
In the hcp system of crystals, if \[r\] is the radius of each sphere, then which of the following are correct?
This question has multiple correct options
A.The number of atoms in this hcp unit cell is six.
B.The area of base of this hcp unit cell is \[6\sqrt 3 {r^2}\] units.
C.The volume of this hcp unit cell is \[24\sqrt {2{r^3}} \] units.
D.The height of this hcp unit cell is \[\sqrt {\dfrac{{32}}{3}} r\] units.
Answer
503.4k+ views
Hint: Crystal structure is the manner in which the atoms, ions or molecules are arranged. The lattice structure is the \[3D\] arrangement of atoms positions. Lattice structures are of seven types. These are cubic, tetragonal, orthorhombic, hexagonal, rhombohedral or trigonal, monoclinic and triclinic. Furthermore, these structures have certain variations in arrangement like primitive, body-centred, face-centred or end-centred.
Complete answer:
A hcp lattice can be visualized as a top and bottom plane of seven atoms that forms a regular hexagon. In between the two planes, there is a half-hexagon that has three atoms.
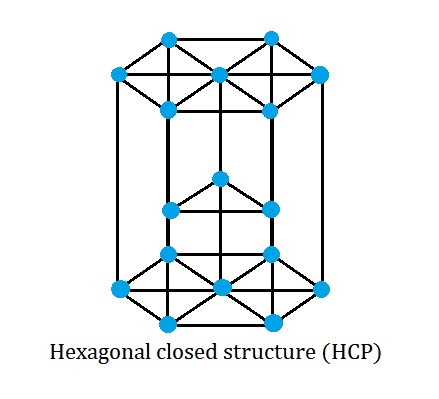
The \[3\] atoms present in the central plane contribute one to the unit cell. \[2\] atoms are present at face centres and each contribute one-half part to the unit cell. At the corners, there are \[12\] atoms and each one contributes one-sixth to the unit cell.
Hence, total number of atoms present in hcp unit cell is \[3 \times 1 + 2 \times \dfrac{1}{2} + 12 \times \dfrac{1}{6} = 3 + 1 + 2 = 6\]
Therefore, option A is correct.
The area of the base of the hexagon is made up of six equilateral triangles and the length of each side is \[2r\]. Here, \[2r\] represents the edge length. Hence, the area of base is, \[A = 6 \times [\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{(2r)^2}] = 6\sqrt 3 {r^2}\]
Therefore, option B is also correct.
Now, let’s first find the height of the hcp unit cell. The unit cell can be understood as two tetrahedra having length 2r on a side. The height of a single tetrahedron is given by \[h = 2r\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{3}} \]. Hence the height of a single unit cell will be \[h = 2(2r\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{3}} ) = 4r\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{3}} \]. The height equation given in the question is \[\sqrt {\dfrac{{32}}{3}} r\] and can be simplifies to \[4r\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{3}} \].
Therefore, option D is also correct.
The volume of the hcp unit cell can be calculated as the product of base and height. Hence, \[V = 6\sqrt 3 {r^2} \times 4r\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{3}} = 24\sqrt 2 {r^3}\].
Therefore, option C is also correct.
Hence, all four options are correct.
Note:
A tetrahedron can be understood as a triangular pyramid. It is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners.
The packing efficiency of hcp unit cell can be calculated by taking the ratio of volume of six atoms in the unit cell to the volume of unit cell as follows,
Packing efficiency \[ = \dfrac{{6 \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {r^3}}}{{24\sqrt 2 {r^3}}} = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{\pi }{{\sqrt 2 }} = \dfrac{\pi }{{3\sqrt 2 }} = 0.74\].
Complete answer:
A hcp lattice can be visualized as a top and bottom plane of seven atoms that forms a regular hexagon. In between the two planes, there is a half-hexagon that has three atoms.

The \[3\] atoms present in the central plane contribute one to the unit cell. \[2\] atoms are present at face centres and each contribute one-half part to the unit cell. At the corners, there are \[12\] atoms and each one contributes one-sixth to the unit cell.
Hence, total number of atoms present in hcp unit cell is \[3 \times 1 + 2 \times \dfrac{1}{2} + 12 \times \dfrac{1}{6} = 3 + 1 + 2 = 6\]
Therefore, option A is correct.
The area of the base of the hexagon is made up of six equilateral triangles and the length of each side is \[2r\]. Here, \[2r\] represents the edge length. Hence, the area of base is, \[A = 6 \times [\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{(2r)^2}] = 6\sqrt 3 {r^2}\]
Therefore, option B is also correct.
Now, let’s first find the height of the hcp unit cell. The unit cell can be understood as two tetrahedra having length 2r on a side. The height of a single tetrahedron is given by \[h = 2r\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{3}} \]. Hence the height of a single unit cell will be \[h = 2(2r\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{3}} ) = 4r\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{3}} \]. The height equation given in the question is \[\sqrt {\dfrac{{32}}{3}} r\] and can be simplifies to \[4r\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{3}} \].
Therefore, option D is also correct.
The volume of the hcp unit cell can be calculated as the product of base and height. Hence, \[V = 6\sqrt 3 {r^2} \times 4r\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{3}} = 24\sqrt 2 {r^3}\].
Therefore, option C is also correct.
Hence, all four options are correct.
Note:
A tetrahedron can be understood as a triangular pyramid. It is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners.
The packing efficiency of hcp unit cell can be calculated by taking the ratio of volume of six atoms in the unit cell to the volume of unit cell as follows,
Packing efficiency \[ = \dfrac{{6 \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {r^3}}}{{24\sqrt 2 {r^3}}} = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{\pi }{{\sqrt 2 }} = \dfrac{\pi }{{3\sqrt 2 }} = 0.74\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




