, for this type of question, we will use various angles from the figure to prove the equation mentioned in the question. Then, we also know that the angle formed on the straight line is always supplementary in nature, that is it adds equal to $ {{180}^{\circ }} $ . Then, by using the conditions of angles and rearranging them, we can prove the final result.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we are supposed to prove that $ \angle ROS=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \angle QOS-\angle POS \right) $ where POQ is a line and Ray OR is perpendicular to the line P and also OS is another ray lying between rays OP and OR.

Now, for this type of question, we will use various angles from the figure to prove the equation mentioned in the question.
So, we can clearly see from the figure that:
$ \angle ROS+{{90}^{\circ }}=\angle QOS $
So, by rearranging the above equation, we get:
$ \angle QOS-\angle ROS={{90}^{\circ }}....\left( i \right) $
Then, we also know that the angle formed on the straight line is always supplementary in nature, that is it adds equal to $ {{180}^{\circ }} $ .
So, by using this condition, we get:
$ \angle QOS+\angle POS={{180}^{\circ }} $
The, we can write 180 as multiplication of 2 and 90 as:
$ \angle QOS+\angle POS=2\times {{90}^{\circ }} $
The, by substituting the value of $ {{90}^{\circ }} $ from equation (i) in the above mentioned expression, we get:
$ \angle QOS+\angle POS=2\times \left( \angle QOS-\angle ROS \right) $
Now, by solving the above expression, we get:
$ \begin{align}
& \angle QOS+\angle POS=2\angle QOS-2\left( \angle ROS \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 2\angle ROS=2\angle QOS-\angle QOS-\angle POS \\
& \Rightarrow 2\angle ROS=\angle QOS-\angle POS \\
& \Rightarrow \angle ROS=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \angle QOS-\angle POS \right) \\
\end{align} $
So, we get the condition $ \angle ROS=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \angle QOS-\angle POS \right) $ as proved.
Hence, the condition is proved.
Note: Now, to solve these type of the questions we need to know the basics of the angles that the perpendicular sign shows the angle of $ {{90}^{\circ }} $ and the angles on the straight line is $ {{180}^{\circ }} $ . So, we should be aware of these things so that we can easily proceed with these types of questions.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we are supposed to prove that $ \angle ROS=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \angle QOS-\angle POS \right) $ where POQ is a line and Ray OR is perpendicular to the line P and also OS is another ray lying between rays OP and OR.

Now, for this type of question, we will use various angles from the figure to prove the equation mentioned in the question.
So, we can clearly see from the figure that:
$ \angle ROS+{{90}^{\circ }}=\angle QOS $
So, by rearranging the above equation, we get:
$ \angle QOS-\angle ROS={{90}^{\circ }}....\left( i \right) $
Then, we also know that the angle formed on the straight line is always supplementary in nature, that is it adds equal to $ {{180}^{\circ }} $ .
So, by using this condition, we get:
$ \angle QOS+\angle POS={{180}^{\circ }} $
The, we can write 180 as multiplication of 2 and 90 as:
$ \angle QOS+\angle POS=2\times {{90}^{\circ }} $
The, by substituting the value of $ {{90}^{\circ }} $ from equation (i) in the above mentioned expression, we get:
$ \angle QOS+\angle POS=2\times \left( \angle QOS-\angle ROS \right) $
Now, by solving the above expression, we get:
$ \begin{align}
& \angle QOS+\angle POS=2\angle QOS-2\left( \angle ROS \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 2\angle ROS=2\angle QOS-\angle QOS-\angle POS \\
& \Rightarrow 2\angle ROS=\angle QOS-\angle POS \\
& \Rightarrow \angle ROS=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \angle QOS-\angle POS \right) \\
\end{align} $
So, we get the condition $ \angle ROS=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \angle QOS-\angle POS \right) $ as proved.
Hence, the condition is proved.
Note: Now, to solve these type of the questions we need to know the basics of the angles that the perpendicular sign shows the angle of $ {{90}^{\circ }} $ and the angles on the straight line is $ {{180}^{\circ }} $ . So, we should be aware of these things so that we can easily proceed with these types of questions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





