
In the projection of point \[P(\mathop p\limits^ \to )\]on the plane\[\mathop r\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to = q\] is the points \[S(\mathop s\limits^ \to )\], then
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: The projection of a point is its shadow on the plane or central projection.
If C is a point, called the centre of projection then the projection of a point P different from C onto a plane that does not contain C is the interaction of the line CP with the plane.
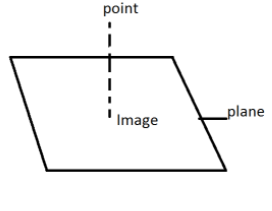
Complete step-by- step solution:
Let us draw a plane and the projection of point \[P(\mathop p\limits^ \to )\]on the plane is \[\mathop s\limits^ \to \].
The intersection is \[\mathop r\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to = q\]
As the line is normal to the plane i.e. perpendicular to the plane and vector \[\mathop P\limits^ \to \] is passing through the plane and parallel to \[\mathop n\limits^ \to \]
\[E{q^n}\] of such a line is\[\overrightarrow r = \overrightarrow p + \lambda \overrightarrow n ……...(1)\]
Given, \[\mathop r\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to = q........(2)\]
As the line is passing through the plane, then the equation (1) will be satisfying equation (2) and that point \[\mathop r\limits^ \to = \mathop s\limits^ \to \]
Substituting equation (1) in (2), we get:
$\Rightarrow$ \[(\mathop p\limits^ \to + \lambda \mathop n\limits^ \to )\mathop n\limits^ \to = q\]
To find the value of \[\lambda \], simplify the above term then we get it as
\[ \Rightarrow \mathop p\limits^ \to . \mathop n\limits^ \to + \lambda \mathop n\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to = q\]
As \[\left[ {\overrightarrow n .\overrightarrow n = {{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|}^2}} \right]\] , we get:
\[ \Rightarrow \lambda {\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|^2} = q - \mathop p\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to \]
\[ \Rightarrow \lambda = \dfrac{{q - \mathop p\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to }}{{{{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|}^2}}}\]______ (3) {On RHS \[{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|^2}\] will be in division as it was multiplication on LHS}
Now using equation (3) in (1), we get:
\[\mathop r\limits^ \to = \mathop p\limits^ \to + (\dfrac{{q - \mathop p\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to }}{{{{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|}^2}}})\mathop n\limits^ \to \]
We know that\[\overrightarrow r = \overrightarrow s \], hence:
\[\mathop s\limits^ \to = \mathop p\limits^ \to + (\dfrac{{q - \mathop p\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to }}{{{{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|}^2}}})\mathop n\limits^ \to \]
Note: Two planes are parallel if they have the same normal vector (i.e. their normal vectors are parallel). If two planes are not parallel, then they intersect in a line.If any line passes through a plane then it always satisfies the equation of that plane.
If C is a point, called the centre of projection then the projection of a point P different from C onto a plane that does not contain C is the interaction of the line CP with the plane.

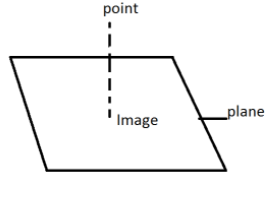
Complete step-by- step solution:

Let us draw a plane and the projection of point \[P(\mathop p\limits^ \to )\]on the plane is \[\mathop s\limits^ \to \].
The intersection is \[\mathop r\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to = q\]
As the line is normal to the plane i.e. perpendicular to the plane and vector \[\mathop P\limits^ \to \] is passing through the plane and parallel to \[\mathop n\limits^ \to \]
\[E{q^n}\] of such a line is\[\overrightarrow r = \overrightarrow p + \lambda \overrightarrow n ……...(1)\]
Given, \[\mathop r\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to = q........(2)\]
As the line is passing through the plane, then the equation (1) will be satisfying equation (2) and that point \[\mathop r\limits^ \to = \mathop s\limits^ \to \]
Substituting equation (1) in (2), we get:
$\Rightarrow$ \[(\mathop p\limits^ \to + \lambda \mathop n\limits^ \to )\mathop n\limits^ \to = q\]
To find the value of \[\lambda \], simplify the above term then we get it as
\[ \Rightarrow \mathop p\limits^ \to . \mathop n\limits^ \to + \lambda \mathop n\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to = q\]
As \[\left[ {\overrightarrow n .\overrightarrow n = {{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|}^2}} \right]\] , we get:
\[ \Rightarrow \lambda {\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|^2} = q - \mathop p\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to \]
\[ \Rightarrow \lambda = \dfrac{{q - \mathop p\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to }}{{{{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|}^2}}}\]______ (3) {On RHS \[{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|^2}\] will be in division as it was multiplication on LHS}
Now using equation (3) in (1), we get:
\[\mathop r\limits^ \to = \mathop p\limits^ \to + (\dfrac{{q - \mathop p\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to }}{{{{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|}^2}}})\mathop n\limits^ \to \]
We know that\[\overrightarrow r = \overrightarrow s \], hence:
\[\mathop s\limits^ \to = \mathop p\limits^ \to + (\dfrac{{q - \mathop p\limits^ \to .\mathop n\limits^ \to }}{{{{\left| {\mathop n\limits^ \to } \right|}^2}}})\mathop n\limits^ \to \]
Note: Two planes are parallel if they have the same normal vector (i.e. their normal vectors are parallel). If two planes are not parallel, then they intersect in a line.If any line passes through a plane then it always satisfies the equation of that plane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




